
What are point mutations? Give one example of point mutation.
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: Deletion or insertion of a new fragment of DNA in normal DNA sequence results in abnormalities as seen mainly in cancer cells. In sickle cell disease, only a single pair of genes are altered.
Complete answer:
The phenomenon that causes an alteration in genes that leads to alteration in the gene called mutations. Mutations result in a change in the genotype and phenotype of an organism. In each chromatid, DNA helix runs continuously from one end to the other end in a highly supercoiled form. Deletion or insertion of a segment of DNA results in an alteration in chromosomes results in abnormalities. They are mainly found in cancer cells.
If a single base pair of DNA changes in the DNA helix it is called point mutation generally seen in sickle cell anemia.
${ Hb }^{ A }$ and ${ Hb }^{ S }$ are the single pair of alleles that control the disease. They are present on chromosome 11.
This disease is expressed by homozygous individuals of sickle cell disease (${ Hb }^{ S }$, ${ Hb }^{ S }$). Heterozygous individuals ${ Hb }^{ A }$, (${ Hb }^{ S }$) are unaffected but they act as carriers of the disease.
It is caused by a point mutation in DNA that codes for the beta globulin polypeptide chain of hemoglobin that results in the addition of valine in the sixth position by replacing glutamic acid.
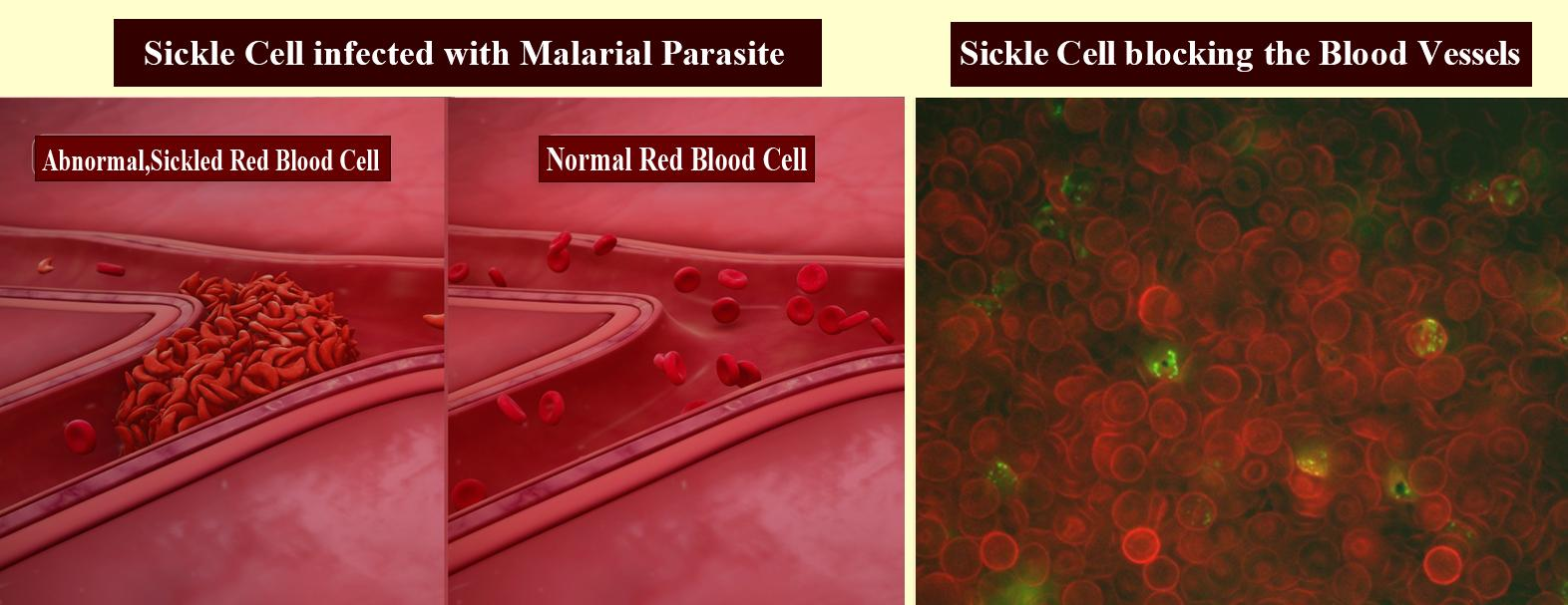
Additional Information: - Sickle cell anemia is an autosomal recessive genetic blood disorder that is characterized by an abnormal shape of red blood cells in hypoxia conditions.
RBC turns into a sickle shape that is previously in biconcave shape and these sickle cells may clump and clog small blood vessels resulting in symptoms like physical weakness, pain, organ damage, and paralysis.
Note: Heterozygous individuals of sickle cell disease are highly resistant to severe effects of malaria caused by plasmodium falciparum. It is called a heterozygous advantage.
Generally, a heterozygous individual can lead a normal life unless he is affected by prolonged hypoxia conditions resulting in experiencing symptoms of sickle cell disease.
Complete answer:
The phenomenon that causes an alteration in genes that leads to alteration in the gene called mutations. Mutations result in a change in the genotype and phenotype of an organism. In each chromatid, DNA helix runs continuously from one end to the other end in a highly supercoiled form. Deletion or insertion of a segment of DNA results in an alteration in chromosomes results in abnormalities. They are mainly found in cancer cells.
If a single base pair of DNA changes in the DNA helix it is called point mutation generally seen in sickle cell anemia.
${ Hb }^{ A }$ and ${ Hb }^{ S }$ are the single pair of alleles that control the disease. They are present on chromosome 11.
This disease is expressed by homozygous individuals of sickle cell disease (${ Hb }^{ S }$, ${ Hb }^{ S }$). Heterozygous individuals ${ Hb }^{ A }$, (${ Hb }^{ S }$) are unaffected but they act as carriers of the disease.
It is caused by a point mutation in DNA that codes for the beta globulin polypeptide chain of hemoglobin that results in the addition of valine in the sixth position by replacing glutamic acid.

Additional Information: - Sickle cell anemia is an autosomal recessive genetic blood disorder that is characterized by an abnormal shape of red blood cells in hypoxia conditions.
RBC turns into a sickle shape that is previously in biconcave shape and these sickle cells may clump and clog small blood vessels resulting in symptoms like physical weakness, pain, organ damage, and paralysis.
Note: Heterozygous individuals of sickle cell disease are highly resistant to severe effects of malaria caused by plasmodium falciparum. It is called a heterozygous advantage.
Generally, a heterozygous individual can lead a normal life unless he is affected by prolonged hypoxia conditions resulting in experiencing symptoms of sickle cell disease.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




