
How are protists and fungi similar?
Answer
517.2k+ views
Hint: One of them is unicellular in nature but can also be found as a colony of cells. Most of these survive in water, damp terrestrial environments, or even as parasites while the other ones are either autotrophs or heterotrophs, instead, they are saprophytes.
Complete answer
Similarities between protists and fungi are as follows:
Note:
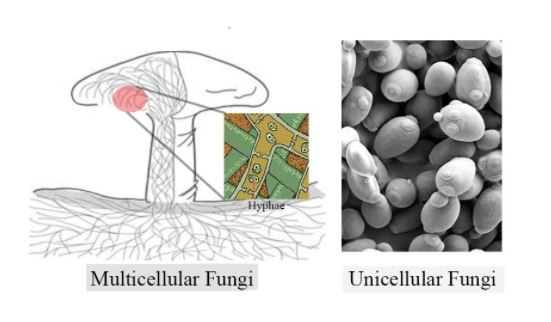
Most protist species are unicellular organisms, however, there are a couple of multicellular protists like kelp. This group shows the process of symbiosis with their other members. For instance, kelp (seaweed) may be a multicellular protist that gives otters protection from predators amidst its thick kelp. In turn, the otters eat sea urchins that tend to prey on kelp. Fungi are heterotrophic in nature; they mostly absorb their food from the surrounding air through their haustorium.
Complete answer
Similarities between protists and fungi are as follows:
| Protists | Fungi |
| It is a eukaryotic organism. | It is also a eukaryotic organism. |
| The nucleus present in them is prominent. | The nucleus present in them is also prominent. |
| They constitute cell organelles. | They also constitute cell organelles. |
| They produce fruiting bodies by the production of spores. | They also produce fruiting bodies by the production of spores. |
| They produce both plants and fungi. | They are formed through protists. |
| The cell is enclosed by the cell wall. | Their cell is enclosed by a cell wall. |
| Its nucleus is enclosed in a nuclear membrane. | Its nucleus is also enclosed in a nuclear membrane. |
| The nucleus is composed of DNA along with histone proteins. | Its nucleus also comprises DNA along with histone proteins. |
| Their cells are motile for some part of their life cycle. | Their cells are also motile for some part of their life cycle. |
| Their life cycle is complex consisting of both sexual and asexual phases. | Their life cycle is also complex consisting of both sexual and asexual phases. |
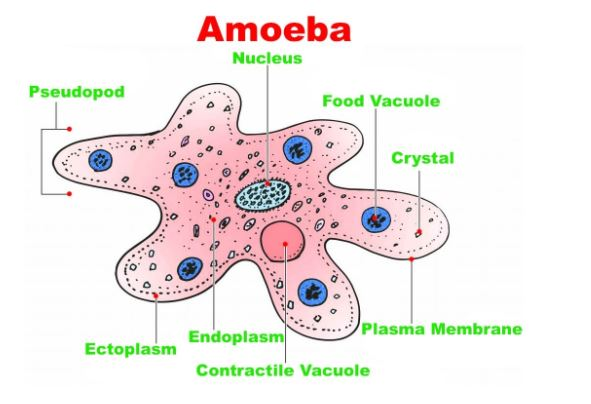
| Examples are amoeba, paramecium, euglena, etc. | Examples are yeast, mushroom, rhizopus, etc. |


Note:
Most protist species are unicellular organisms, however, there are a couple of multicellular protists like kelp. This group shows the process of symbiosis with their other members. For instance, kelp (seaweed) may be a multicellular protist that gives otters protection from predators amidst its thick kelp. In turn, the otters eat sea urchins that tend to prey on kelp. Fungi are heterotrophic in nature; they mostly absorb their food from the surrounding air through their haustorium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




