
What are the 6 models of the atom?
Answer
528.6k+ views
Hint: There are in total six proposed models of an atom. These models were given in order to better understand the positioning of electrons and protons in an atom. We shall study these models of atoms in order of their historical presentation, that is, which was the first model proposed to what is the latest (modern) model of an atom.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The six models of atom are listed below:
(1) Solid Sphere Model: This model was proposed by John Dalton in 1803. He was the first to state that atoms are indivisible units that cannot be further cut. He also stated that these are spherical in shape and atoms of any pure substance is made up of these similar spheres.
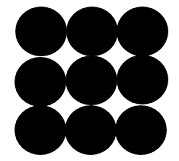
Here, each black sphere represents an indivisible atom.
(2) Plum Pudding Model: This model was proposed by J.J. Thompson in 1904. After discovering electrons, he suggested that these electrons are spread over the spherical cloud of positive charge just like a plum pudding.
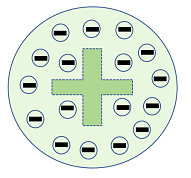
Here, the dashed positive sign indicates a positive charged at the center with electrons spread around it like a pudding.
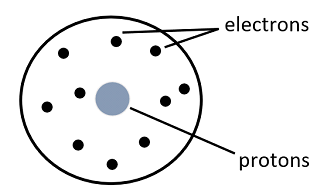
(3) Nuclear Model: This model was proposed by Rutherford in 1911. In his experiment of firing positively charged alpha-particles at thin gold foil, he noticed most of the alpha-particles went undeflected. This meant an atom mostly consisted of empty space with positive charge being at the center and electrons revolving around it.
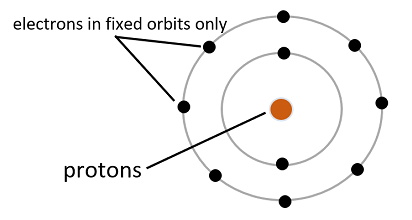
(4) Planetary Model: This model was proposed by Neils Bohr in 1913. He stated that electrons can only move in a fixed orbit around the nucleus containing certain energy levels and not in any orbit of their choice, that is, the energy of an electron is quantized.
(5) Quantum Model: This model was proposed by Erwin Schrodinger in 1926. He stated that electrons do not move in paths but in waves. And the location where the probability to find an electron is high is termed as an orbital.
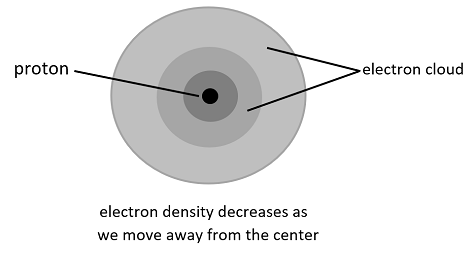
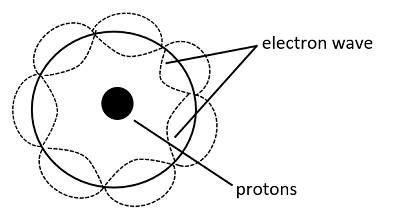
(6) Wave Mechanical Model: This model is mostly an extension to Schrodinger’s statement of an electron wave model and uses the same principle, that is, electrons do not move in paths but in waves and their electron density probability can be calculated using their respective wave function.
Note: These are the models which were first proposed by scientists. And some of them were proposed at a time when there wasn’t even a concept of atom, electron and proton. Also, every successive model was a slight enhancement over the previous model until Schrodinger gave his equation which is used as a base even today to understand the actual model of an atom.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The six models of atom are listed below:
(1) Solid Sphere Model: This model was proposed by John Dalton in 1803. He was the first to state that atoms are indivisible units that cannot be further cut. He also stated that these are spherical in shape and atoms of any pure substance is made up of these similar spheres.

Here, each black sphere represents an indivisible atom.
(2) Plum Pudding Model: This model was proposed by J.J. Thompson in 1904. After discovering electrons, he suggested that these electrons are spread over the spherical cloud of positive charge just like a plum pudding.

Here, the dashed positive sign indicates a positive charged at the center with electrons spread around it like a pudding.
(3) Nuclear Model: This model was proposed by Rutherford in 1911. In his experiment of firing positively charged alpha-particles at thin gold foil, he noticed most of the alpha-particles went undeflected. This meant an atom mostly consisted of empty space with positive charge being at the center and electrons revolving around it.

(4) Planetary Model: This model was proposed by Neils Bohr in 1913. He stated that electrons can only move in a fixed orbit around the nucleus containing certain energy levels and not in any orbit of their choice, that is, the energy of an electron is quantized.

(5) Quantum Model: This model was proposed by Erwin Schrodinger in 1926. He stated that electrons do not move in paths but in waves. And the location where the probability to find an electron is high is termed as an orbital.

(6) Wave Mechanical Model: This model is mostly an extension to Schrodinger’s statement of an electron wave model and uses the same principle, that is, electrons do not move in paths but in waves and their electron density probability can be calculated using their respective wave function.

Note: These are the models which were first proposed by scientists. And some of them were proposed at a time when there wasn’t even a concept of atom, electron and proton. Also, every successive model was a slight enhancement over the previous model until Schrodinger gave his equation which is used as a base even today to understand the actual model of an atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




