
What are the conditions for hyperconjugation?
Answer
548.4k+ views
Hint: There are two main conditions for hyperconjugation. One of them involves the presence of a hydrogen atom in a specific position while the other one involves the presence of a lone pair of electrons at a particular position.
Complete answer:
Hyperconjugation is also known as $\sigma -$conjugation or no bond resonance. It refers to the delocalization of the electrons which takes place in the presence of mainly $\sigma -$character bonds. Hyperconjugation increases the stability of the system.
Another type of hyperconjugation may occur by the parallel overlap of the p – orbitals including the hybrid orbitals which are actually involved in $\sigma -$bonds. We can say that in resonance pi – pi delocalization takes place while in hyperconjugation sigma pi delocalization takes place. In this case, a sigma bond is severed.
The hyperconjugation is shown below:
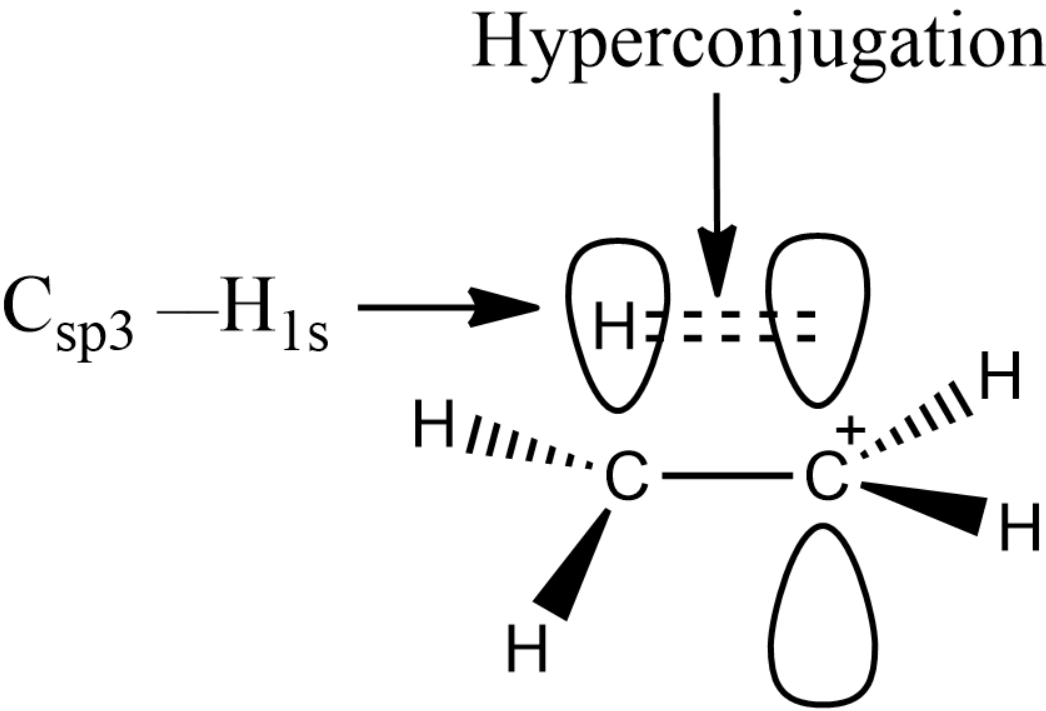
The alpha hydrogen present in the carbon will form the hyperconjugation with the empty p-orbital and hence there will be a sigma pi overlap. Thus, one of the conditions for the hyperconjugation to take place will be the presence of alpha hydrogen.
Similarly, if there is a lone pair of electrons present which is adjacent to a $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybrid carbon or atoms like oxygen, nitrogen etc., hyperconjugation will take place.
Hence, these are the two main conditions for hyperconjugation.
Note:
Resonance and hyperconjugation are similar, but there are some differences which separate them. Resonance involves bond formation during delocalization of electrons but hyperconjugation doesn’t form any bonds for the delocalization of the electrons.
Complete answer:
Hyperconjugation is also known as $\sigma -$conjugation or no bond resonance. It refers to the delocalization of the electrons which takes place in the presence of mainly $\sigma -$character bonds. Hyperconjugation increases the stability of the system.
Another type of hyperconjugation may occur by the parallel overlap of the p – orbitals including the hybrid orbitals which are actually involved in $\sigma -$bonds. We can say that in resonance pi – pi delocalization takes place while in hyperconjugation sigma pi delocalization takes place. In this case, a sigma bond is severed.
The hyperconjugation is shown below:

The alpha hydrogen present in the carbon will form the hyperconjugation with the empty p-orbital and hence there will be a sigma pi overlap. Thus, one of the conditions for the hyperconjugation to take place will be the presence of alpha hydrogen.
Similarly, if there is a lone pair of electrons present which is adjacent to a $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybrid carbon or atoms like oxygen, nitrogen etc., hyperconjugation will take place.
Hence, these are the two main conditions for hyperconjugation.
Note:
Resonance and hyperconjugation are similar, but there are some differences which separate them. Resonance involves bond formation during delocalization of electrons but hyperconjugation doesn’t form any bonds for the delocalization of the electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




