
What are the different types of Amplitude Modulation?
Answer
502.5k+ views
Hint: Amplitude modulation, or simply AM, is one of the oldest modulation techniques for sending data over the radio. This technology was developed in the twentieth century when Landell de Moura and Reginald Fessenden were performing radiotelephone experiments in the \[1900\] s. The modulation technique was established and employed in electronic communication after successful experiments.
In general, amplitude modulation is defined as a type of modulation in which the carrier wave's amplitude varies in a proportional relationship to the modulating data or signal.
Complete step by step solution:
Amplitude Modulation Types:
Amplitude modulation can be divided into three categories.
Double sideband-suppressed carrier modulation is one of them (DSB-SC).
Modulation of a single sideband (SSB).
Modulation of the Vestigial Sideband (VSB).
DSB – SC (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier):
The modulating signal's frequency spectrum is symmetrically below and above the carrier signal's frequency in this case. The lower and upper frequencies of the incoming information signal correspond to sidebands. Upper sidebands have greater frequency components than carrier frequencies, while lower sidebands have lower frequency components than carrier frequencies.
For DSB- SC, the amplitude modulated signal equation is as follows:
\[DSB - SC\left( t \right) = Accoswct + \dfrac{{Ai}}{2}cos\left( {wc + wi} \right)t + \dfrac{{Ai}}{2}cos\left( {wi - wc} \right)t\]
The first term in the equation corresponds to the carrier signal, the second term to a modulating signal with a frequency shift of wc to the left, and the third term to a modulating signal with a frequency shift of wc to the right.
The wave spectrum modified by DSB-SC is represented as,
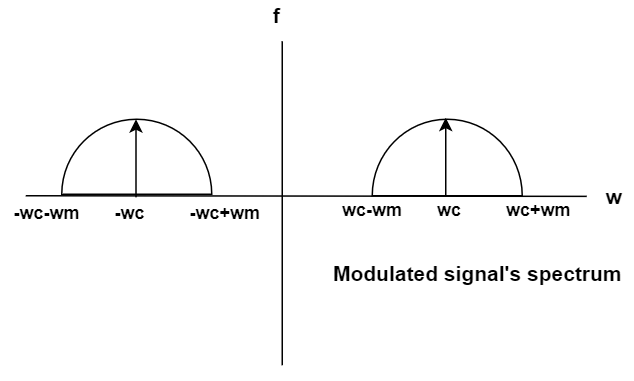
DSB-SC modulation index and bandwidth are as follows:
\[DSB - SC\left( t \right) = Ac\left( {1 + \mu coswit} \right)coswct\]
The difference between the maximum and minimum frequencies of the resulting modulated signal is defined as bandwidth.\[{\text{Bandwidth}} = ({f_c} + {f_i}) - ({f_c} - {f_i}) = 2{f_i}\]
As a result, the modulating signal's bandwidth is doubled. The modulation procedure in DSB-SC is simple and does not require sideband filters.
Single Sideband:
Single sideband amplification refers to the transmission of only one sideband through an antenna. It has a sideband on either the top or lower half. A DSB wave can be modulated with SSB by passing it via a bandpass filter. As indicated in the diagram below, the bandpass filter filters either the upper or lower sidebands of the DSB SC wave.
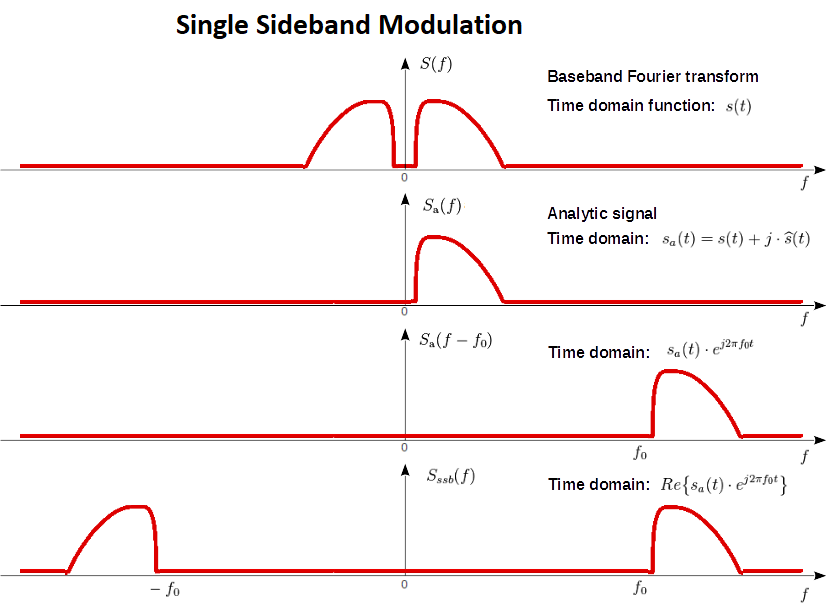
The modulated wave's bandwidth is equal to the modulating signal's bandwidth in this case. Because only one sideband is sent, it can save power.
Vestigial Sideband:
The bandpass filter does not have the capacity to block off frequencies outside of the cutoff zone. And this issue could lead to some distracting noises. Vestigial sideband modulation (VSBM) is used to solve this problem. In this case, one of the sidebands (upper or lower) is transmitted but a portion of the other is not.
The VSB signal has a bandwidth that is halfway between the SSB and DSB-SC transmissions and it is
\[{\text{Bandwidth}} = {f_i} + (25\% ){f_i}\]
Note:Amplitude modulation has a wide range of uses.
Radios for air traffic control.
Remote controls that do not require a key.
The transmission of television signals.
Communication via the internet.
In general, amplitude modulation is defined as a type of modulation in which the carrier wave's amplitude varies in a proportional relationship to the modulating data or signal.
Complete step by step solution:
Amplitude Modulation Types:
Amplitude modulation can be divided into three categories.
Double sideband-suppressed carrier modulation is one of them (DSB-SC).
Modulation of a single sideband (SSB).
Modulation of the Vestigial Sideband (VSB).
DSB – SC (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier):
The modulating signal's frequency spectrum is symmetrically below and above the carrier signal's frequency in this case. The lower and upper frequencies of the incoming information signal correspond to sidebands. Upper sidebands have greater frequency components than carrier frequencies, while lower sidebands have lower frequency components than carrier frequencies.
For DSB- SC, the amplitude modulated signal equation is as follows:
\[DSB - SC\left( t \right) = Accoswct + \dfrac{{Ai}}{2}cos\left( {wc + wi} \right)t + \dfrac{{Ai}}{2}cos\left( {wi - wc} \right)t\]
The first term in the equation corresponds to the carrier signal, the second term to a modulating signal with a frequency shift of wc to the left, and the third term to a modulating signal with a frequency shift of wc to the right.
The wave spectrum modified by DSB-SC is represented as,

DSB-SC modulation index and bandwidth are as follows:
\[DSB - SC\left( t \right) = Ac\left( {1 + \mu coswit} \right)coswct\]
The difference between the maximum and minimum frequencies of the resulting modulated signal is defined as bandwidth.\[{\text{Bandwidth}} = ({f_c} + {f_i}) - ({f_c} - {f_i}) = 2{f_i}\]
As a result, the modulating signal's bandwidth is doubled. The modulation procedure in DSB-SC is simple and does not require sideband filters.
Single Sideband:
Single sideband amplification refers to the transmission of only one sideband through an antenna. It has a sideband on either the top or lower half. A DSB wave can be modulated with SSB by passing it via a bandpass filter. As indicated in the diagram below, the bandpass filter filters either the upper or lower sidebands of the DSB SC wave.

The modulated wave's bandwidth is equal to the modulating signal's bandwidth in this case. Because only one sideband is sent, it can save power.
Vestigial Sideband:
The bandpass filter does not have the capacity to block off frequencies outside of the cutoff zone. And this issue could lead to some distracting noises. Vestigial sideband modulation (VSBM) is used to solve this problem. In this case, one of the sidebands (upper or lower) is transmitted but a portion of the other is not.
The VSB signal has a bandwidth that is halfway between the SSB and DSB-SC transmissions and it is
\[{\text{Bandwidth}} = {f_i} + (25\% ){f_i}\]
Note:Amplitude modulation has a wide range of uses.
Radios for air traffic control.
Remote controls that do not require a key.
The transmission of television signals.
Communication via the internet.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




