
How are the following conversions carried out from ${\text{2 - methyl - 1 - propene}}$ to ${\text{2 - chloro - 2 - methylpropane}}$?
Answer
565.8k+ views
Hint: First draw the structure of the reactant and product and analyze the functional group present in them because if we know the functional group properly, we can select proper reagents for the conversion of the reactant in this.
Complete step by step answer:
First let us see the structure of reactants and product
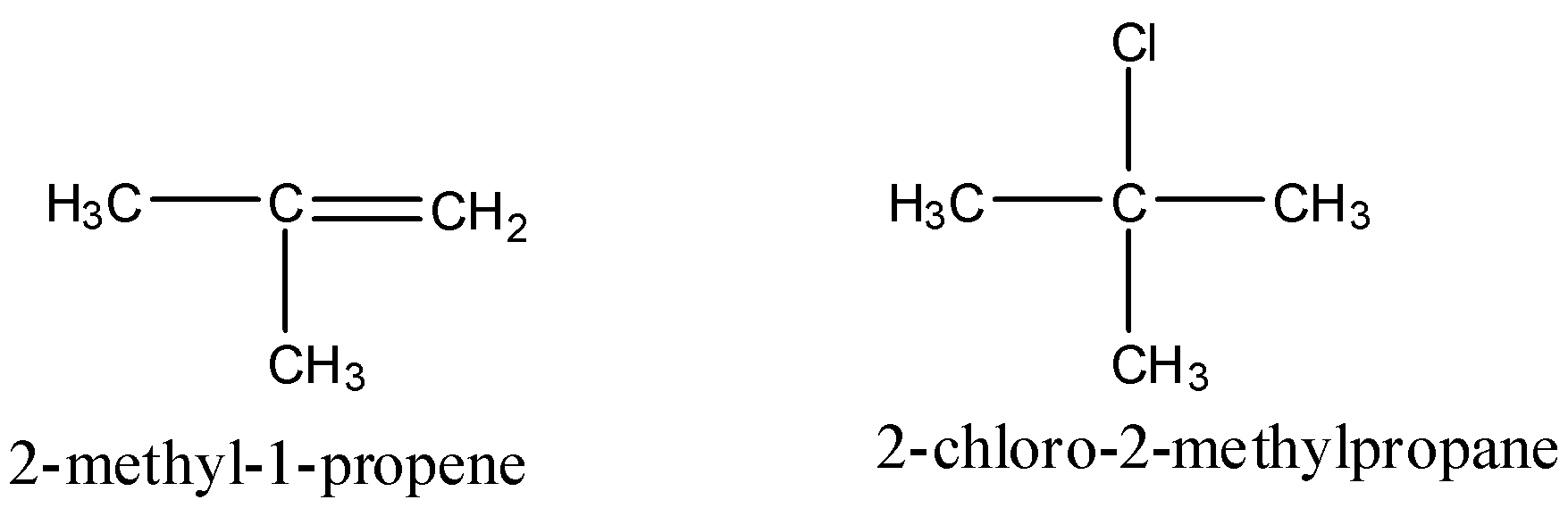
By observing the reactant and product we can see that there is addition of chlorine and hydrogen on the double bond and the addition of HCl is such that the hydrogen attaches itself to carbon which has more hydrogen. This reaction is a markovnikov reaction.
According to markovnikov rule the addition of a polar protic acid on an unsaturated unsymmetrical alkene happens in such a way that the proton adds itself to carbon having less substituents and the nucleophile part adds itself to the carbon having more substituent.
The mechanism is as follows:
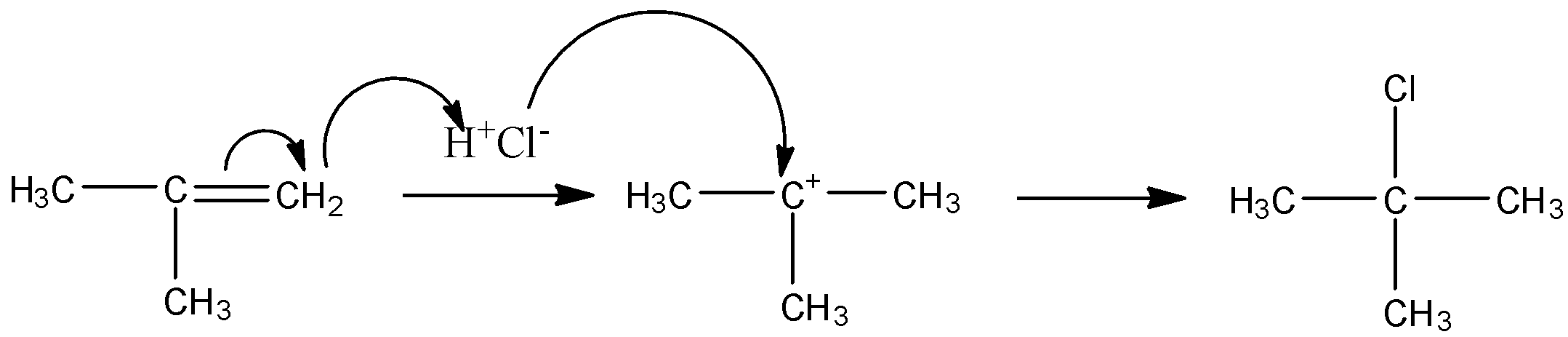
So, this is how the reactant is converted into a product.
Additional information:
The markovnikov rule is applied on unsymmetrical alkenes and addition is such that hydrogen is added to carbon having more hydrogen but when we react HCl in presence of benzoyl peroxide or hydrogen peroxide then anti – markovnikov rule is applied which is totally opposite to markovnikov rule. In anti – markovnikov rule the hydrogen attaches to that carbon where there is less hydrogen.
Note: The electrophile proton attacks first in this mechanism because alkene is electron rich compound so the first step always will be electrophile attack and then table carbocation is formed and nucleophile attacks on it.
Complete step by step answer:
First let us see the structure of reactants and product

By observing the reactant and product we can see that there is addition of chlorine and hydrogen on the double bond and the addition of HCl is such that the hydrogen attaches itself to carbon which has more hydrogen. This reaction is a markovnikov reaction.
According to markovnikov rule the addition of a polar protic acid on an unsaturated unsymmetrical alkene happens in such a way that the proton adds itself to carbon having less substituents and the nucleophile part adds itself to the carbon having more substituent.
The mechanism is as follows:

So, this is how the reactant is converted into a product.
Additional information:
The markovnikov rule is applied on unsymmetrical alkenes and addition is such that hydrogen is added to carbon having more hydrogen but when we react HCl in presence of benzoyl peroxide or hydrogen peroxide then anti – markovnikov rule is applied which is totally opposite to markovnikov rule. In anti – markovnikov rule the hydrogen attaches to that carbon where there is less hydrogen.
Note: The electrophile proton attacks first in this mechanism because alkene is electron rich compound so the first step always will be electrophile attack and then table carbocation is formed and nucleophile attacks on it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




