
_______ are the longest cells in the human body.
A. Nerve cells
B. Epithelial cells
C. Mast cells
D. Kupffer cells
Answer
597.9k+ views
Hint: The answer to this question is the active component of the neuron system. They communicate with each other as well as with other cells through electric signals which in turn allows effector organs to respond to the appropriate stimuli.
Step by step answer:
The answer of the question is Nerve cells. We should know that neurons or nerve cells can be up to 3 feet long. A typical neuron has a cell morphology called soma, hair-like structures called dendrites and an axon. Neurons are specialized in conveying knowledge throughout the body. The sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons are three types of neurons. Neurons have a membrane built to forward information to other cells.
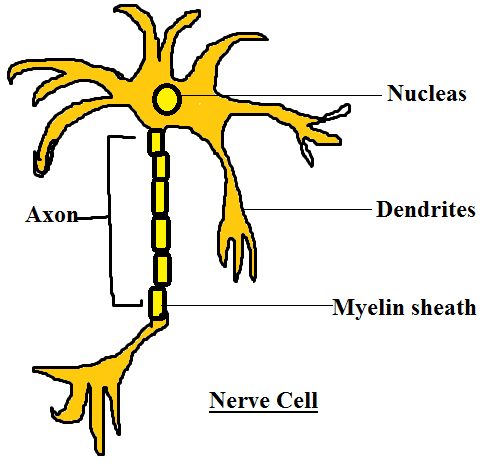
Now we will see why other options are incorrect.
Epithelial cells: We should know that epithelial cells are cells that come from surfaces of our body, such as our skin, blood vessels, urinary tract, or organs. They serve as a barrier between the inside and outside of our body, and protect it from viruses. The results show a range of epithelial cell diameters from 8-21 microns with 97% of the measurements lying in the 9-17 microns range.
Mast cells: we should know that Mast cells are mononuclear cells. Most characteristically, they contain many small secretory granules, ranging in size from 0.2 to 0.8 micrometres.
Kupffer cells: Kupffer cells are amoeboid-shaped and are attached to the sinusoidal endothelial cells. Their surface contains microvilli, pseudopodia, and lamellipodia, which can project out in all directions. The microvilli and pseudopodia are involved in endocytosis of particles. They also contain Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, centrioles, microfilaments, and microtubules in their cytoplasm. Kupffer cells range from size ~15- to 20-micron.
Notes: We should know that our body is made up of trillions of cells, each with their own structure and function. These cells all work in harmony to carry out all the basic functions necessary for us to survive. There are about 200 different types of cells in the body. Here are just a few examples:
Red blood cells (erythrocytes)
Skin cells
Neurons (nerve cells)
Fat cells
We are multicellular, complex organisms. The cells inside our bodies are “specialized.” This means that each type of cell performs a unique and special function. For this reason, each of the 200 different types of cells in the body has a different structure, size, shape, and function, and contains different organelles
Step by step answer:
The answer of the question is Nerve cells. We should know that neurons or nerve cells can be up to 3 feet long. A typical neuron has a cell morphology called soma, hair-like structures called dendrites and an axon. Neurons are specialized in conveying knowledge throughout the body. The sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons are three types of neurons. Neurons have a membrane built to forward information to other cells.

Now we will see why other options are incorrect.
Epithelial cells: We should know that epithelial cells are cells that come from surfaces of our body, such as our skin, blood vessels, urinary tract, or organs. They serve as a barrier between the inside and outside of our body, and protect it from viruses. The results show a range of epithelial cell diameters from 8-21 microns with 97% of the measurements lying in the 9-17 microns range.
Mast cells: we should know that Mast cells are mononuclear cells. Most characteristically, they contain many small secretory granules, ranging in size from 0.2 to 0.8 micrometres.
Kupffer cells: Kupffer cells are amoeboid-shaped and are attached to the sinusoidal endothelial cells. Their surface contains microvilli, pseudopodia, and lamellipodia, which can project out in all directions. The microvilli and pseudopodia are involved in endocytosis of particles. They also contain Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, centrioles, microfilaments, and microtubules in their cytoplasm. Kupffer cells range from size ~15- to 20-micron.
Notes: We should know that our body is made up of trillions of cells, each with their own structure and function. These cells all work in harmony to carry out all the basic functions necessary for us to survive. There are about 200 different types of cells in the body. Here are just a few examples:
Red blood cells (erythrocytes)
Skin cells
Neurons (nerve cells)
Fat cells
We are multicellular, complex organisms. The cells inside our bodies are “specialized.” This means that each type of cell performs a unique and special function. For this reason, each of the 200 different types of cells in the body has a different structure, size, shape, and function, and contains different organelles
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




