
What are the molecular scissors?
Answer
597.9k+ views
Hint: DNA replicates itself but there are some sequences present in which we can cut and add another sequence in order to create a new DNA known as recombination DNA with the help of certain enzymes.
Complete answer:
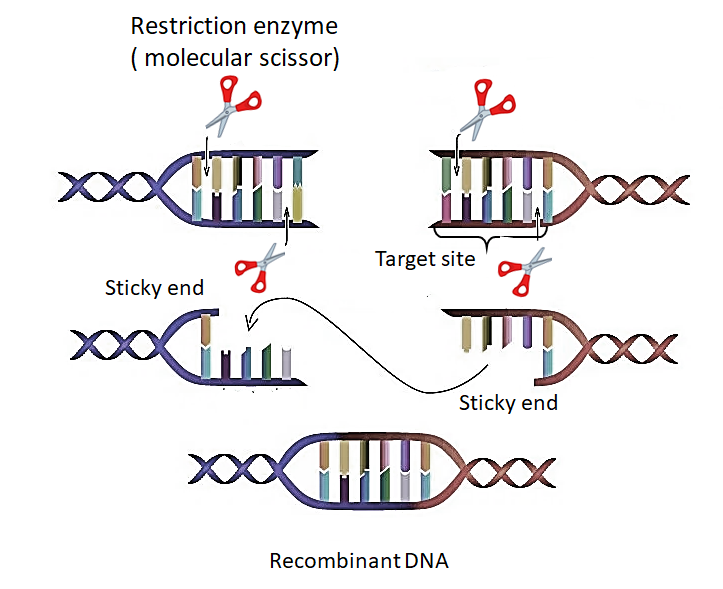
Restriction enzymes are also known as ‘molecular scissors’ that cut the DNA at restriction sites. Most of the restriction enzymes are particular for a single target site. They are found in bacteria and archaea that provide a defense mechanism against bacteriophage viruses. In bacteria mainly two enzymes are responsible for controlling the growth of bacteriophage. One is a methyltransferase that adds the methyl groups to DNA while the other cuts the DNA known as restriction endonuclease. These enzymes catalyze the phosphodiester bond in each of the two strands of double-helix DNA that require Mg2+ or other divalent ions for their activity. The example of a recognition site for E.coli includes -
5’ GAATTC 3’
3’ CTTAAG 5’
Application of restriction enzymes-
1. The common application of restriction enzymes includes the generation of recombinant DNA molecules.
2. The restriction endonucleases are used to obtain structural information of the DNA fragment or genome that is known as restriction mapping.
3. A large DNA molecule can be sequenced by digesting with the help of restriction endonucleases and processing the resulting fragments through a DNA sequencer, the phenomenon is known as gene sequencing.
4. The restriction enzymes are used in the RFLP for the digestion of DNA samples into fragments. These fragments get separated based on length by gel electrophoresis and transferred into a membrane.
Note:
1. Under the suboptimal conditions, some of the restriction enzymes cleave the DNA at nonspecific sites i.e. different from the specific recognition sequence. This phenomenon is known as star activity.
2. Sticky end and a blunt end. The blunt end possesses a 5’-phosphate group that helps in ligation. However, the sticky ends possess 3’- or 5’-overhangs of 1–4 nucleotide that helps in the self-ligation or ligation with a complementary region from another DNA molecule.
Complete answer:
Restriction enzymes are also known as ‘molecular scissors’ that cut the DNA at restriction sites. Most of the restriction enzymes are particular for a single target site. They are found in bacteria and archaea that provide a defense mechanism against bacteriophage viruses. In bacteria mainly two enzymes are responsible for controlling the growth of bacteriophage. One is a methyltransferase that adds the methyl groups to DNA while the other cuts the DNA known as restriction endonuclease. These enzymes catalyze the phosphodiester bond in each of the two strands of double-helix DNA that require Mg2+ or other divalent ions for their activity. The example of a recognition site for E.coli includes -
5’ GAATTC 3’
3’ CTTAAG 5’
Application of restriction enzymes-
1. The common application of restriction enzymes includes the generation of recombinant DNA molecules.
2. The restriction endonucleases are used to obtain structural information of the DNA fragment or genome that is known as restriction mapping.
3. A large DNA molecule can be sequenced by digesting with the help of restriction endonucleases and processing the resulting fragments through a DNA sequencer, the phenomenon is known as gene sequencing.
4. The restriction enzymes are used in the RFLP for the digestion of DNA samples into fragments. These fragments get separated based on length by gel electrophoresis and transferred into a membrane.
Note:
1. Under the suboptimal conditions, some of the restriction enzymes cleave the DNA at nonspecific sites i.e. different from the specific recognition sequence. This phenomenon is known as star activity.
2. Sticky end and a blunt end. The blunt end possesses a 5’-phosphate group that helps in ligation. However, the sticky ends possess 3’- or 5’-overhangs of 1–4 nucleotide that helps in the self-ligation or ligation with a complementary region from another DNA molecule.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




