
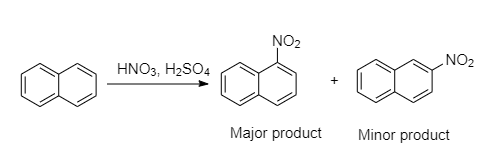
When the aromatic hydrocarbon naphthalene reacts with nitric and sulfuric acid, two compounds containing one nitro group are formed. What are the structures of these two compounds?
Answer
495.9k+ views
Hint: The reaction of aromatic hydrocarbon naphthalene with nitric and sulfuric acid is an electrophilic aromatic substitution. The electrophilic substitution reaction contains: nitration, halogenation and alkylation reaction.
Complete answer:
In electrophilic aromatic substitution, naphthalene reacts more readily than benzene. The two compounds formed by the nitration of naphthalene is an electrophilic aromatic substitution which gives two products namely: 1-nitronaphthalene and 2-nitronaphthalene.
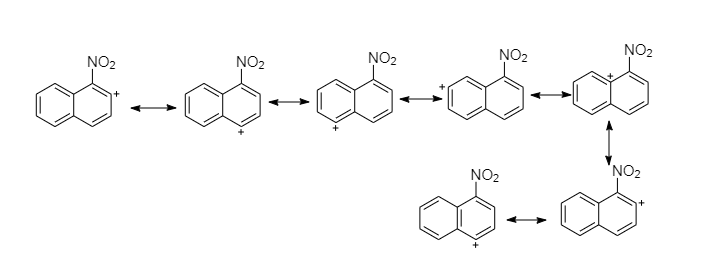
The nitronium ion, $N{O_2}^ + $ is the active nitrating agent in nitric acid-sulfuric acid mixture. Substitution usually occurs more readily at the one position than at the two positions because the intermediate for $1 - $ substitution is more stable than $2 - $ substitution. The reason is that the most favorable resonance structures for either intermediate are those that have one fully aromatic ring.
Nitration at ${1^{st}} - C$ produces a carbocation that has seven resonance structures, which preserve the atomicity of the second ring more favorably.
Nitration at ${2^{nd}} - C$ produces a carbocation that has six resonance structures, but preserve the atomicity of the second ring less than the first.
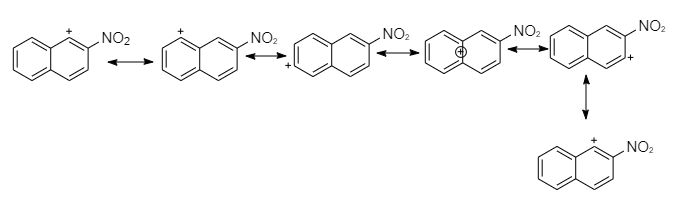
So the attack at first position is more stable intermediate than the attack at the second position intermediate form.
So, the major product is 1-nitronaphthalene and the minor product will be 2-nitronaphthalene.
Note:
The chlorination and bromination of naphthalene proceeds without a catalyst to give 1-chloronaphthalene and 1-bromonaphthalene, respectively. Naphthalene can also be easily alkylated by reaction with alkenes or alcohols, using sulfuric acid or phosphoric acid.
Complete answer:
In electrophilic aromatic substitution, naphthalene reacts more readily than benzene. The two compounds formed by the nitration of naphthalene is an electrophilic aromatic substitution which gives two products namely: 1-nitronaphthalene and 2-nitronaphthalene.

The nitronium ion, $N{O_2}^ + $ is the active nitrating agent in nitric acid-sulfuric acid mixture. Substitution usually occurs more readily at the one position than at the two positions because the intermediate for $1 - $ substitution is more stable than $2 - $ substitution. The reason is that the most favorable resonance structures for either intermediate are those that have one fully aromatic ring.
Nitration at ${1^{st}} - C$ produces a carbocation that has seven resonance structures, which preserve the atomicity of the second ring more favorably.

Nitration at ${2^{nd}} - C$ produces a carbocation that has six resonance structures, but preserve the atomicity of the second ring less than the first.

So the attack at first position is more stable intermediate than the attack at the second position intermediate form.
So, the major product is 1-nitronaphthalene and the minor product will be 2-nitronaphthalene.
Note:
The chlorination and bromination of naphthalene proceeds without a catalyst to give 1-chloronaphthalene and 1-bromonaphthalene, respectively. Naphthalene can also be easily alkylated by reaction with alkenes or alcohols, using sulfuric acid or phosphoric acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




