
Arrange the following amines in the decreasing order of their basic nature.
(A) \[Aniline\], \[propan - 1 - amine\] and $N$\[ - methylethanamine\]
(B) \[Benzene - 1,4 - diamine\], \[\;ammonia\] and $4$\[ - aminobenzoic{\text{ }}acid\]
(C) $N$\[ - Methylaniline\], \[Phenylmethylamine\] and \[N - phenylaniline\]
Answer
559.8k+ views
Hint:As we know that due to the presence of lone pairs of electrons on nitrogen, amines exhibit basic characters. The amines are stronger bases than water and are therefore in the aqueous solution they are easily protonated by water. Alkyl groups have electron releasing inductive effects.
Complete step-by-step answer:As we know that due to the presence of lone pair of electrons on nitrogen, amines exhibit basic characters. Alkyl groups present in alkylamines possess electron releasing effect, this increases the electron density on nitrogen and hence make the lone pair of nitrogen more easily available for sharing with acids.
Also, among primary, secondary and tertiary aliphatic amines, the electron releasing effect is maximum in tertiary amines and minimum in primary amines. The basic strength of these amines increase from primary amine to tertiary amine.
We also know that aromatic amines like aniline are less basic than ammonia and aliphatic amines because in aniline and other arylamines, the $ - N{H_2}$ group is attached directly to the benzene ring. The unshared pair of electrons in nitrogen is in conjugation with the benzene ring and thus makes it less available for protonation.
Therefore, from the above explanation we can say that the order of decreasing order on the basis of basic character is as follows:
(A)\[\;N - methylethanamine > propan - 1 - amine > Aniline\]
We can show this with the help of structures of compound as:
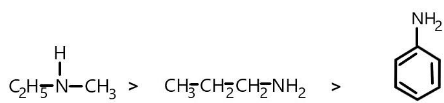
Order of its \[p{K_b}\] values will be as follows:
$3.29 < 3.46 < 9.13$
(B) \[Ammonia > \]\[Benzene - 1,4 - diamine > \]\[4 - aminobenzoic{\text{ }}acid\]
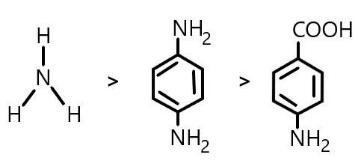
Order of its \[p{K_b}\] values will be reversed as the stronger basic compounds possess a less \[p{K_b}\] value. So the order will be:
\[Ammonia < \]\[Benzene - 1,4 - diamine < \]\[4 - aminobenzoic{\text{ }}acid.\]
(C) \[N - Methylaniline\]\[ \approx Phenylmethylamine > \] \[N - phenylaniline\]
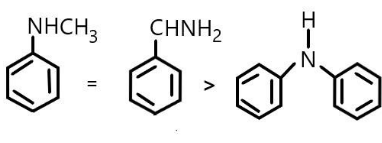
Order of their \[p{K_b}\] values will be reversed as the stronger basic compounds possess a less \[p{K_b}\] value. So the order will be:
\[N - Methylaniline\]\[ \approx Phenylmethylamine < \] \[N - phenylaniline\]
Note:Remember the basic character of amines is due to the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen and amine and also it depends on the electron releasing effect and steric and hydration effect as well. Higher the number of alkyl groups attached higher will be the steric hindrance and greater the extent of hydrogen bonding in protonated amine, more will be the basic strength. Also, remember that greater the number of resonance structures greater will be the stability of amines.
Complete step-by-step answer:As we know that due to the presence of lone pair of electrons on nitrogen, amines exhibit basic characters. Alkyl groups present in alkylamines possess electron releasing effect, this increases the electron density on nitrogen and hence make the lone pair of nitrogen more easily available for sharing with acids.
Also, among primary, secondary and tertiary aliphatic amines, the electron releasing effect is maximum in tertiary amines and minimum in primary amines. The basic strength of these amines increase from primary amine to tertiary amine.
We also know that aromatic amines like aniline are less basic than ammonia and aliphatic amines because in aniline and other arylamines, the $ - N{H_2}$ group is attached directly to the benzene ring. The unshared pair of electrons in nitrogen is in conjugation with the benzene ring and thus makes it less available for protonation.
Therefore, from the above explanation we can say that the order of decreasing order on the basis of basic character is as follows:
(A)\[\;N - methylethanamine > propan - 1 - amine > Aniline\]
We can show this with the help of structures of compound as:
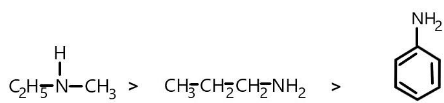
Order of its \[p{K_b}\] values will be as follows:
$3.29 < 3.46 < 9.13$
(B) \[Ammonia > \]\[Benzene - 1,4 - diamine > \]\[4 - aminobenzoic{\text{ }}acid\]

Order of its \[p{K_b}\] values will be reversed as the stronger basic compounds possess a less \[p{K_b}\] value. So the order will be:
\[Ammonia < \]\[Benzene - 1,4 - diamine < \]\[4 - aminobenzoic{\text{ }}acid.\]
(C) \[N - Methylaniline\]\[ \approx Phenylmethylamine > \] \[N - phenylaniline\]

Order of their \[p{K_b}\] values will be reversed as the stronger basic compounds possess a less \[p{K_b}\] value. So the order will be:
\[N - Methylaniline\]\[ \approx Phenylmethylamine < \] \[N - phenylaniline\]
Note:Remember the basic character of amines is due to the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen and amine and also it depends on the electron releasing effect and steric and hydration effect as well. Higher the number of alkyl groups attached higher will be the steric hindrance and greater the extent of hydrogen bonding in protonated amine, more will be the basic strength. Also, remember that greater the number of resonance structures greater will be the stability of amines.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




