
Assertion: Isogametes are formed in the majority of sexually reproducing organisms.
Reason: Morphologically distinct types of gametes are called isogametes.
(A) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion
(B) Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion
(C) Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect
(D) Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: Isogametes are seen in algae like Spirogyra, Chlamydomonas, and a few more species. Humans have two different types of gametes known as heterogametes. They both have a dissimilar appearance i.e size, shape everything is different.
Complete step by step answer:
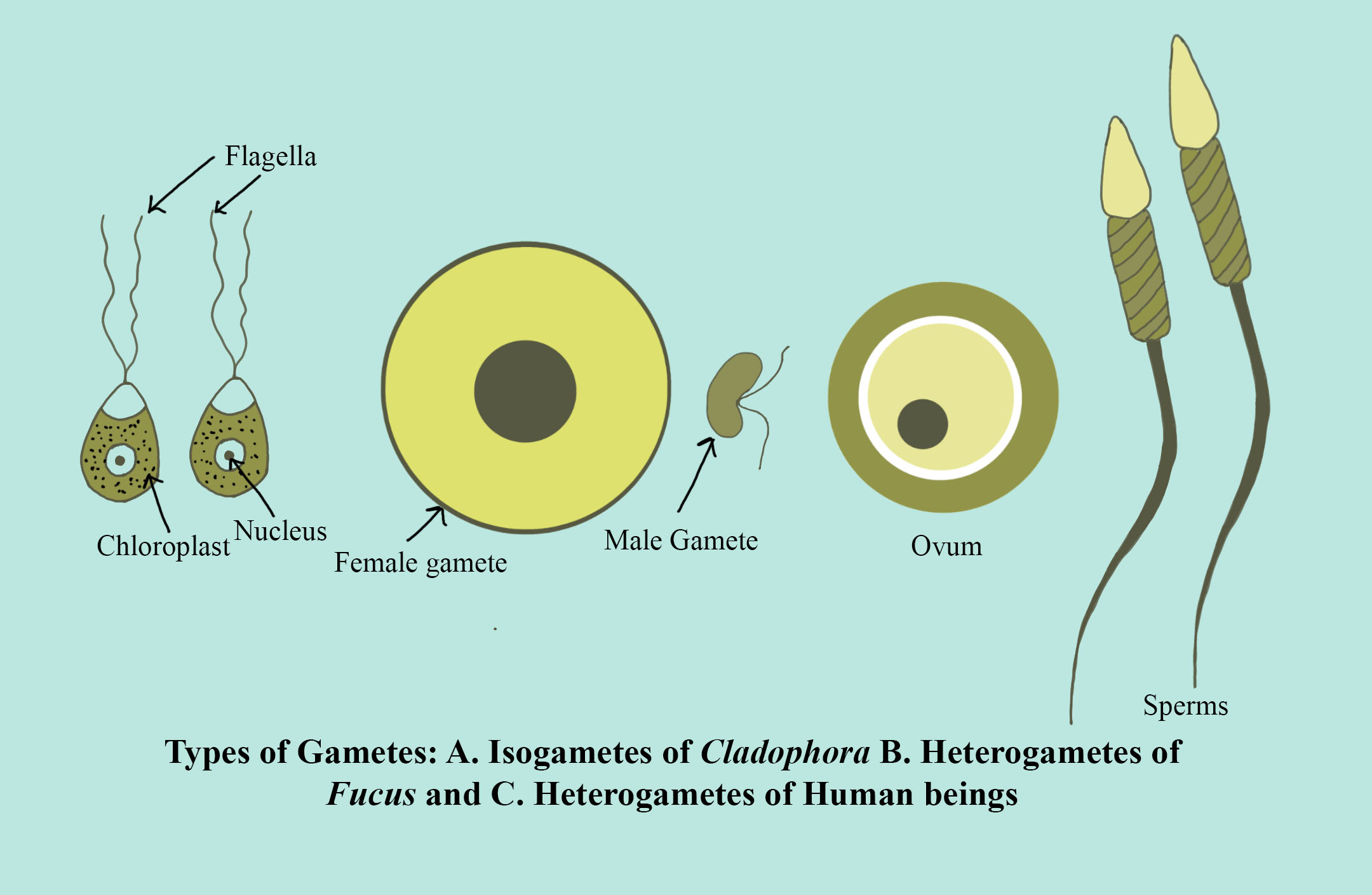
The gametes which have the same size and structure are known as Isogametes or homogametic, and the gametes which have different size and structure are known as anisogametes. Isogametes are very similar and due to this, it is not possible to differentiate them in a male and female gamete. On the other side, sexually reproducing organisms have different gametes and they can easily be identified as male and female gametes.
So, the correct answer is ‘Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect’.
Additional Information: There are several sorts of isogamy. One is when both gametes are flagellated and thus motile as seen in some algae. Another type is when neither of the gametes is flagellated. There are several sorts of anisogamy. Both gametes are flagellated and thus motile. Alternatively, both of the gametes are non-flagellated. The latter situation occurs in some algae and plants. The form of anisogamy that is seen in animals, including humans, is oogamy, where a large-sized, non-motile egg (ovum) is fertilized by a small, motile sperm (spermatozoon). The egg is optimized for longevity, whereas the tiny sperm is optimized for motility and speed. The size and resources of the ovum provide the assembly of pheromones, which acts as a magnet for the swimming sperm cells.
Note: Organisms that are isogamous i.e have gametes that look similar morphologically tend to have different mating types, most commonly noted as "+" and "−" strains. The fusion of two opposite strains known as conjugation. This occurs in some of the green algae like Spirogyra. It is assumed that positive strains are males and negative strains are female.
Complete step by step answer:
The gametes which have the same size and structure are known as Isogametes or homogametic, and the gametes which have different size and structure are known as anisogametes. Isogametes are very similar and due to this, it is not possible to differentiate them in a male and female gamete. On the other side, sexually reproducing organisms have different gametes and they can easily be identified as male and female gametes.

So, the correct answer is ‘Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect’.
Additional Information: There are several sorts of isogamy. One is when both gametes are flagellated and thus motile as seen in some algae. Another type is when neither of the gametes is flagellated. There are several sorts of anisogamy. Both gametes are flagellated and thus motile. Alternatively, both of the gametes are non-flagellated. The latter situation occurs in some algae and plants. The form of anisogamy that is seen in animals, including humans, is oogamy, where a large-sized, non-motile egg (ovum) is fertilized by a small, motile sperm (spermatozoon). The egg is optimized for longevity, whereas the tiny sperm is optimized for motility and speed. The size and resources of the ovum provide the assembly of pheromones, which acts as a magnet for the swimming sperm cells.
Note: Organisms that are isogamous i.e have gametes that look similar morphologically tend to have different mating types, most commonly noted as "+" and "−" strains. The fusion of two opposite strains known as conjugation. This occurs in some of the green algae like Spirogyra. It is assumed that positive strains are males and negative strains are female.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




