
How many ATP is needed to reproduce one molecule of RUDP in Calvin cycle?
A. 6
B. 2
C. 1
D. 18
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: Calvin cycle is a cyclic reaction that occurs in the dark phase of photosynthesis. In this reaction, carbon dioxide is converted into sugar and is therefore a carbon sequestration process. This reaction occurs in the stroma, the fluid-filled chloroplast area outside the thylakoid membrane. This reaction takes over the products (ATP and NADPH) of the light-dependent reaction and performs additional chemical processes on it.
Complete answer:
Like the photosynthetic reactions which are powered by light energy, the reactions that combine hydrogen and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates also require energy. The main source of this energy is the assimilation power of photolytic regeneration (ATP, NADPH$_2$).
1. Carboxylation- In carboxylation carbon dioxide is combined with ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) to form two 4-phosphoglycerate (PGA) molecules. This reaction is catalysed by RuBP carboxylase, a complex enzyme with a high affinity for carbon dioxide.
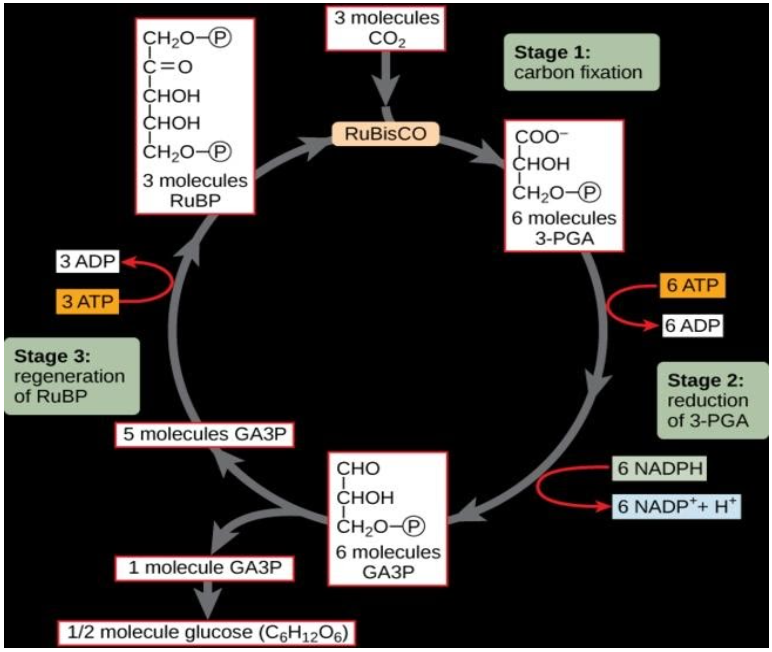
2. Reduction-In this step, PGA is reduced at the expense of the assimilation power to obtain triose phosphate. Reduction consumes ATP and NADPH (generated during primary photochemical reactions) and converts 3-PGA to 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde or triose phosphate.
3. Regeneration of RuBP and Formation of Hexose Sugar: In this step, the five triose phosphate molecules are rearranged to regenerate 3 carbon dioxide acceptor molecules. The formation of hexose sugars and regeneration of RuBP which consumes additional ATP so that the cycle continues.
For the generation of one carbon dioxide molecule from the pathway six carbon molecules is required, so six turns of the cycle required for regeneration of one molecule of RuBP one ATP is required and for the generation of six molecules of RuBP six ATP molecules are required.
Hence the correct option is (A).
Note:
The Calvin cycle was first observed by Melvin Calvin and his colleagues in the 1950's. Calvin received the Nobel Prize in 1961 for this work. In this cycle, the first stable compound in the Calvin cycle is a 3-carbon compound (3-phosphoglyceric acid). This cycle is also known as the C3 or PCR cycle (Photosynthetic Reduction of Carbon).
Although the Calvin cycle is referred to as a "dark reaction," it does not occur in the dark or at night. This is because the process requires reduced NADP, which is short-lived and originates from light-dependent reactions.
The Calvin cycle is also known as the pentose phosphate reductive cycle (RPP).
Complete answer:
Like the photosynthetic reactions which are powered by light energy, the reactions that combine hydrogen and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates also require energy. The main source of this energy is the assimilation power of photolytic regeneration (ATP, NADPH$_2$).
1. Carboxylation- In carboxylation carbon dioxide is combined with ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) to form two 4-phosphoglycerate (PGA) molecules. This reaction is catalysed by RuBP carboxylase, a complex enzyme with a high affinity for carbon dioxide.

2. Reduction-In this step, PGA is reduced at the expense of the assimilation power to obtain triose phosphate. Reduction consumes ATP and NADPH (generated during primary photochemical reactions) and converts 3-PGA to 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde or triose phosphate.
3. Regeneration of RuBP and Formation of Hexose Sugar: In this step, the five triose phosphate molecules are rearranged to regenerate 3 carbon dioxide acceptor molecules. The formation of hexose sugars and regeneration of RuBP which consumes additional ATP so that the cycle continues.
For the generation of one carbon dioxide molecule from the pathway six carbon molecules is required, so six turns of the cycle required for regeneration of one molecule of RuBP one ATP is required and for the generation of six molecules of RuBP six ATP molecules are required.
Hence the correct option is (A).
Note:
The Calvin cycle was first observed by Melvin Calvin and his colleagues in the 1950's. Calvin received the Nobel Prize in 1961 for this work. In this cycle, the first stable compound in the Calvin cycle is a 3-carbon compound (3-phosphoglyceric acid). This cycle is also known as the C3 or PCR cycle (Photosynthetic Reduction of Carbon).
Although the Calvin cycle is referred to as a "dark reaction," it does not occur in the dark or at night. This is because the process requires reduced NADP, which is short-lived and originates from light-dependent reactions.
The Calvin cycle is also known as the pentose phosphate reductive cycle (RPP).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




