
Azide ion $\left( {N_3^ - } \right)$ exhibits on $N - N$ bond order of $2$ and may be represented by resonance structures ${\rm I},{\rm I}{\rm I}$ and ${\rm I}{\rm I}{\rm I}$ given below:
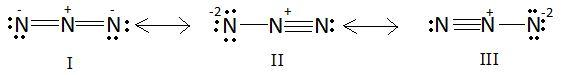
Select correct statements.
A: Structures ${\rm I}$ and ${\rm I}{\rm I}$ make greater contributions than ${\rm I}{\rm I}{\rm I}$.
B: Structures ${\rm I}{\rm I}$ and ${\rm I}{\rm I}{\rm I}$ make smaller contributions than ${\rm I}$.
C: Structures ${\rm I}$ and ${\rm I}{\rm I}{\rm I}$ make greater contributions than ${\rm I}{\rm I}$.
D: All the three structures make equal contributions.
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: Resonance structures are also called canonical structures. Resonance is a way of describing bonding in chemical molecules. In resonance structures delocalization of charge takes place. This delocalization of charge makes the molecule more stable.
Complete step by step answer:
Azide is an anion. Anion is the species with negative charge. Chemical formula of azide is $N_3^ - $. This ion is represented by some resonating structures. These structures are as follows:
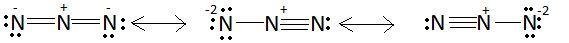
Out of these three structures, the first structure is the most stable. In the first structure there is a small charge on three nitrogen atoms but in the other two structures there is a $ - 2$ charge on a nitrogen atom which is quite large for a small atom like nitrogen. Also there is a triple bond present between two nitrogen atoms in the second and third structure due to which the molecule will tend to convert to nitrogen gas. Due to these reasons, the second and third structure is less stable as compared to the first structure. So, we can say that structures ${\rm I}{\rm I}$ and ${\rm I}{\rm I}{\rm I}$ make smaller contributions than ${\rm I}$.
Therefore the correct answer is option B.
Additional information: In resonating structures, the position of all the atoms is the same in all the structures but the position of double bond, charge and lone pair may vary. A true resonating structure of a molecule is the structure which is the average of the resonating structure for that molecule.
Note:
Most stable resonance structure is called resonance hybrid. A molecule can have resonating structures when it has a lone pair or double bond on the atom next to a double bond. Resonating structures are used when there is more than one way to show the position of double bond or lone pair in a molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
Azide is an anion. Anion is the species with negative charge. Chemical formula of azide is $N_3^ - $. This ion is represented by some resonating structures. These structures are as follows:
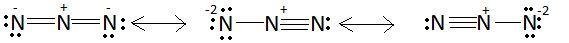
Out of these three structures, the first structure is the most stable. In the first structure there is a small charge on three nitrogen atoms but in the other two structures there is a $ - 2$ charge on a nitrogen atom which is quite large for a small atom like nitrogen. Also there is a triple bond present between two nitrogen atoms in the second and third structure due to which the molecule will tend to convert to nitrogen gas. Due to these reasons, the second and third structure is less stable as compared to the first structure. So, we can say that structures ${\rm I}{\rm I}$ and ${\rm I}{\rm I}{\rm I}$ make smaller contributions than ${\rm I}$.
Therefore the correct answer is option B.
Additional information: In resonating structures, the position of all the atoms is the same in all the structures but the position of double bond, charge and lone pair may vary. A true resonating structure of a molecule is the structure which is the average of the resonating structure for that molecule.
Note:
Most stable resonance structure is called resonance hybrid. A molecule can have resonating structures when it has a lone pair or double bond on the atom next to a double bond. Resonating structures are used when there is more than one way to show the position of double bond or lone pair in a molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




