
Back Cross is
(a) F1 x Any parent
(b) F1 x Recessive parent
(c) F1 x Dominant parent
(d) All of the above
Answer
592.8k+ views
Hint:A back cross is related to the crossing of the F1 generation with another related generation.
Complete answer:
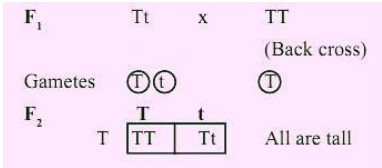
A back cross is a cross between the F1 hybrid progeny with any one of its parent progeny.
A test cross is included within the back cross. A back cross is done to find out some genotypic characters of F1 progeny.
Additional Information:
-A test cross is a cross between F1 generation and recessive parent to find out whether an individual is homozygous or heterozygous dominant
-A reciprocal cross is a type of cross wherein one cross individual A is used as a male and B as female and in the next cross, individual A is used as female and B as male.
-Depending on the number of contrasting characters used in crossbreeding the cross may be monohybrid, dihybrid, trihybrid, etc.
-While performing crosses the checkerboard pattern is used to figure out the outcome. This was used for the first time by C. Punnett.
-Epistasis- In epistasis one gene suppresses the expression of another non- allelic gene. It is of two types, dominant epistasis, and recessive epistasis.
Complementary Genes are a pair of genes that produce a similar effect independently but when they are present together in dominant form they express a new trait.
So, the correct answer is, “All of the above.”
Note: It should be remembered that the test cross is a type of back cross where F1 generation is crossed with F0 generation.
-Pleiotropy - It is the name given to a gene when a single gene can regulate or influence multiple phenotypic characters.
-Polygenic Inheritance- When a single phenotypic character is controlled by two or more genes, it is known as polygenic inheritance.
Complete answer:
A back cross is a cross between the F1 hybrid progeny with any one of its parent progeny.
A test cross is included within the back cross. A back cross is done to find out some genotypic characters of F1 progeny.
Additional Information:
-A test cross is a cross between F1 generation and recessive parent to find out whether an individual is homozygous or heterozygous dominant
-A reciprocal cross is a type of cross wherein one cross individual A is used as a male and B as female and in the next cross, individual A is used as female and B as male.
-Depending on the number of contrasting characters used in crossbreeding the cross may be monohybrid, dihybrid, trihybrid, etc.
-While performing crosses the checkerboard pattern is used to figure out the outcome. This was used for the first time by C. Punnett.
-Epistasis- In epistasis one gene suppresses the expression of another non- allelic gene. It is of two types, dominant epistasis, and recessive epistasis.
Complementary Genes are a pair of genes that produce a similar effect independently but when they are present together in dominant form they express a new trait.
So, the correct answer is, “All of the above.”
Note: It should be remembered that the test cross is a type of back cross where F1 generation is crossed with F0 generation.
-Pleiotropy - It is the name given to a gene when a single gene can regulate or influence multiple phenotypic characters.
-Polygenic Inheritance- When a single phenotypic character is controlled by two or more genes, it is known as polygenic inheritance.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




