
Benzene reacts with $C{H_3}Cl$ in the presence of anhydrous $AlC{l_3}$ to form:
A. Xylene
B. toluene
C. Chlorobenzene
D. benzyl chloride
Answer
501.6k+ views
Hint: A Friedel-Crafts reaction is a type of organic coupling reaction that uses an electrophilic aromatic substitution to attach substituents to aromatic rings. Alkylation and acylation reactions are the two most common Friedel-Crafts reactions.
Complete answer:
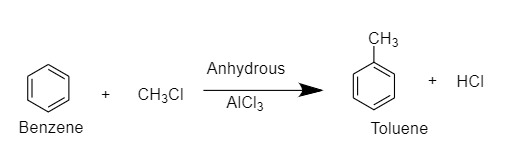
Benzene reacts with $C{H_3}Cl$ in the presence of anhydrous $AlC{l_3}$ to give toluene.
$C{H_3}Cl$ in the presence of anhydrous $AlC{l_3}$ acts as an alkylation agent and introduces an alkyl group. This reaction is known as Friedel- Crafts alkylation of benzene.
The reaction is as follows:
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation refers to the substitution of an alkyl group for an aromatic proton. With the help of a carbocation, an electrophilic attack on the aromatic ring is carried out. The Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction uses alkyl halides as reactants to produce alkylbenzenes.
Limitations of Friedel Crafts Alkylation
The Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction has a few drawbacks, while resolving some of the constraints of the related alkylation reaction (such as carbocation rearrangement and polyalkylation).
Ketones are the only products of the acylation process. When exposed to these conditions, formyl chloride $H(C = O)Cl$ decomposes into $CO$ and $HCl$.
If the aromatic compound is less reactive than a mono-halobenzene, it cannot participate in this reaction.
Because aryl amines form very unreactive complexes with the Lewis acid catalyst, they cannot be employed in this reaction.
Hence, the correct option is B. toluene.
Note:
It should be noted that in Friedel Craft ‘s reactions, a hydrogen atom (which was originally linked to the aromatic ring) is replaced with an electrophile. Since it works as a Lewis acid and coordinates with the halogens, forming an electrophile in the process, aluminium trichloride ($AlC{l_3}$) is frequently used as a catalyst in Friedel-Crafts processes.
Complete answer:
Benzene reacts with $C{H_3}Cl$ in the presence of anhydrous $AlC{l_3}$ to give toluene.
$C{H_3}Cl$ in the presence of anhydrous $AlC{l_3}$ acts as an alkylation agent and introduces an alkyl group. This reaction is known as Friedel- Crafts alkylation of benzene.
The reaction is as follows:

Friedel-Crafts Alkylation refers to the substitution of an alkyl group for an aromatic proton. With the help of a carbocation, an electrophilic attack on the aromatic ring is carried out. The Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction uses alkyl halides as reactants to produce alkylbenzenes.
Limitations of Friedel Crafts Alkylation
The Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction has a few drawbacks, while resolving some of the constraints of the related alkylation reaction (such as carbocation rearrangement and polyalkylation).
Ketones are the only products of the acylation process. When exposed to these conditions, formyl chloride $H(C = O)Cl$ decomposes into $CO$ and $HCl$.
If the aromatic compound is less reactive than a mono-halobenzene, it cannot participate in this reaction.
Because aryl amines form very unreactive complexes with the Lewis acid catalyst, they cannot be employed in this reaction.
Hence, the correct option is B. toluene.
Note:
It should be noted that in Friedel Craft ‘s reactions, a hydrogen atom (which was originally linked to the aromatic ring) is replaced with an electrophile. Since it works as a Lewis acid and coordinates with the halogens, forming an electrophile in the process, aluminium trichloride ($AlC{l_3}$) is frequently used as a catalyst in Friedel-Crafts processes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




