
Benzyl alcohol with concentrated \[{H_2}S{O_4}\] gives a resinous material which has a high boiling point. Predict the structure of this resinous material.
Answer
505.8k+ views
Hint: Benzyl alcohol is an aromatic alcohol with the formula \[{C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}OH\]. It is a colourless liquid with a mild pleasant aromatic odour. It is a useful solvent due to its polarity, low toxicity, and low vapor pressure. Whenever concentrated sulphuric acid is used with an alcohol compound, a dehydration reaction occurs.
Complete answer: The above reaction of benzyl alcohol with conc. \[{H_2}S{O_4}\] is as follows:
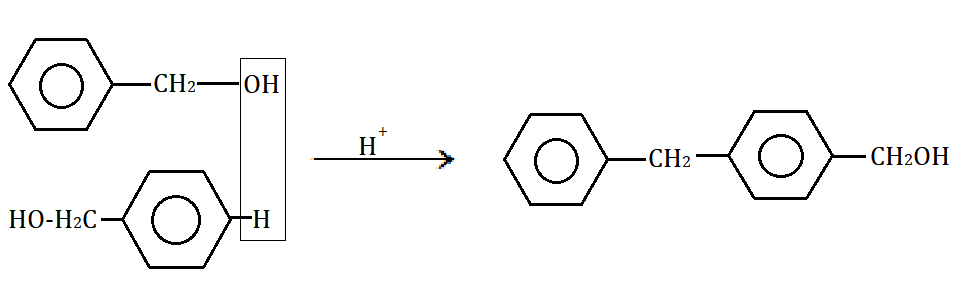
Here, one hydrogen oxide or water molecule is removed due to dehydration.
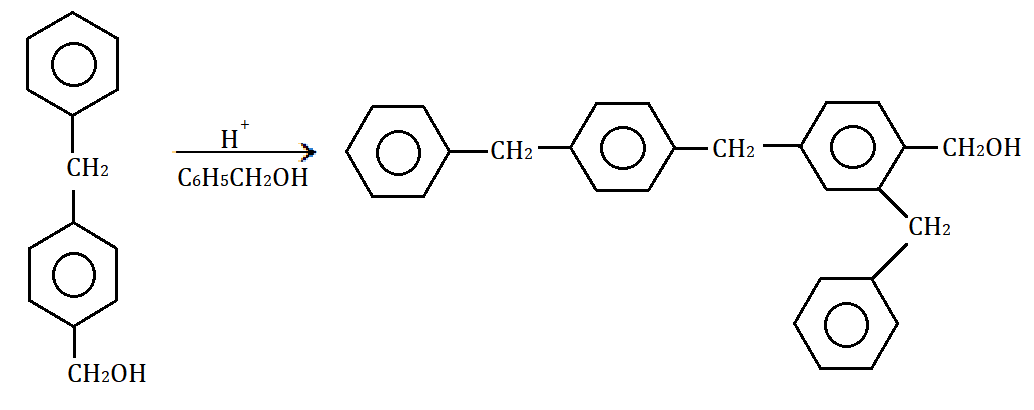
The product again goes into dehydration deriving its long chain structure as shown below:
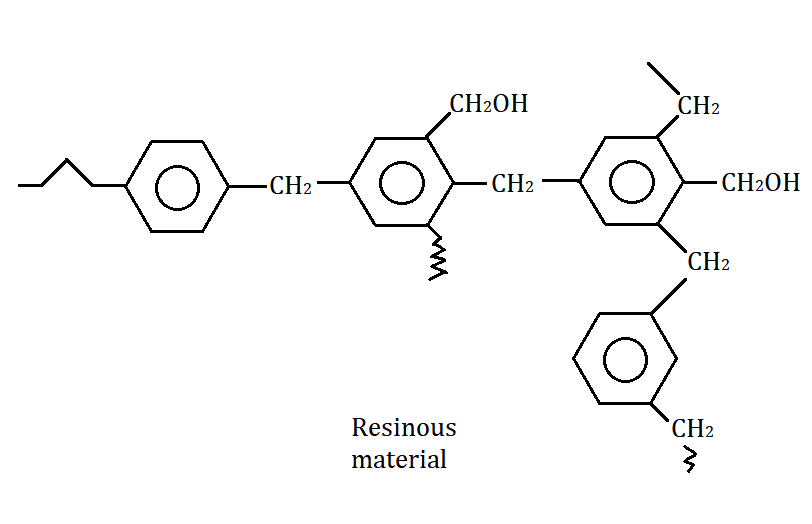
As shown above, the resinous material has a large molecular mass. Also, the covalent bonding is very strong here which gives it a high boiling point.
Additional information:
Dehydration reaction also known as condensation reaction is a conversion that involves the loss of water from the reacting molecule or ion. Dehydration reactions are common processes and are the reverse of a hydration reaction. Common dehydrating agents used in organic synthesis include sulfuric acid and alumina. Often dehydration reactions are affected with heating.
The process of hydrolysis or hydration reaction is the reverse reaction, meaning that the water is recombined with the two hydroxyl groups and the disaccharide reverts to being monosaccharides.
Note:
The above reaction may seem as an aldol condensation reaction at first glance. However, in aldol condensation, an enol or an enolate ion reacts with a carbonyl compound to form a \[\beta - \]hydroxyaldehyde or \[\beta - \]hydroxyketone (an aldol reaction), followed by dehydration to give a conjugated enone.
Complete answer: The above reaction of benzyl alcohol with conc. \[{H_2}S{O_4}\] is as follows:

Here, one hydrogen oxide or water molecule is removed due to dehydration.

The product again goes into dehydration deriving its long chain structure as shown below:

As shown above, the resinous material has a large molecular mass. Also, the covalent bonding is very strong here which gives it a high boiling point.
Additional information:
Dehydration reaction also known as condensation reaction is a conversion that involves the loss of water from the reacting molecule or ion. Dehydration reactions are common processes and are the reverse of a hydration reaction. Common dehydrating agents used in organic synthesis include sulfuric acid and alumina. Often dehydration reactions are affected with heating.
The process of hydrolysis or hydration reaction is the reverse reaction, meaning that the water is recombined with the two hydroxyl groups and the disaccharide reverts to being monosaccharides.
Note:
The above reaction may seem as an aldol condensation reaction at first glance. However, in aldol condensation, an enol or an enolate ion reacts with a carbonyl compound to form a \[\beta - \]hydroxyaldehyde or \[\beta - \]hydroxyketone (an aldol reaction), followed by dehydration to give a conjugated enone.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




