
$\beta -D-glucopyranose$ is represented as:
A)
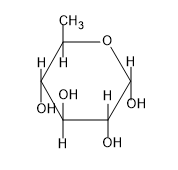
B)
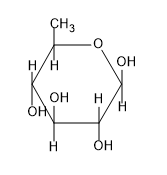
C)
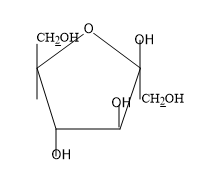
D) None of these



Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: The $\beta -D-glucopyranose$ is formed by the cyclisation of the open chain of a glucose molecule through intermolecular nucleophilic addition reaction.
- The name glucopyranose is in analogue with the structure of pyran.
Complete Solution :
- In the organic chemistry branch of chemistry we mainly deal with the hydrocarbons i.e. we study about the compounds formed by the carbon and hydrogen mainly. Stereochemistry is one of the hot topics in organic chemistry and the question is solved by knowing the basics of stereochemistry.
So in the question we are asked to draw that correct structure of $\beta -D-glucopyranose$.
- We know that the glucose molecule which possesses the formulae ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}$. It is a monosaccharide which possesses an aldehyde group in them. So basically glucose is an aldehyde and it shows positive results towards the aldehyde group tests.
- The glucose exists in two structures i.e. in open chain structure and in ring structure.
Since the glucose molecule contains six carbon atoms and one aldehyde group it is called as aldohexose.
The open chain structure of glucose on cyclisation gives the cyclic structure of glucose.
The cyclic ring structure of glucose is called as the D-glucopyranose and it possesses two anomers $\alpha -D-glucopyranose $ and $\beta -D-glucopyranose$.
When the glucose is present in aqueous state almost every glucose molecule will be in cyclic structure and cyclic structure of the glucose is obtained by the cyclization reaction of the open chain structure enhanced by the nucleophile addition between the -OH group in the C-5 and aldehyde group in C-1. Here –OH group is the nucleophile and the cyclisation yields a hemiacetal group, -C-(OH)-H-O at C-1 and this ring is referred to as pyranose.
- The letter D refers to dextrorotatory i.e. it rotates the plane polarized light in the clockwise direction.
The $\alpha -D-glucopyranose$ and $\beta -D-glucopyranose$ differ by the position of the hydroxyl group in the C-1 carbon.
- If the –OH group is in the same direction to the other flanking substituents then it is $\alpha -D-glucopyranose$ and if it is opposite to other substituents, it is called as the $\beta -D-glucopyranose$.

So from the above figure we can know the structure of $\beta -D-glucopyranose$ and the structure is not given in the option.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: In $\beta -D-glucopyranose$ the –OH group is place in the right of the C-5 in the open ring structure of glucose and it will be placed in the left side in $\alpha -D-glucopyranose$, In the open chain of glucose there is only four stereogenic centres but in cyclic structure there is five stereogenic centres.
- The name glucopyranose is in analogue with the structure of pyran.
Complete Solution :
- In the organic chemistry branch of chemistry we mainly deal with the hydrocarbons i.e. we study about the compounds formed by the carbon and hydrogen mainly. Stereochemistry is one of the hot topics in organic chemistry and the question is solved by knowing the basics of stereochemistry.
So in the question we are asked to draw that correct structure of $\beta -D-glucopyranose$.
- We know that the glucose molecule which possesses the formulae ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}$. It is a monosaccharide which possesses an aldehyde group in them. So basically glucose is an aldehyde and it shows positive results towards the aldehyde group tests.
- The glucose exists in two structures i.e. in open chain structure and in ring structure.
Since the glucose molecule contains six carbon atoms and one aldehyde group it is called as aldohexose.
The open chain structure of glucose on cyclisation gives the cyclic structure of glucose.
The cyclic ring structure of glucose is called as the D-glucopyranose and it possesses two anomers $\alpha -D-glucopyranose $ and $\beta -D-glucopyranose$.
When the glucose is present in aqueous state almost every glucose molecule will be in cyclic structure and cyclic structure of the glucose is obtained by the cyclization reaction of the open chain structure enhanced by the nucleophile addition between the -OH group in the C-5 and aldehyde group in C-1. Here –OH group is the nucleophile and the cyclisation yields a hemiacetal group, -C-(OH)-H-O at C-1 and this ring is referred to as pyranose.
- The letter D refers to dextrorotatory i.e. it rotates the plane polarized light in the clockwise direction.
The $\alpha -D-glucopyranose$ and $\beta -D-glucopyranose$ differ by the position of the hydroxyl group in the C-1 carbon.
- If the –OH group is in the same direction to the other flanking substituents then it is $\alpha -D-glucopyranose$ and if it is opposite to other substituents, it is called as the $\beta -D-glucopyranose$.

So from the above figure we can know the structure of $\beta -D-glucopyranose$ and the structure is not given in the option.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: In $\beta -D-glucopyranose$ the –OH group is place in the right of the C-5 in the open ring structure of glucose and it will be placed in the left side in $\alpha -D-glucopyranose$, In the open chain of glucose there is only four stereogenic centres but in cyclic structure there is five stereogenic centres.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




