
What is Bioreactor? Explain its functioning?
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: Bioreactors are the artificial conditions set up for obtaining the foreign gene product on a large scale. With the help of recombinant DNA technology, a foreign gene gets expressed into target protein in a heterologous host called recombinant protein.
Complete Answer:
A bioreactor refers to a process(aerobic or anaerobic) where a system supports a biologically active environment. It is a chemical process where a system is created for growing organisms such as yeast, bacteria, or animal cells in a controlled way. These bioreactors are also used in industries for creating vaccines and antibodies.
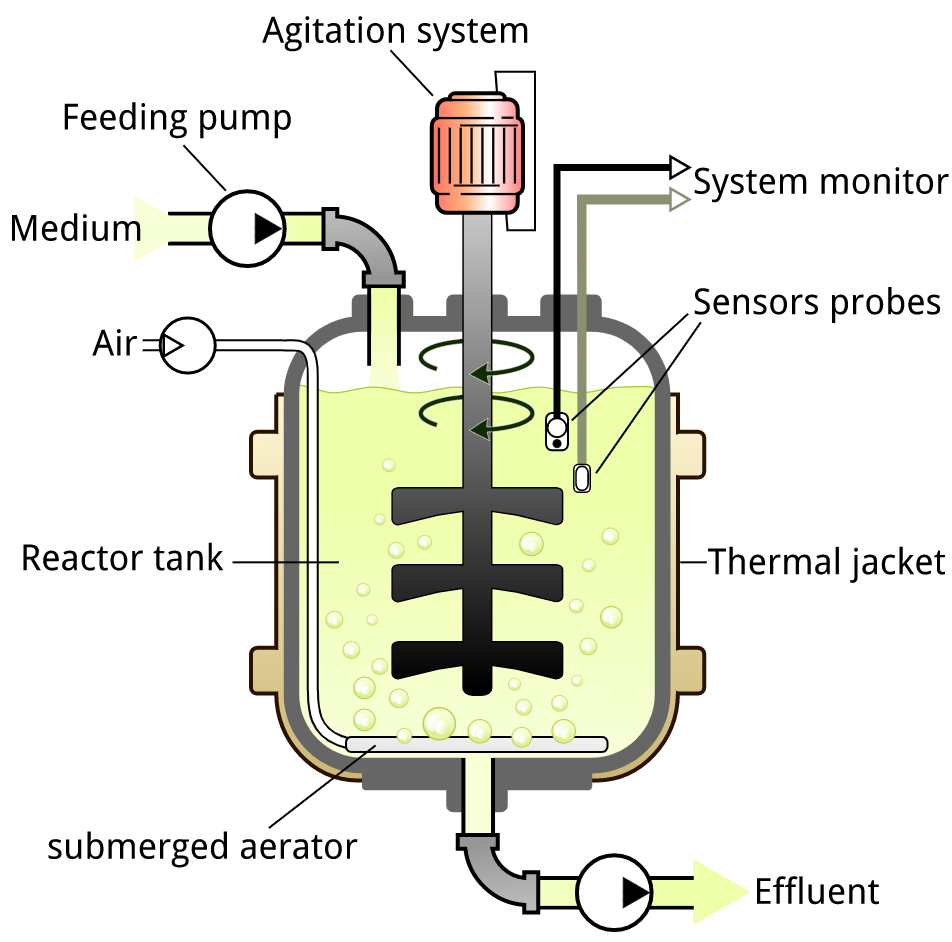
In this chemical process, organisms are placed in vessels. They are cylindrical and are made of stainless steel. Bioreactors produce the same kind of environment and ensure the same temperature, oxygen level and pH level.
The process of obtaining foreign gene products from bioreactors includes 3 stages:
1. Upstream Processing where the raw material is an origin where it is converted into a suitable form.
2. Bioreaction where it is next transferred into another bioreaction stage.
3. Downstream Processing where the material is further processed into more
useful byproduct.
The ecological conditions inside the bioreactor, for example, temperature, supplement fixations, pH, and disintegrated gases influence the development and efficiency of the creatures grown in the bioreactor. The temperature of the ageing medium is kept up by a cooling coat, curls, or both.
Note: For maintaining the optimal conditions, bioreactors contain several systems. They are agitator system, oxygen delivery system, foam control system, temperature control system, Ph control system, sampling ports to withdraw a small volume of culture.
Complete Answer:
A bioreactor refers to a process(aerobic or anaerobic) where a system supports a biologically active environment. It is a chemical process where a system is created for growing organisms such as yeast, bacteria, or animal cells in a controlled way. These bioreactors are also used in industries for creating vaccines and antibodies.
In this chemical process, organisms are placed in vessels. They are cylindrical and are made of stainless steel. Bioreactors produce the same kind of environment and ensure the same temperature, oxygen level and pH level.

The process of obtaining foreign gene products from bioreactors includes 3 stages:
1. Upstream Processing where the raw material is an origin where it is converted into a suitable form.
2. Bioreaction where it is next transferred into another bioreaction stage.
3. Downstream Processing where the material is further processed into more
useful byproduct.
The ecological conditions inside the bioreactor, for example, temperature, supplement fixations, pH, and disintegrated gases influence the development and efficiency of the creatures grown in the bioreactor. The temperature of the ageing medium is kept up by a cooling coat, curls, or both.
Note: For maintaining the optimal conditions, bioreactors contain several systems. They are agitator system, oxygen delivery system, foam control system, temperature control system, Ph control system, sampling ports to withdraw a small volume of culture.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




