
Why is boron trifluoride written in two ways in lewis dot diagram?
Answer
522.6k+ views
Hint: Lewis dot structure is satisfied by their charges. So to determine if the given lewis dot structure is correct or not, one should look for the formal charge on that atom in a molecule. Formal charges are the charge on an atom of a molecule, assuming that all electrons are equally shared in a bond.
Complete answer:
To solve this question, we have to understand about the lewis dot structure and its formal charge.
So, lewis dot structure or formulas are the diagrams that represent the bonding between the atoms of a molecule, it also depicts about the number of lone pairs and the shared electrons.
So, in case of \[B{F_3}\] we have two lewis dot structures, this fact can be attributed because of overlapping phenomena in case of fluorine bonding with boron.
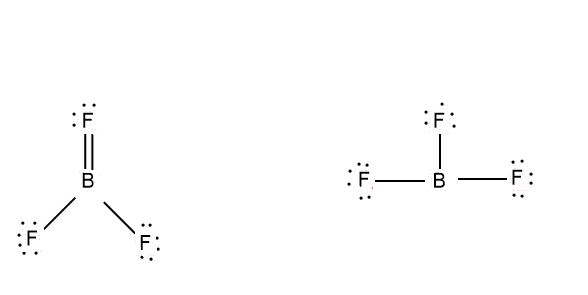
This is because fluorine lone pairs are of the appropriate size and exact symmetry to overlap with the empty \[p\] orbitals of boron.
Generally in lewis dot structure, we can see that the structure of a molecule is satisfied by each atom sharing or having complete 8 valence electrons in the valence shell. But we can say Boron is an exception, it can be satisfied by 6 electrons in its valence shell.
Note:
Also for the molecule \[^ + F = B = {F_2}\]
We can calculate the formal charge as , the fluorine with double bond has \[6\] electrons around it , which is one less than required so , its formal charge is \[1\] and fluorine with single bond has formal charge \[0\] has they have 7 electrons around them , as required . But when we talk about Boron it has \[4\] electrons, which is \[1\] more than required, so charge is + \[1\], so this is a quite contrary structure
Complete answer:
To solve this question, we have to understand about the lewis dot structure and its formal charge.
So, lewis dot structure or formulas are the diagrams that represent the bonding between the atoms of a molecule, it also depicts about the number of lone pairs and the shared electrons.
So, in case of \[B{F_3}\] we have two lewis dot structures, this fact can be attributed because of overlapping phenomena in case of fluorine bonding with boron.

This is because fluorine lone pairs are of the appropriate size and exact symmetry to overlap with the empty \[p\] orbitals of boron.
Generally in lewis dot structure, we can see that the structure of a molecule is satisfied by each atom sharing or having complete 8 valence electrons in the valence shell. But we can say Boron is an exception, it can be satisfied by 6 electrons in its valence shell.
Note:
Also for the molecule \[^ + F = B = {F_2}\]
We can calculate the formal charge as , the fluorine with double bond has \[6\] electrons around it , which is one less than required so , its formal charge is \[1\] and fluorine with single bond has formal charge \[0\] has they have 7 electrons around them , as required . But when we talk about Boron it has \[4\] electrons, which is \[1\] more than required, so charge is + \[1\], so this is a quite contrary structure
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




