
But-2-ene can be obtained by the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of:
A. 2, 3-dimethyl maleic acid
B. 2, 2-dimethylbutane dioic acid
C. 2-methyl butane dioic acid
D. 2, 3-dimethylbutane dioic acid
Answer
544.8k+ views
Hint: The Kolbe Electrolysis is the electrochemical oxidative decarboxylation of carboxylic acids leasing to the formation of the radicals that dimerise resulting in the formation of an alkene molecule.
Complete step-by-step answer:When a solution of 2, 3-dimethyl maleic acid is hydrolysed then it leads to the formation of but-2-ene. The carboxylate anion releases two electrons and it results in the formation of the carboxylic radical and then two molecules of carbon dioxide then it forms but-2-ene. There are certain side-products that are formed along with the products in the reaction. The reaction mechanism can be represented as follows:
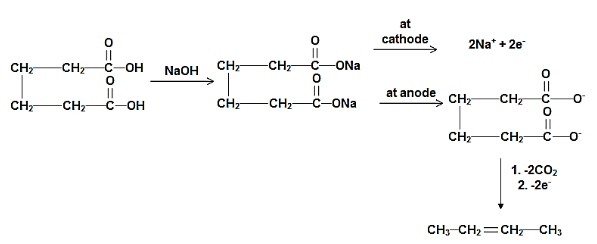
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note: The Kolbe reaction is named after Hermann Kolbe. The Kolbe reaction is formally a decarboxylative dimerization of two carboxylate anions or acids.
The carboxylic acids can be formed from the alkenes by the oxidation using different oxidising agents such as osmium tetroxide and potassium permanganate and potassium dichromate. Ozonolysis is yet another route for the preparation of acids from alkenes.
The reaction of carbon dioxide with Grignard’s reagent also gives rise to carboxylic acids.
In the haloform reaction with iodine, bromine, and chlorine, methyl ketones are converted to the corresponding haloalkanes and the carboxylic acids.
Complete step-by-step answer:When a solution of 2, 3-dimethyl maleic acid is hydrolysed then it leads to the formation of but-2-ene. The carboxylate anion releases two electrons and it results in the formation of the carboxylic radical and then two molecules of carbon dioxide then it forms but-2-ene. There are certain side-products that are formed along with the products in the reaction. The reaction mechanism can be represented as follows:

Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note: The Kolbe reaction is named after Hermann Kolbe. The Kolbe reaction is formally a decarboxylative dimerization of two carboxylate anions or acids.
The carboxylic acids can be formed from the alkenes by the oxidation using different oxidising agents such as osmium tetroxide and potassium permanganate and potassium dichromate. Ozonolysis is yet another route for the preparation of acids from alkenes.
The reaction of carbon dioxide with Grignard’s reagent also gives rise to carboxylic acids.
In the haloform reaction with iodine, bromine, and chlorine, methyl ketones are converted to the corresponding haloalkanes and the carboxylic acids.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




