
Calculate the oxidation number of Sulphur in \[{S_2}{O_8}^{2 - }\].
Answer
508.8k+ views
Hint: The oxidation number of sulphur atom in \[{S_2}{O_8}^{2 - }\] can be determined by knowing its structure as each atoms has a unique oxidation number depending upon the kinds of bonds it makes with other atoms. All oxygen atoms in \[{S_2}{O_8}^{2 - }\] do not contribute equally to the net oxidation number.
Complete answer:
Oxidation number is a hypothetical number assigned to each atom in a molecule to measure the number of electrons contributed by that atom in forming the bonds of the molecule.
In order to determine the oxidation number of the sulphur atom in \[{S_2}{O_8}^{2 - }\], its complete structure must be known.
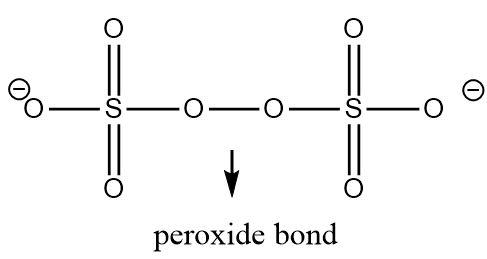
Both the sulphur atoms are symmetrically bonded and have the same set of atoms around them which means that their oxidation number would be the same. Let its oxidation number be \[x\].
There are two oxygen atoms in the structure that are linked to each through a peroxide bond. Thus one electron in each oxygen atom participating in a peroxide linkage is utilized in making an oxygen-oxygen bond. The peroxide bond altogether contributes two electrons (from both the free ends) in its bonds with sulphur, hence the oxidation number of an oxygen atom linked through a peroxide bond is \[ - 1\] and not \[ - 2\]. The remaining oxygen atoms linked to sulphur contribute two electrons each and have an oxidation number of \[ - 2\] .
The total molecule has a charge of \[ - 2\] and the unknown oxidation number of sulphur can be found out by equating the sum of oxidation numbers of each atom to the total charge on the molecule.
\[( - 2) \times ({\text{6 atoms of O) + (}} - 1) \times (2{\text{ atoms in peroxide linkage) + (}}x) \times (2{\text{ sulphur atoms) = }} - 2\]
\[( - 2 \times 6) + ( - 1 \times 2) + 2x = - 2\]
\[ - 14 + 2x = - 2\]
On solving this simple linear equation in one variable we get,
\[2x = 12\]
\[x = \dfrac{{12}}{2} = + 6\]
Hence the oxidation number of sulphur atoms in \[{S_2}{O_8}^{2 - }\] is \[ + 6\].
Note:
The oxidation number should not be confused with valency as an atom is capable of showing variable oxidation states in different types of molecules. The oxidation number can be higher or lower than the valency of the atom and is never fixed.
Complete answer:
Oxidation number is a hypothetical number assigned to each atom in a molecule to measure the number of electrons contributed by that atom in forming the bonds of the molecule.
In order to determine the oxidation number of the sulphur atom in \[{S_2}{O_8}^{2 - }\], its complete structure must be known.

Both the sulphur atoms are symmetrically bonded and have the same set of atoms around them which means that their oxidation number would be the same. Let its oxidation number be \[x\].
There are two oxygen atoms in the structure that are linked to each through a peroxide bond. Thus one electron in each oxygen atom participating in a peroxide linkage is utilized in making an oxygen-oxygen bond. The peroxide bond altogether contributes two electrons (from both the free ends) in its bonds with sulphur, hence the oxidation number of an oxygen atom linked through a peroxide bond is \[ - 1\] and not \[ - 2\]. The remaining oxygen atoms linked to sulphur contribute two electrons each and have an oxidation number of \[ - 2\] .
The total molecule has a charge of \[ - 2\] and the unknown oxidation number of sulphur can be found out by equating the sum of oxidation numbers of each atom to the total charge on the molecule.
\[( - 2) \times ({\text{6 atoms of O) + (}} - 1) \times (2{\text{ atoms in peroxide linkage) + (}}x) \times (2{\text{ sulphur atoms) = }} - 2\]
\[( - 2 \times 6) + ( - 1 \times 2) + 2x = - 2\]
\[ - 14 + 2x = - 2\]
On solving this simple linear equation in one variable we get,
\[2x = 12\]
\[x = \dfrac{{12}}{2} = + 6\]
Hence the oxidation number of sulphur atoms in \[{S_2}{O_8}^{2 - }\] is \[ + 6\].
Note:
The oxidation number should not be confused with valency as an atom is capable of showing variable oxidation states in different types of molecules. The oxidation number can be higher or lower than the valency of the atom and is never fixed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




