
Carbocation are stabilized by three main structural factors, such factors are neighbouring carbon-carbon multiple bonds and neighbouring atoms with lone pairs. Most stable among the following carbocation is?
A.
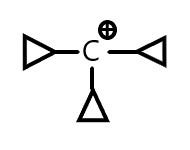
B. ${C_2}{H_5} - {H_2}\mathop C\limits^ \oplus $
C.
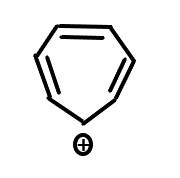
D. $C{H_3} - \mathop C\limits^ \oplus H - C{H_3}$


Answer
560.4k+ views
Hint: As we know that a carbocation is basically that molecule where carbon atom possess a positive charge and even electron cation and includes a factor that help in stabilisation of carbocation which involves the increase in number of carbon atoms adjacent to the primary carbon.
Complete step by step solution:
- As we have discussed that the increasing the carbon atoms adjacent to a primary carbon atom can increase the stability of the carbocation and as we can see that the first option contains a tertiary carbocation which is more stable than the others because all the other compounds either contains a primary carbocation or a secondary carbocation.
- Also, the positive charge on the carbon atom in option (A) which is tri cyclopropyl cyclopropenium is stabilized by the positive inductive effect on the neighbouring atoms which basically pulled in the electrons.
- The second option is a primary carbocation and thus least stable. The compound of the third option is a secondary carbocation and the last option is also a secondary carbocation.
Thus the order of stability of carbocation becomes:
${3^\circ } > {2^\circ } > {1^\circ }$
Hence the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Always remember that the tertiary carbocation is most stable followed by a secondary carbocation and lastly a primary carbocation. The three factor that helps in stabilisation of a carbocation are: increase in number of carbon atoms adjacent to the primary carbon, increase in adjacent pi-bonds which will allow the p-orbital of carbocation to be a part of conjugation system and increasing the adjacent atoms with lone pairs of electrons.
Complete step by step solution:
- As we have discussed that the increasing the carbon atoms adjacent to a primary carbon atom can increase the stability of the carbocation and as we can see that the first option contains a tertiary carbocation which is more stable than the others because all the other compounds either contains a primary carbocation or a secondary carbocation.
- Also, the positive charge on the carbon atom in option (A) which is tri cyclopropyl cyclopropenium is stabilized by the positive inductive effect on the neighbouring atoms which basically pulled in the electrons.
- The second option is a primary carbocation and thus least stable. The compound of the third option is a secondary carbocation and the last option is also a secondary carbocation.
Thus the order of stability of carbocation becomes:
${3^\circ } > {2^\circ } > {1^\circ }$
Hence the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Always remember that the tertiary carbocation is most stable followed by a secondary carbocation and lastly a primary carbocation. The three factor that helps in stabilisation of a carbocation are: increase in number of carbon atoms adjacent to the primary carbon, increase in adjacent pi-bonds which will allow the p-orbital of carbocation to be a part of conjugation system and increasing the adjacent atoms with lone pairs of electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




