
Chylomicrons are associated with
(a) Digestion of fats
(b) Absorption of fats
(c) Digestion of proteins
(d) Absorption of proteins
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: Lipoprotein particles composed of triglycerides ($85\%$ - $92\%$), phospholipids ($6\%$ - $12\%$), cholesterol ($1\%$ - $3\%$), and proteins ($1\%$ - $2\%$) are chylomicrons from Greek chylous, meaning juice, and microns, meaning small particles, also known as ultra low- density lipoproteins (ULDL) .
Complete answer:
- They carry dietary lipids to other sites in the body from the intestines.
- Chylomicrons transport lipids absorbed into adipose, cardiac, and skeletal muscle tissue from the intestine, where their triglyceride components are hydrolyzed by lipoprotein lipase action, enabling the tissues to absorb the released free fatty acids.
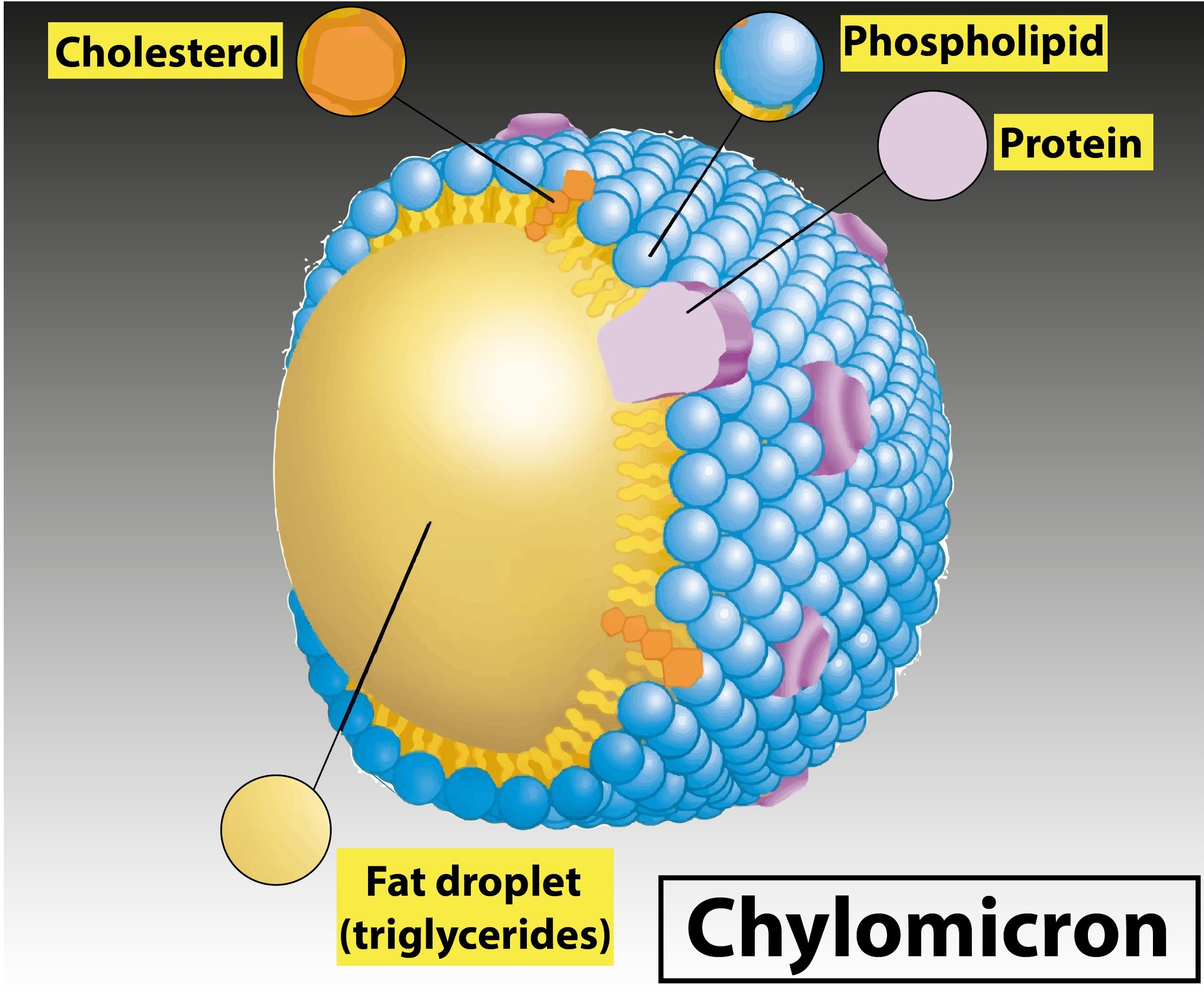
- There is an inverse relationship between the density and size of lipoprotein particles: the larger particles that have a higher proportion of internal fat molecules compared to the shell's outer emulsifying protein molecules, and fats.
Additional Information:
- ULDLs is one of the five major lipoproteins (density- sorted) groups that allow fats and cholesterol to move within the bloodstream water- based solution.
- Chylomicron residues are produced and taken up by the liver after a significant portion of the triglyceride core has been hydrolyzed, thus also moving dietary fat to the liver.
- Chylomicrons in the absorptive cells (enterocytes) of the small intestine are produced in the endoplasmic reticulum.
- The villi, lined with the brush border's microvilli, provide absorption of a lot of surface area. Via the basolateral membrane, freshly formed chylomicrons are secreted into the lacteals, where they enter lymph to become chylous.
- Hence, unlike the saccharides and amino acids that digestion releases from the diet's carbohydrates and proteins (respectively) , the diet's lipids bypass the hepatic portal system, which ensures that the lymphatic system prevents metabolism from first passing.
So, the correct answer is ‘(b) Absorption of fats’.
Note:
- The chylous is borne by the lymphatic vessels to the venous return to the systemic circulation.
- The chylomicrons provide the tissue from there with fat consumed from the diet.
Complete answer:
- They carry dietary lipids to other sites in the body from the intestines.
- Chylomicrons transport lipids absorbed into adipose, cardiac, and skeletal muscle tissue from the intestine, where their triglyceride components are hydrolyzed by lipoprotein lipase action, enabling the tissues to absorb the released free fatty acids.

- There is an inverse relationship between the density and size of lipoprotein particles: the larger particles that have a higher proportion of internal fat molecules compared to the shell's outer emulsifying protein molecules, and fats.
Additional Information:
- ULDLs is one of the five major lipoproteins (density- sorted) groups that allow fats and cholesterol to move within the bloodstream water- based solution.
- Chylomicron residues are produced and taken up by the liver after a significant portion of the triglyceride core has been hydrolyzed, thus also moving dietary fat to the liver.
- Chylomicrons in the absorptive cells (enterocytes) of the small intestine are produced in the endoplasmic reticulum.
- The villi, lined with the brush border's microvilli, provide absorption of a lot of surface area. Via the basolateral membrane, freshly formed chylomicrons are secreted into the lacteals, where they enter lymph to become chylous.
- Hence, unlike the saccharides and amino acids that digestion releases from the diet's carbohydrates and proteins (respectively) , the diet's lipids bypass the hepatic portal system, which ensures that the lymphatic system prevents metabolism from first passing.
So, the correct answer is ‘(b) Absorption of fats’.
Note:
- The chylous is borne by the lymphatic vessels to the venous return to the systemic circulation.
- The chylomicrons provide the tissue from there with fat consumed from the diet.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




