
Complete the following reaction by filling most stable intermediate A and B.

A.
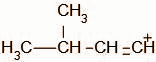
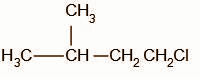
B.
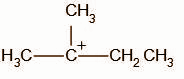
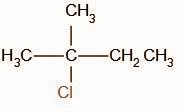
C.
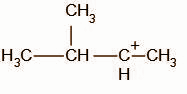

D.
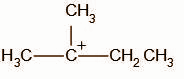
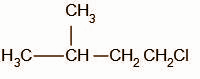

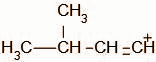
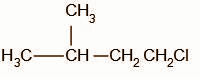





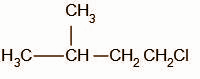
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: When an alkene is reacted with a hydrogen halide, alkyl halides are formed. The reaction proceeds with the formation of a carbocation intermediate. The intermediate so formed must be stable. The positive charge must be neutralized as much as possible for the carbocation to be stable.
Complete step by step solution:
When a hydrogen halide reacts with an alkene, the first step of the reaction is the protonation of the alkene. The proton attacks on the terminal atom of the alkene forming the intermediate,
We know that tertiary carbocations are more stable than secondary carbocations, the compound undergoes rearrangement to form a tertiary carbocation intermediate.
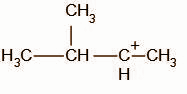
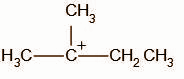
The secondary carbocation undergoes a hydride shift and the intermediate, A, obtained is:
In the second step, the chloride ion attacks the carbocation intermediate. The nucleophilic chloride ion attacks the positively charged carbon atom resulting in the formation of alkyl halide.
The obtained product B is,
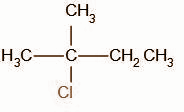
Thus, the correct option is B.
Note: The order of reactivity of hydrogen halides depends on the ease of the breaking of the bond between the hydrogen atom and halogen atom. Thus, hydrogen iodide is most reactive followed by hydrogen bromide, hydrogen chloride and the least reactive of all is hydrogen fluoride. The addition of the alkyl halides in case of unsymmetrical alkenes follows Markovnikov’s rule.
According to Markovnikov's rule, the hydrogen atom of the hydrogen halide becomes bonded to the carbon atom that has the greater number of hydrogen atoms in the starting alkene. Thus the formation of a secondary or tertiary alkyl halide is preferred.
Complete step by step solution:
When a hydrogen halide reacts with an alkene, the first step of the reaction is the protonation of the alkene. The proton attacks on the terminal atom of the alkene forming the intermediate,

We know that tertiary carbocations are more stable than secondary carbocations, the compound undergoes rearrangement to form a tertiary carbocation intermediate.
The secondary carbocation undergoes a hydride shift and the intermediate, A, obtained is:

In the second step, the chloride ion attacks the carbocation intermediate. The nucleophilic chloride ion attacks the positively charged carbon atom resulting in the formation of alkyl halide.
The obtained product B is,

Thus, the correct option is B.
Note: The order of reactivity of hydrogen halides depends on the ease of the breaking of the bond between the hydrogen atom and halogen atom. Thus, hydrogen iodide is most reactive followed by hydrogen bromide, hydrogen chloride and the least reactive of all is hydrogen fluoride. The addition of the alkyl halides in case of unsymmetrical alkenes follows Markovnikov’s rule.
According to Markovnikov's rule, the hydrogen atom of the hydrogen halide becomes bonded to the carbon atom that has the greater number of hydrogen atoms in the starting alkene. Thus the formation of a secondary or tertiary alkyl halide is preferred.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




