
Component of actin filament of a sarcomere is
A. Myosin and troponin
B. Troponin and actin
C. Actin and myosin
D. Actin, troponin and tropomyosin
Answer
570k+ views
Hint:-A sarcomere is the unit of muscle fiber. It is composed of two filaments- actin and myosin.
The actin and myosin filaments are responsible for the contraction of muscles. It can be explained by the “Sliding theory of muscle contraction” which was explained by J.E. Huxley and Hanson in 1954.
Complete Answer:-
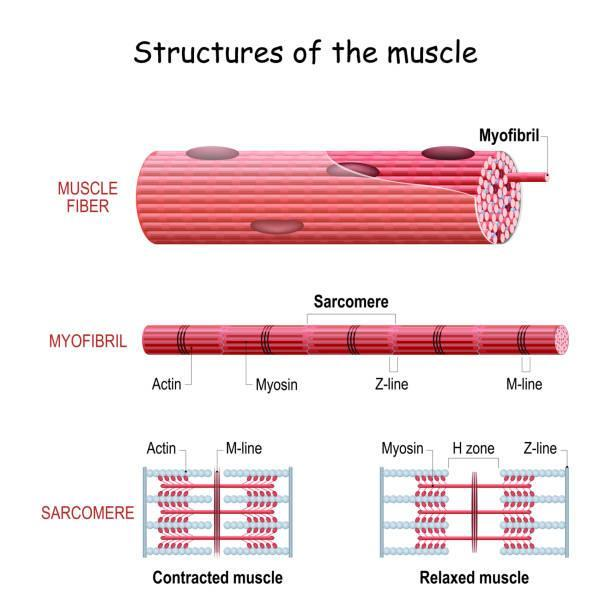
The myofibrils are the proteinaceous rod-like structures that are present in sarcoplasm. It is made up of two types of myofibrils-
- Thick and long myosin filament
- Thin and short actin filament
The actin filament is made up of three types of proteins:
F-actin: It consists of two chains of helically arranged globular actin (G-actin). It acts as the myosin binding site. It has a globular structure. It becomes active in the presence of ATP.
Tropomyosin: It runs close to F-actin along its entire length.
Troponin: It is the protein which is present on the tropomyosin at short distances. It is made up of three subunits-
T-subunit: It is the binding site for tropomyosin.
C-subunit: It is the binding site for calcium ions.
I-subunit: It is the binding site for inhibitory substances.
During relaxation of muscles, troponin and tropomyosin covers the G-actin due to which myosin filament is unable to bind with actin filament.
So, the correct answer is option D, actin, troponin and tropomyosin.
The myosin filament is the polymer of meromyosin. It consists of two parts- tail (light meromyosin) and globular head (heavy meromyosin). The globular head of meromyosin has binding sites for ATP and actin filament.
Note:- The sarcomere is the distance between two Z-lines, which can be defined as the line that bisects the actin filament. The sliding of actin filament over myosin filament towards the center results in the shortening of sarcomere.
The actin and myosin filaments are responsible for the contraction of muscles. It can be explained by the “Sliding theory of muscle contraction” which was explained by J.E. Huxley and Hanson in 1954.
Complete Answer:-
The myofibrils are the proteinaceous rod-like structures that are present in sarcoplasm. It is made up of two types of myofibrils-
- Thick and long myosin filament
- Thin and short actin filament
The actin filament is made up of three types of proteins:
F-actin: It consists of two chains of helically arranged globular actin (G-actin). It acts as the myosin binding site. It has a globular structure. It becomes active in the presence of ATP.
Tropomyosin: It runs close to F-actin along its entire length.
Troponin: It is the protein which is present on the tropomyosin at short distances. It is made up of three subunits-
T-subunit: It is the binding site for tropomyosin.
C-subunit: It is the binding site for calcium ions.
I-subunit: It is the binding site for inhibitory substances.
During relaxation of muscles, troponin and tropomyosin covers the G-actin due to which myosin filament is unable to bind with actin filament.
So, the correct answer is option D, actin, troponin and tropomyosin.

The myosin filament is the polymer of meromyosin. It consists of two parts- tail (light meromyosin) and globular head (heavy meromyosin). The globular head of meromyosin has binding sites for ATP and actin filament.
Note:- The sarcomere is the distance between two Z-lines, which can be defined as the line that bisects the actin filament. The sliding of actin filament over myosin filament towards the center results in the shortening of sarcomere.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




