
How many conformational isomers of butane are chiral?
A.$2$
B.$3$
C.$4$
D.None
Answer
571.2k+ views
Hint: In conformational isomers, isomers are interconverted by rotations. Different conformations are the arrangement of two atoms in a molecule that differ by rotation. The study of energy between different conformations is known as conformational analysis.
Complete answer:
Isomers are defined as the molecules that contain the same molecular formula, but they differ on the arrangement of atoms in a molecule. It is not necessary that the isomers will share similar chemical properties as well as physical properties.
Let us discuss the types of conformational isomers.
There are two types of conformational isomers:
-Eclipsed conformational isomers: In these isomers, the carbons are aligned so that the hydrogens are lined up with each other.
-Staggered conformational isomers: In these isomers, atoms are equally spaced from each other.
We see that staggered isomers are more stable than the eclipsed isomers because in eclipsed isomers, carbon and hydrogen create steric hindrance between each other.
Chiral molecule is defined as a molecule that cannot be superimposed on its mirror images by any rotations. Achiral molecule occurs when there is a presence of a plane of symmetry and centre of symmetry. Plane of symmetry is defined as a plane that can bisects a molecule into two equal halves that show identical mirror images.
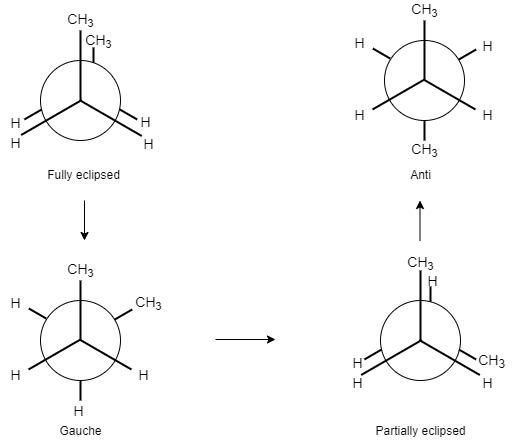
When two methyl groups lie apart at a dihedral angle of $180{}^\circ $ , this conformation is known as Anti.
When two methyl groups lie apart at a dihedral angle of $60{}^\circ $ , it is known as Gauche.
When two methyl groups overlap each other with an angle of $0{}^\circ $ , it is known as Fully eclipsed.
When two methyl groups lie apart at a dihedral angle of $120{}^\circ $ , it is known as Partially eclipsed.
Butane contains two enantiomeric chiral conformations because of the lack of plane of symmetry.
The gauche conformation of butane is chiral as there is a lack of improper rotation axis.
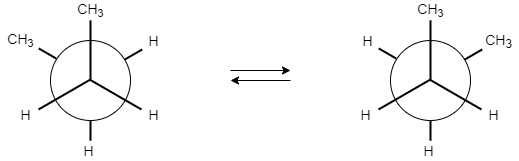
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: Gauche conformation is stable because there is no steric hindrance because the relationship between the groups shows dihedral angle more than ${{0}^{\circ }}$ but less than ${{120}^{\circ }}$ .
-Center of symmetry is defined as a point from where if we move towards a group, it shows equal distance when we move in the opposite direction of the equivalent group.
Complete answer:
Isomers are defined as the molecules that contain the same molecular formula, but they differ on the arrangement of atoms in a molecule. It is not necessary that the isomers will share similar chemical properties as well as physical properties.
Let us discuss the types of conformational isomers.
There are two types of conformational isomers:
-Eclipsed conformational isomers: In these isomers, the carbons are aligned so that the hydrogens are lined up with each other.
-Staggered conformational isomers: In these isomers, atoms are equally spaced from each other.
We see that staggered isomers are more stable than the eclipsed isomers because in eclipsed isomers, carbon and hydrogen create steric hindrance between each other.
Chiral molecule is defined as a molecule that cannot be superimposed on its mirror images by any rotations. Achiral molecule occurs when there is a presence of a plane of symmetry and centre of symmetry. Plane of symmetry is defined as a plane that can bisects a molecule into two equal halves that show identical mirror images.

When two methyl groups lie apart at a dihedral angle of $180{}^\circ $ , this conformation is known as Anti.
When two methyl groups lie apart at a dihedral angle of $60{}^\circ $ , it is known as Gauche.
When two methyl groups overlap each other with an angle of $0{}^\circ $ , it is known as Fully eclipsed.
When two methyl groups lie apart at a dihedral angle of $120{}^\circ $ , it is known as Partially eclipsed.
Butane contains two enantiomeric chiral conformations because of the lack of plane of symmetry.
The gauche conformation of butane is chiral as there is a lack of improper rotation axis.

Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: Gauche conformation is stable because there is no steric hindrance because the relationship between the groups shows dihedral angle more than ${{0}^{\circ }}$ but less than ${{120}^{\circ }}$ .
-Center of symmetry is defined as a point from where if we move towards a group, it shows equal distance when we move in the opposite direction of the equivalent group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




