
How to convert a carboxylic acid to an alcohol?
Answer
510.3k+ views
Hint: In organic chemistry, the carboxylic acids are the compound which have $ COOH $ group as a functional group and are generally represented as $ R - COOH $ where as in alcohol, the functional group is $ OH $ and can generally be represented as $ R - C{H_2}OH $ . So, on converting carboxylic acid into alcohol, addition of hydrogen atoms and removal of oxygen atoms is observed i.e., the compound is reduced. Therefore, the conversion can be achieved using proper reducing agents.
Complete answer:
The reduction of carboxylic acid can be performed in many ways which are discussed as follows:
(a) Reduction by using $ LiAl{H_4} $ :
When carboxylic acid reacts with lithium aluminium hydride which is a strong base, then it converts into respective primary alcohol as per following reaction:
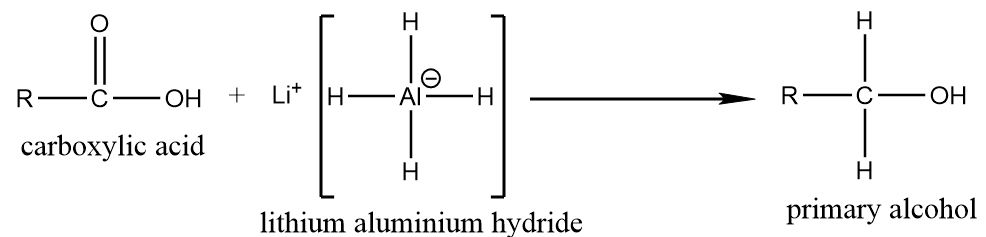
(b) Reduction by using $ B{H_3}|THF $ :
When carboxylic acid reacts with borane in the presence of tetrahydrofuran followed by acidic workup, then it readily converts into respective primary alcohol. The reaction proceeds as follows:
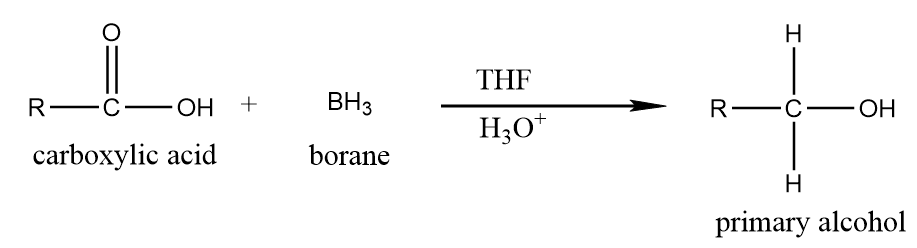
Additional Information:
Sodium borohydride i.e., $ NaB{H_4} $ is another important reducing agent in organic chemistry but it is less reactive than lithium aluminium hydride and thus can only reduce aldehydes, ketones and acid chlorides to respective alcohols. It is not strong enough to reduce esters, amides, carboxylic acids and nitriles because intermediate produced during the reaction is much reactive and it cannot be isolated.
Note:
THF is used as a solvent in most of the organic reactions because it has tendency to dissolve a wide variety of organic compounds and due to its low boiling point, it is easier to remove THF from chemical reactions via the evaporation process. The molecular structure of THF is as follows:
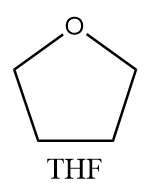
Complete answer:
The reduction of carboxylic acid can be performed in many ways which are discussed as follows:
(a) Reduction by using $ LiAl{H_4} $ :
When carboxylic acid reacts with lithium aluminium hydride which is a strong base, then it converts into respective primary alcohol as per following reaction:

(b) Reduction by using $ B{H_3}|THF $ :
When carboxylic acid reacts with borane in the presence of tetrahydrofuran followed by acidic workup, then it readily converts into respective primary alcohol. The reaction proceeds as follows:

Additional Information:
Sodium borohydride i.e., $ NaB{H_4} $ is another important reducing agent in organic chemistry but it is less reactive than lithium aluminium hydride and thus can only reduce aldehydes, ketones and acid chlorides to respective alcohols. It is not strong enough to reduce esters, amides, carboxylic acids and nitriles because intermediate produced during the reaction is much reactive and it cannot be isolated.
Note:
THF is used as a solvent in most of the organic reactions because it has tendency to dissolve a wide variety of organic compounds and due to its low boiling point, it is easier to remove THF from chemical reactions via the evaporation process. The molecular structure of THF is as follows:

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




