
How will you convert benzene into p-nitrobromobenzene?
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: Try to recall electrophilic aromatic substitution also called EAS in organic reactions. You need to determine whether the bromine atom or nitro group will be attached first for the compound to be formed in the same configuration. Identify the reagents required and then you can write the reaction process as well as the mechanism.
Complete Solution :
Electrophilic aromatic substitution also called E.A.S is an organic reaction in which an atom gets attached to the present aromatic system and replaces the hydrogen atom present.
Some of the most important and known Electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions are:
- Aromatic nitration
- Aromatic halogenation
- Aromatic sulfonation
- Friedel-Crafts acylation
- Friedel-Crafts alkylation
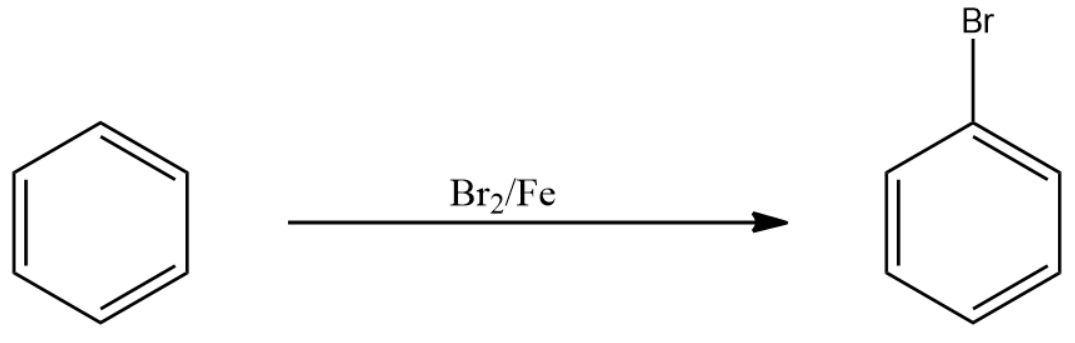
First of all, we need to convert the benzene into bromobenzene. This is an aromatic halogenation class of reactions under Electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. For this, we react to bromine in the presence of iron with benzene to form bromobenzene.
The reaction is shown below:
Bromobenzene is then reacted with a nitrating mixture. Nitrating mixture is the mixture of hot conc. sulphuric acid and conc. nitric acid.
Sulphuric acid acts as an acid and releases hydrogen ion which reacts with nitric acid. This leads to the generation of the nitro group which acts as an incoming electrophile to the aromatic system.
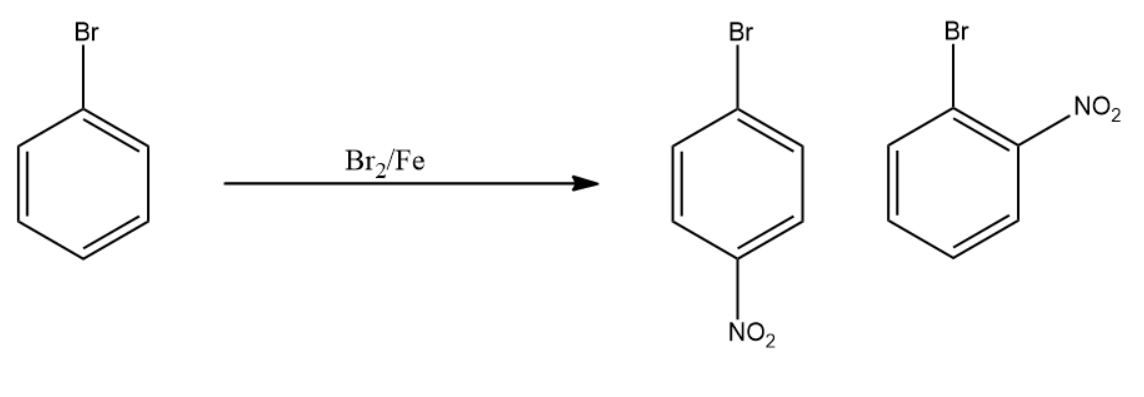
Note: In the nitration reaction of bromobenzene we get a mixture of compounds having the same molecular formula. The first product obtained is the major product due to lesser electronic repulsion. However, the second product is minor in quantity due to increased electron repulsions.
Complete Solution :
Electrophilic aromatic substitution also called E.A.S is an organic reaction in which an atom gets attached to the present aromatic system and replaces the hydrogen atom present.
Some of the most important and known Electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions are:
- Aromatic nitration
- Aromatic halogenation
- Aromatic sulfonation
- Friedel-Crafts acylation
- Friedel-Crafts alkylation
First of all, we need to convert the benzene into bromobenzene. This is an aromatic halogenation class of reactions under Electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. For this, we react to bromine in the presence of iron with benzene to form bromobenzene.
The reaction is shown below:

Bromobenzene is then reacted with a nitrating mixture. Nitrating mixture is the mixture of hot conc. sulphuric acid and conc. nitric acid.
Sulphuric acid acts as an acid and releases hydrogen ion which reacts with nitric acid. This leads to the generation of the nitro group which acts as an incoming electrophile to the aromatic system.

Note: In the nitration reaction of bromobenzene we get a mixture of compounds having the same molecular formula. The first product obtained is the major product due to lesser electronic repulsion. However, the second product is minor in quantity due to increased electron repulsions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




