
What is the correct succession of stages of a lithosere?
(a)$Foliose\quad lichens\quad \longrightarrow \quad Crustose\quad lichens\quad \longrightarrow \quad Mosses\quad \longrightarrow \quad Annual\quad grasses\quad \longrightarrow \quad Perennial\quad grasses\quad \longrightarrow \quad Shrubs\quad \longrightarrow \quad Trees$
(b)$Crustose\quad lichens\quad \longrightarrow \quad Foliose\quad lichens\quad \longrightarrow \quad Mosses\quad \longrightarrow \quad Perennial\quad grasses\quad \longrightarrow \quad Annual\quad grasses\quad \longrightarrow \quad Shrubs\quad \longrightarrow \quad Trees$
(c)$Crustose\quad lichens\quad \longrightarrow \quad Foliose\quad lichens\quad \longrightarrow \quad Mosses\quad \longrightarrow \quad Annual\quad grasses\quad \longrightarrow \quad Perennial\quad grasses\quad \longrightarrow \quad Shrubs\quad \longrightarrow \quad Trees$
(d)$Crustose\quad lichens\quad \longrightarrow \quad Foliose\quad lichens\quad \longrightarrow \quad Mosses\quad \longrightarrow \quad Annual\quad grasses\quad \longrightarrow \quad Shrubs\quad \longrightarrow \quad Perennial\quad grasses\quad \longrightarrow \quad Trees$
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: A lithosere is a pioneer species that begins its life on rock surfaces, as the name ‘litho’ suggests. The succession should ideally start with an organism that can produce their own food and water, do not require soil, and are weather-resistant. The succession should proceed with the colonization of these organisms, weathering of the rocks, increase in the fertility, and development of higher grasses, plants, and trees.
Complete answer:
- A lithosere is a sere that originates on a rock (litho = rock) and is a plant succession that begins life on a newly exposed rock surface. They are pioneer species that colonize the area. Examples of newly exposed rock surfaces include glacial retreats, tectonic uplifts, or volcanic eruptions.
- The seven main stages of a lithosere are 1. Crustose Lichen Stage 2. Foliose and Fruticose Lichen Stage 3. Moss Stage 4. Herb Stage 5. Shrub Stage 6. Trees Stage.
- Lichen species are the pioneer species of lithoseres as they tolerate low-nutrient areas and extreme climates. The first lichens to colonize rocks are crustose lichens. They produce organic acid that leaches into the rocks. They also absorb moisture from the atmosphere. When they die, their thalli (plural of thallus) decomposes and helps in the formation of soil along with the weathering caused due to the extreme climate conditions. Foliose lichen follows next. They absorb more water and accumulate more soil, forming a fine soil layer on the rocks. They carry out further absorption and accumulation of dust and soil, with their death leading to decomposition of thalli into the rock, leading to more soil formation. This leads to moss growth. Mosses are moisture-loving and are rich in organic and inorganic compounds. They further penetrate rocks and gather soil particles. These make more favorable conditions and attract the growth of herbs or hardy annual grasses like Aristida. The decomposition of annual grasses leads to the growth of perennial grasses, whose roots penetrate deep down the rock, secrete acids, and promote the process of weathering. The arid conditions begin to subside due to the presence of moisture and fertile soil, which leads to the growth of bacterial and fungal populations. This leads to the growth of shrub populations like Physocarpus that promote the formation of dense and organic soil, thus diminishing the growth of grasses. The root size is also relatively large, furthering weathering of the rocks. This leads to the growth of trees among the shrubs. The kind of trees growing depends on the soil of that area. The soil is enriched through leaf litter and decaying roots.
- The final stage is the climax stage where a steady state is reached between the environment and the biotic community.
Additional Information: - A sere is an intermediate stage found in a plant or ecological succession. When the change occurs in the structure of species of the ecological community over a period of time then this process is called Ecological succession.
- Other examples of seres are hydrosere, psammosere, and xerosere.
- Hydrosere occurs in an area of freshwater and its transition into the land, for example, oxbow lakes.
- Psammosere occurs on newly exposed coastal sands.
- Xerosere occurs in extremely dry conditions with limited water availability such as rock and sand deserts.
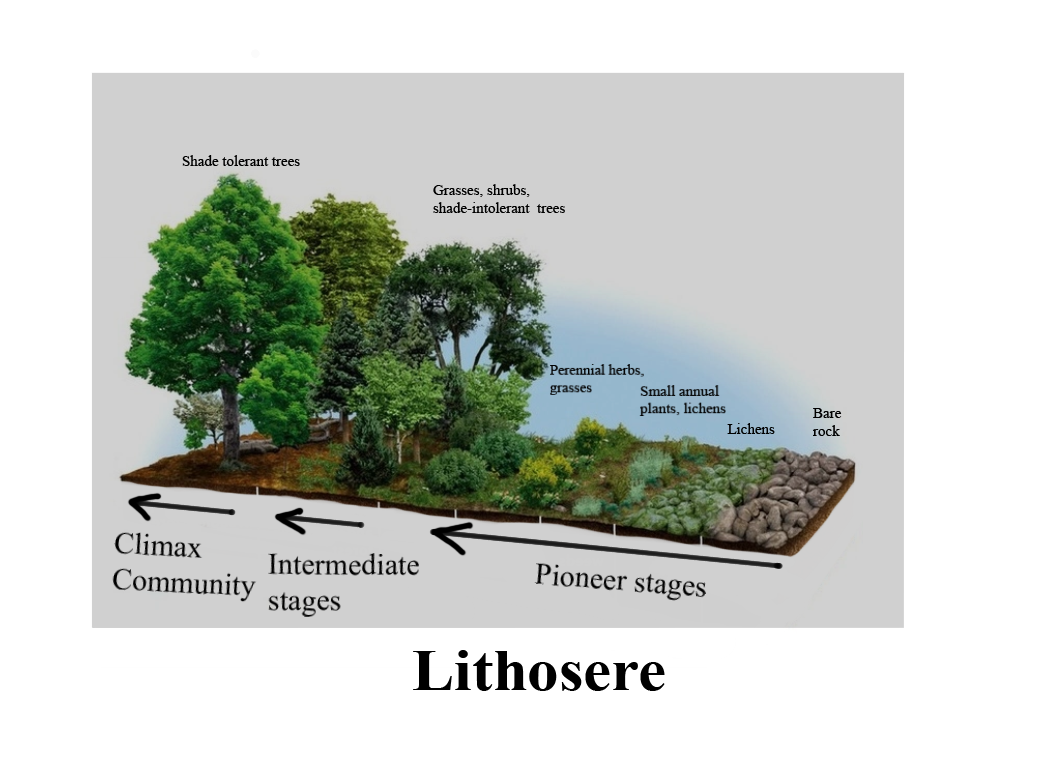
So, the correct answer is ‘$Crustose\quad lichens\quad \longrightarrow \quad Foliose\quad lichens\quad \longrightarrow \quad Mosses\quad \longrightarrow \quad Annual\quad grasses\quad \longrightarrow \quad Perennial\quad grasses\quad \longrightarrow \quad Shrubs\quad \longrightarrow \quad Trees$’
Note: - The equilibrium of a lithosere that is the climax community is marked by fast-growing trees such as birch and then by slower-growing but larger trees like oak. This is the point where plant succession does not go any further.
- Sometimes a phenomenon may occur known as a disclimax, where an intervention removes most of the lifeforms in the areas and causes a loss of the climax community.
Complete answer:
- A lithosere is a sere that originates on a rock (litho = rock) and is a plant succession that begins life on a newly exposed rock surface. They are pioneer species that colonize the area. Examples of newly exposed rock surfaces include glacial retreats, tectonic uplifts, or volcanic eruptions.
- The seven main stages of a lithosere are 1. Crustose Lichen Stage 2. Foliose and Fruticose Lichen Stage 3. Moss Stage 4. Herb Stage 5. Shrub Stage 6. Trees Stage.
- Lichen species are the pioneer species of lithoseres as they tolerate low-nutrient areas and extreme climates. The first lichens to colonize rocks are crustose lichens. They produce organic acid that leaches into the rocks. They also absorb moisture from the atmosphere. When they die, their thalli (plural of thallus) decomposes and helps in the formation of soil along with the weathering caused due to the extreme climate conditions. Foliose lichen follows next. They absorb more water and accumulate more soil, forming a fine soil layer on the rocks. They carry out further absorption and accumulation of dust and soil, with their death leading to decomposition of thalli into the rock, leading to more soil formation. This leads to moss growth. Mosses are moisture-loving and are rich in organic and inorganic compounds. They further penetrate rocks and gather soil particles. These make more favorable conditions and attract the growth of herbs or hardy annual grasses like Aristida. The decomposition of annual grasses leads to the growth of perennial grasses, whose roots penetrate deep down the rock, secrete acids, and promote the process of weathering. The arid conditions begin to subside due to the presence of moisture and fertile soil, which leads to the growth of bacterial and fungal populations. This leads to the growth of shrub populations like Physocarpus that promote the formation of dense and organic soil, thus diminishing the growth of grasses. The root size is also relatively large, furthering weathering of the rocks. This leads to the growth of trees among the shrubs. The kind of trees growing depends on the soil of that area. The soil is enriched through leaf litter and decaying roots.
- The final stage is the climax stage where a steady state is reached between the environment and the biotic community.
Additional Information: - A sere is an intermediate stage found in a plant or ecological succession. When the change occurs in the structure of species of the ecological community over a period of time then this process is called Ecological succession.
- Other examples of seres are hydrosere, psammosere, and xerosere.
- Hydrosere occurs in an area of freshwater and its transition into the land, for example, oxbow lakes.
- Psammosere occurs on newly exposed coastal sands.
- Xerosere occurs in extremely dry conditions with limited water availability such as rock and sand deserts.

So, the correct answer is ‘$Crustose\quad lichens\quad \longrightarrow \quad Foliose\quad lichens\quad \longrightarrow \quad Mosses\quad \longrightarrow \quad Annual\quad grasses\quad \longrightarrow \quad Perennial\quad grasses\quad \longrightarrow \quad Shrubs\quad \longrightarrow \quad Trees$’
Note: - The equilibrium of a lithosere that is the climax community is marked by fast-growing trees such as birch and then by slower-growing but larger trees like oak. This is the point where plant succession does not go any further.
- Sometimes a phenomenon may occur known as a disclimax, where an intervention removes most of the lifeforms in the areas and causes a loss of the climax community.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




