
What is the criss-cross inheritance of traits?
Answer
603k+ views
Hint: It is also known as skip generation inheritance, and involves the transmission of genes.
Complete answer:
The patterns of inheritance, where a trait is inherited to the second generation through the carrier of the first generation are called criss-cross inheritance or skip generation inheritance. In simple words, it is the transmission of a gene from mother to son or father to daughter.
Natural selection favors diverse combinations of traits so that when the environment changes, there is a bigger chance of some individuals surviving.
Species that show X, Y sex determination (most mammalian species), go through the following two different mechanisms of addressing gene dosage:
- In early embryonic cells, random inactivation of one X or the other.
- Half down-regulation of gene expression from both the X chromosomes. (Drosophila)
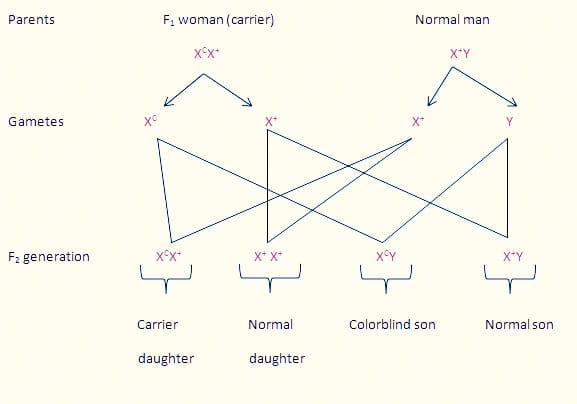
Either way, traits encoded by genes on the X chromosome show X-linked inheritance. A criss-cross inheritance is produced when a female carries two recessive X-linked alleles, crossed with a wild-type male because the Y chromosomes from the male behave as null alleles. As a result, the recessive allele from the female parent is always expressed in the male offspring. However, her female offspring will receive one wild-type allele from the father.
The other, normally paired chromosomes are called autosomes.
Since females have two X sex chromosomes and males have an X and Y, mutations on the X chromosome in females may be masked by the presence of a normal allele on the second X. In contrast, a mutation on the X chromosome in males more often causes observable biological defects, as there is no normal X to compensate. Trait variations arising from mutations on the X chromosome are called 'X-linked'. Some well-studied examples of such disorders are:
1)Colour blindness.
2)Hemophilia.
Notes:
- Information from one gene is taken for the synthesis of a functional gene, this is called gene expression. The products are often proteins.
- Gene regulation is a wide range of mechanisms used by cells to increase or decrease the production of specific genes.
- Drosophila is a genus of flies, also called "small fruit flies", pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, linger around overripe or rotting fruit.
- About the characteristic of many species to A genetic mutation is a nonfunctional allele. Such mutations can cause a complete lack of production of the associated gene product or a product that does not function properly are caused by a null allele
Complete answer:
The patterns of inheritance, where a trait is inherited to the second generation through the carrier of the first generation are called criss-cross inheritance or skip generation inheritance. In simple words, it is the transmission of a gene from mother to son or father to daughter.
Natural selection favors diverse combinations of traits so that when the environment changes, there is a bigger chance of some individuals surviving.
Species that show X, Y sex determination (most mammalian species), go through the following two different mechanisms of addressing gene dosage:
- In early embryonic cells, random inactivation of one X or the other.
- Half down-regulation of gene expression from both the X chromosomes. (Drosophila)
Either way, traits encoded by genes on the X chromosome show X-linked inheritance. A criss-cross inheritance is produced when a female carries two recessive X-linked alleles, crossed with a wild-type male because the Y chromosomes from the male behave as null alleles. As a result, the recessive allele from the female parent is always expressed in the male offspring. However, her female offspring will receive one wild-type allele from the father.
The other, normally paired chromosomes are called autosomes.

Since females have two X sex chromosomes and males have an X and Y, mutations on the X chromosome in females may be masked by the presence of a normal allele on the second X. In contrast, a mutation on the X chromosome in males more often causes observable biological defects, as there is no normal X to compensate. Trait variations arising from mutations on the X chromosome are called 'X-linked'. Some well-studied examples of such disorders are:
1)Colour blindness.
2)Hemophilia.
Notes:
- Information from one gene is taken for the synthesis of a functional gene, this is called gene expression. The products are often proteins.
- Gene regulation is a wide range of mechanisms used by cells to increase or decrease the production of specific genes.
- Drosophila is a genus of flies, also called "small fruit flies", pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, linger around overripe or rotting fruit.
- About the characteristic of many species to A genetic mutation is a nonfunctional allele. Such mutations can cause a complete lack of production of the associated gene product or a product that does not function properly are caused by a null allele
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




