
Define breathing. Explain the mechanism of breathing in human beings.
Answer
530.5k+ views
Hint: Inspiration is an active process while expiration is a passive process.
Breathing rate is inversely proportional to the body size of an organism.
One breathing cycle completes in 5 seconds.
Complete answer:
Breathing is the process of intake of fresh air from the environment and expulsion of foul air from the body. It is performed by the different respiratory organs.
When we breathe, we intake oxygen from the air and give out carbon dioxide which is utilized by the plants. The process of intake oxygen rich air is known as inhalation while the process of giving out carbon dioxide air is known as exhalation.
Breathing rate can be defined as the number of breathing per minute. It is inversely proportional to the body size of an organism. For example, the breathing rate of an adult is 15-16 times while that of a newborn baby is 40-50 times.
The breathing mechanism involves two processes – inspiration and expiration.
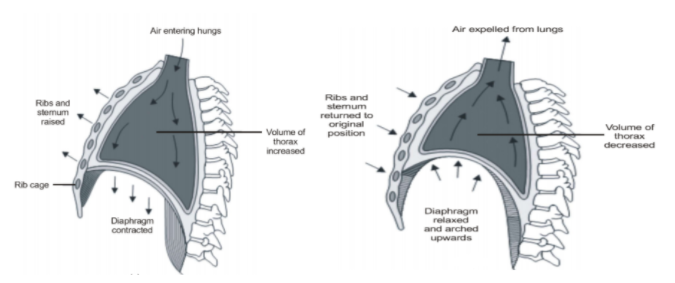
1. Inspiration: It is the process of intake of the atmospheric air. It involves the contraction of diaphragm and external intercostal muscles.
The intercostal muscles are the muscles which are present between the ribs. They are of 2 types- internal and external intercostal muscles. The internal intercostal muscles form the middle layer of intercostal muscles, while the external intercostal muscles originate on the interior surface of ribs.
It is an active process and completes in 2 second.
When the radial muscle of diaphragm contracts, it becomes flattened. So intrapulmonary volume increases and the intrapulmonary pressure decreases. When external intercostal muscles contract, ribs and sternum move upward and outward respectively. It also increases the intrapulmonary volume and increases intrapulmonary pressure. As a result, environmental air enters into the lungs through the respiratory tract.
2. Expiration: It is the process of giving out of air. It involves the relaxation of diaphragm and external intercostal muscles.
It is a passive process and completes in 5 second.
When the radial muscles of the diaphragm relax, it becomes dome-shaped. So intrapulmonary volume decreases and intrapulmonary pressure increases. When external intercostal muscles relax, ribs and sternum move downward and inward respectively. It also decreases intrapulmonary volume and increases intrapulmonary pressure. As a result, air expels out of the lungs through the respiratory tract.
Note: During forceful expiration, abdominal muscle and internal intercostal muscle contracts, which decreases the intrapulmonary volume decreases and intrapulmonary pressure increases. As a result, air expels out of the lungs.
Breathing is a physical process while respiration also includes a biochemical process of oxidation of food.
Breathing rate is inversely proportional to the body size of an organism.
One breathing cycle completes in 5 seconds.
Complete answer:
Breathing is the process of intake of fresh air from the environment and expulsion of foul air from the body. It is performed by the different respiratory organs.
When we breathe, we intake oxygen from the air and give out carbon dioxide which is utilized by the plants. The process of intake oxygen rich air is known as inhalation while the process of giving out carbon dioxide air is known as exhalation.
Breathing rate can be defined as the number of breathing per minute. It is inversely proportional to the body size of an organism. For example, the breathing rate of an adult is 15-16 times while that of a newborn baby is 40-50 times.
The breathing mechanism involves two processes – inspiration and expiration.
1. Inspiration: It is the process of intake of the atmospheric air. It involves the contraction of diaphragm and external intercostal muscles.
The intercostal muscles are the muscles which are present between the ribs. They are of 2 types- internal and external intercostal muscles. The internal intercostal muscles form the middle layer of intercostal muscles, while the external intercostal muscles originate on the interior surface of ribs.
It is an active process and completes in 2 second.
When the radial muscle of diaphragm contracts, it becomes flattened. So intrapulmonary volume increases and the intrapulmonary pressure decreases. When external intercostal muscles contract, ribs and sternum move upward and outward respectively. It also increases the intrapulmonary volume and increases intrapulmonary pressure. As a result, environmental air enters into the lungs through the respiratory tract.
2. Expiration: It is the process of giving out of air. It involves the relaxation of diaphragm and external intercostal muscles.
It is a passive process and completes in 5 second.
When the radial muscles of the diaphragm relax, it becomes dome-shaped. So intrapulmonary volume decreases and intrapulmonary pressure increases. When external intercostal muscles relax, ribs and sternum move downward and inward respectively. It also decreases intrapulmonary volume and increases intrapulmonary pressure. As a result, air expels out of the lungs through the respiratory tract.

Note: During forceful expiration, abdominal muscle and internal intercostal muscle contracts, which decreases the intrapulmonary volume decreases and intrapulmonary pressure increases. As a result, air expels out of the lungs.
Breathing is a physical process while respiration also includes a biochemical process of oxidation of food.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




