
Define critical angle.
Answer
594.6k+ views
Hint: Going through the concept of total internal reflection, we can understand the definition of critical angle. Whenever refraction takes place, partial reflection is also accompanied with it and it increases with the increase in angle of incidence.
Complete step by step answer:
In optics, the smallest angle of incidence that causes the total internal reflection of light is known as the critical angle. Total internal reflection refers to the complete reflection of a light ray at the interface of two mediums with different refractive index and the light ray approaches from the denser medium and if is incident on the interface with an angle equal to or greater than critical angle gets reflected back instead of undergoing refraction.
Suppose the light ray is incident through a medium of refractive index $n_1$ and hit the interface of another medium with refractive index $n_2$, such that $n_2 \le n_1$, then the critical angle is given by $\theta_c =sin^{-1}\left(\dfrac{n_2}{n_1}\right)$.
In the diagram below, we can see that, at the critical angle, the light rays gazes upon the surface of the interface and as we increase the angle further, total internal reflection takes place.
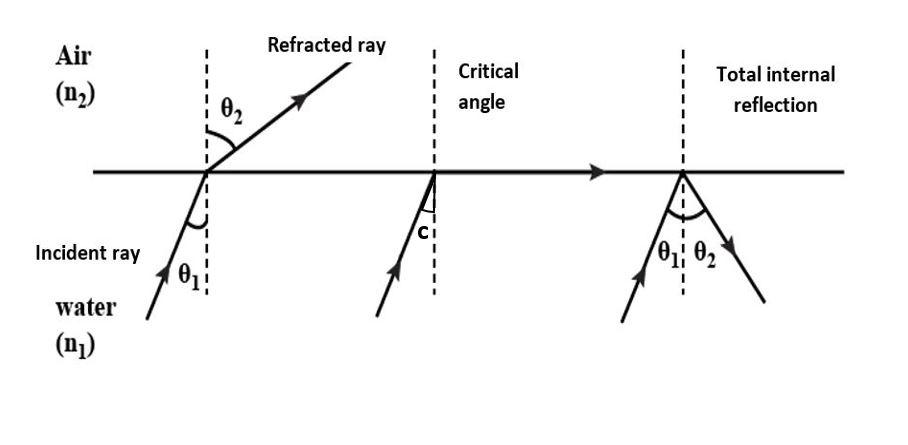
Additional Information
The phenomenon of critical angle and total internal reflection can be seen at many places in our daily life. Like, if we stand beside an aquarium such that one of our eyes are just below the aquarium’s water level, we will most likely be able to see the fishes or the objects inside it reflected in the water-air surface.
Another good example can be the diamond, which is cut in such a way so as the total internal reflection happens twice inside it and comes out of the other face making it sparkle.
Note:
The concept of critical angle can also be understood by using Snell's law at the interface. At a critical angle, the reflected ray just grazes upon the interface and as we increase the incident angle, total internal reflection takes place.
Complete step by step answer:
In optics, the smallest angle of incidence that causes the total internal reflection of light is known as the critical angle. Total internal reflection refers to the complete reflection of a light ray at the interface of two mediums with different refractive index and the light ray approaches from the denser medium and if is incident on the interface with an angle equal to or greater than critical angle gets reflected back instead of undergoing refraction.
Suppose the light ray is incident through a medium of refractive index $n_1$ and hit the interface of another medium with refractive index $n_2$, such that $n_2 \le n_1$, then the critical angle is given by $\theta_c =sin^{-1}\left(\dfrac{n_2}{n_1}\right)$.
In the diagram below, we can see that, at the critical angle, the light rays gazes upon the surface of the interface and as we increase the angle further, total internal reflection takes place.

Additional Information
The phenomenon of critical angle and total internal reflection can be seen at many places in our daily life. Like, if we stand beside an aquarium such that one of our eyes are just below the aquarium’s water level, we will most likely be able to see the fishes or the objects inside it reflected in the water-air surface.
Another good example can be the diamond, which is cut in such a way so as the total internal reflection happens twice inside it and comes out of the other face making it sparkle.
Note:
The concept of critical angle can also be understood by using Snell's law at the interface. At a critical angle, the reflected ray just grazes upon the interface and as we increase the incident angle, total internal reflection takes place.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




