
Define nervous tissue. Draw a well labeled diagram of nervous tissue.
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: Nervous tissue is found mainly in brain, spinal cord, and nerves. Nerve tissues control and coordinate many body activities. Structure of nerve cell includes: Dendrites, cell body or soma, axon, myelin sheath, node of ranvier and axon terminal. Nerve cell transfers the impulse from sensory neuron to motor neuron to generate response to the stimuli.
Complete answer: Nerve cells are an important part of the nervous system. Nervous tissues have nerve cells that generate and conduct impulses. Location of Nervous tissues is: Brain, spinal cord, and nerves. Nervous tissue stimulates muscle contraction, creates an awareness of the environment, and plays a major role in emotions, memory, and reasoning.
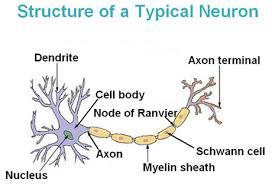
Neuron has three main parts: the dendrites, the cell body, and one axon. Dendrites extend from the large soma body. These are thin structures, or branching projections that receive electrochemical signaling (neurotransmitters) to create a change in voltage of the cell. The part of the neuron is the axon that carries action potential away from the cell body. It has a myelin sheath on the outer surface. There are gaps between myelin sheath called as node of ranvier. Axon terminals are the bulb-like structures which are separated from the dendrites by the gap called synaptic cleft. During synapses neurotransmitters are released and impulse is transferred from one neuron to another.
Note:
Nerve cells are also known as neuroglial cells. There are mainly two types of nervous system: central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. Both the systems have different types of neuroglial cells. On the basis of function of the neurons they are classified into three types: sensory neuron(afferent) , motor neuron(efferent) , and interneurons. Structural classification includes: multipolar, bipolar, pseudounipolar neurons and unipolar brush cells.
Complete answer: Nerve cells are an important part of the nervous system. Nervous tissues have nerve cells that generate and conduct impulses. Location of Nervous tissues is: Brain, spinal cord, and nerves. Nervous tissue stimulates muscle contraction, creates an awareness of the environment, and plays a major role in emotions, memory, and reasoning.

Neuron has three main parts: the dendrites, the cell body, and one axon. Dendrites extend from the large soma body. These are thin structures, or branching projections that receive electrochemical signaling (neurotransmitters) to create a change in voltage of the cell. The part of the neuron is the axon that carries action potential away from the cell body. It has a myelin sheath on the outer surface. There are gaps between myelin sheath called as node of ranvier. Axon terminals are the bulb-like structures which are separated from the dendrites by the gap called synaptic cleft. During synapses neurotransmitters are released and impulse is transferred from one neuron to another.
Note:
Nerve cells are also known as neuroglial cells. There are mainly two types of nervous system: central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. Both the systems have different types of neuroglial cells. On the basis of function of the neurons they are classified into three types: sensory neuron(afferent) , motor neuron(efferent) , and interneurons. Structural classification includes: multipolar, bipolar, pseudounipolar neurons and unipolar brush cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




