
Define the term hyperconjugation.
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: Proceed this question using the concept of hyperconjugation, which is a special case of resonance that involves the delocalization of the sigma electrons of the carbon hydrogen bond of any alkyl group.
Complete step by step solution:
Hyperconjugation is the interaction of the electrons present in the sigma bond with an adjacent empty or the partially filled non-bonding p-orbitals. The partially filled non-bonding p-orbitals can be antibonding $\alpha \text{ or }\pi \text{ }$orbitals or the filled $\pi $orbitals which gives the extended molecular orbital that increases the stability of the system.
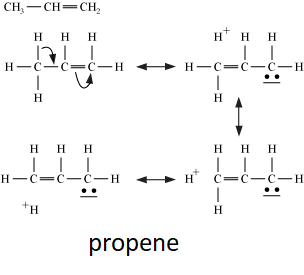
Let’s take an example of propene, hyperconjugation arises due to the partial overlapping of the $s{{p}^{3}}$sigma bond and the empty p-orbital of the adjacent carbon atom.
The hyperconjugation structure of propene are mentioned below:
Additional information:
The hyperconjugation and inductive effect are quite opposite, because the inductive effect is through sigma bond and the hyperconjugation is through the charge transfer. Hyperconjugation is very useful in explaining the physical and the chemical properties of the organic molecules which includes the shortening of carbon-carbon single chain which is adjacent to multiple bonds. Hyperconjugation also defines the stability of carbocations, free radicals and the relative stability of alkenes.
Note: In this particular question we should also know that the hyperconjugation is also known as no bond resonance. We know that the resonance involves delocalization of $\pi $electrons but in hyperconjugation the $\alpha $ electrons are delocalized not the$\pi $. The normal length of the carbon- carbon single bond is around 1.54 Angstrom. But in some of the compounds like propene, it is a little bit shorter because of the presence of the double bond character in the carbon-carbon single bond due to hyperconjugation.
Complete step by step solution:
Hyperconjugation is the interaction of the electrons present in the sigma bond with an adjacent empty or the partially filled non-bonding p-orbitals. The partially filled non-bonding p-orbitals can be antibonding $\alpha \text{ or }\pi \text{ }$orbitals or the filled $\pi $orbitals which gives the extended molecular orbital that increases the stability of the system.
Let’s take an example of propene, hyperconjugation arises due to the partial overlapping of the $s{{p}^{3}}$sigma bond and the empty p-orbital of the adjacent carbon atom.
The hyperconjugation structure of propene are mentioned below:

Additional information:
The hyperconjugation and inductive effect are quite opposite, because the inductive effect is through sigma bond and the hyperconjugation is through the charge transfer. Hyperconjugation is very useful in explaining the physical and the chemical properties of the organic molecules which includes the shortening of carbon-carbon single chain which is adjacent to multiple bonds. Hyperconjugation also defines the stability of carbocations, free radicals and the relative stability of alkenes.
Note: In this particular question we should also know that the hyperconjugation is also known as no bond resonance. We know that the resonance involves delocalization of $\pi $electrons but in hyperconjugation the $\alpha $ electrons are delocalized not the$\pi $. The normal length of the carbon- carbon single bond is around 1.54 Angstrom. But in some of the compounds like propene, it is a little bit shorter because of the presence of the double bond character in the carbon-carbon single bond due to hyperconjugation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




