
Derive Bragg’s equation.
Answer
522.5k+ views
Hint: Bragg’s Law explains the molecular structure and crystals being identified using X-ray diffraction techniques. It gives us the relationship between the incident X-ray light and its reflection from the crystal surface.
Complete step by step answer:
-Bragg’s Law was first given by Sir W.H. Bragg and his son Sir W.L. Bragg.
-This law simply states that when the X-ray is incident onto a crystal surface, its angle of incidence is ‘$\theta $’ and it is reflected back with the same angle of scattering ‘$\theta $’. And if the path difference ‘d’ is equal to a whole number ‘n’ of wavelength, constructive interference will occur.
-Bragg’s equation is: $n\lambda = 2d\sin \theta $
-To derive this equation, first understand the following diagram:
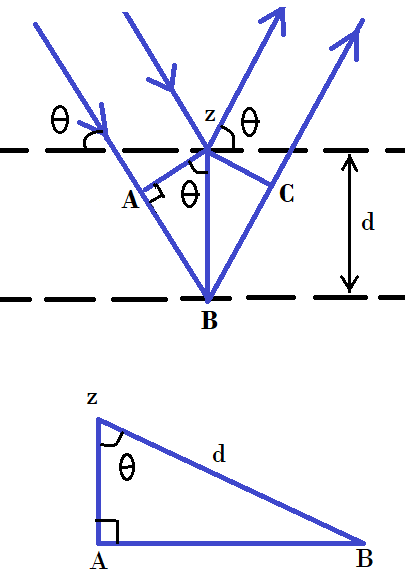
When the incident angle equals the reflecting angle, the phases of the 2 beams of X-ray coincide. The 2 beams of incident ray are parallel till point z. Point z is the point where the top beam strikes the top layer. The next beam passes up to the next layer and is scattered by B. This beam has travelled an extra distance of AB+BC than the previous one. This distance is an integral multiple of the wavelength of the ray.
So, $n\lambda = AB + BC$ (but, AB=BC)
Hence we can say: $n\lambda = 2AB$ (1)
In triangle ABz: d is the hypotenuse and AB is opposite to angle $\theta $.
$\sin \theta = P/H$
Where P=perpendicular and H=hypotenuse
Here, $\sin \theta = AB/d$
Hence, $AB = d\sin \theta $ (2)
Now put the value of AB obtained in equation (2) in equation (1). We get:
$n\lambda = 2d\sin \theta $
This is Bragg's equation. Hence derived.
Note: Remember that Bragg’s law is valid only if both the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are equal to each other and the path difference is equal to an integer number of wavelengths. If these conditions are satisfied constructive interference will occur.
Complete step by step answer:
-Bragg’s Law was first given by Sir W.H. Bragg and his son Sir W.L. Bragg.
-This law simply states that when the X-ray is incident onto a crystal surface, its angle of incidence is ‘$\theta $’ and it is reflected back with the same angle of scattering ‘$\theta $’. And if the path difference ‘d’ is equal to a whole number ‘n’ of wavelength, constructive interference will occur.
-Bragg’s equation is: $n\lambda = 2d\sin \theta $
-To derive this equation, first understand the following diagram:

When the incident angle equals the reflecting angle, the phases of the 2 beams of X-ray coincide. The 2 beams of incident ray are parallel till point z. Point z is the point where the top beam strikes the top layer. The next beam passes up to the next layer and is scattered by B. This beam has travelled an extra distance of AB+BC than the previous one. This distance is an integral multiple of the wavelength of the ray.
So, $n\lambda = AB + BC$ (but, AB=BC)
Hence we can say: $n\lambda = 2AB$ (1)
In triangle ABz: d is the hypotenuse and AB is opposite to angle $\theta $.
$\sin \theta = P/H$
Where P=perpendicular and H=hypotenuse
Here, $\sin \theta = AB/d$
Hence, $AB = d\sin \theta $ (2)
Now put the value of AB obtained in equation (2) in equation (1). We get:
$n\lambda = 2d\sin \theta $
This is Bragg's equation. Hence derived.
Note: Remember that Bragg’s law is valid only if both the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are equal to each other and the path difference is equal to an integer number of wavelengths. If these conditions are satisfied constructive interference will occur.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




