
Describe briefly various major events that occur in the process of embryonic development.
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: Human embryonic growth refers to the human embryo's development and creation. It is distinguished by the cell division process and the embryo's cellular differentiation that takes place during the early stages of development.
Complete answer:
In developmental biology, embryonic development is the development of an embryo, also known as embryogenesis.
The stages involved in embryonic development are as follows:
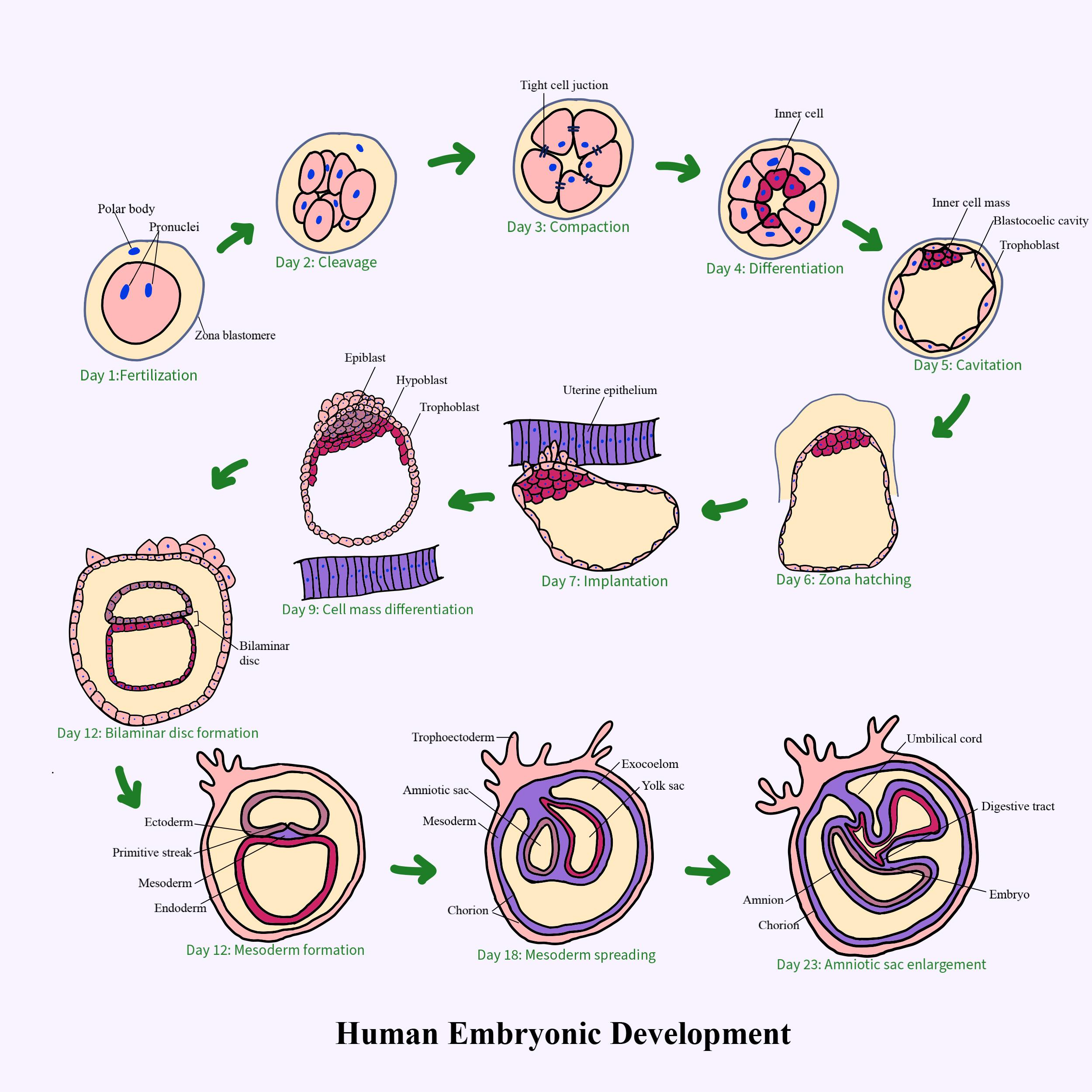
1.Germinal stage
The germinal process refers to the time from fertilization through early embryo development to completion of implantation in the uterus. It takes about 10 days for the germinal process.
-Fertilization:
When the spermatozoon has successfully reached the ovum, fertilization takes place and the two sets of genetic material transported by the gametes fuse together, resulting in the zygote (a single diploid cell).
-Cleavage:
The division of cells in the early embryo is cleavage in developmental biology. When the zygote divides into two cells through mitosis, the beginning of the cleavage process is marked.
-Blastulation:
The creation of a blastula from a morula is blastulation. Morula is an embryo similarly packed with cells (blastomeres), but a fluid cavity called blastocoel is found in the blastula.
-Implantation:
Implantation is a mechanism in which a developing embryo makes contact with the uterine wall and stays attached to it until birth, passing through the uterus as a blastocyst.
-Embryonic disc
The floor of the amniotic cavity is formed by the embryonic disc (or embryonic disc). It consists of the embryonic ectoderm, a layer of prismatic cells originating from the inner cell mass and lying in opposition to the endoderm.
2.Gastrulation
Gastrulation is defined as an early developmental phase in which an embryo transforms into a multilayered and multidimensional structure called the gastrula, from a one-dimensional layer of epithelial cells (blastula).
3.Neurulation
In vertebrate embryos, neurulation refers to the folding process, which involves the creation of neural tubes from the neural plate. To form the neural tube, the neural plate folds in on itself, which will later separate into the spinal cord and the brain, finally forming the central nervous system.
4.Organogenesis
Organogenesis is the development of the organs, which starts and lasts until birth during the third to eighth week. Often, after birth, complete growth, as in the lungs, continues. In the development of the many organ systems of the body, different organs take part.
Physical Feature Development:
The face and neck grow from the third until the eighth week. From the third week to the tenth week, the eyes start forming. At the end of the fourth week, the growth of limbs continues.
Note: The foetus has more identifiable external characteristics and a more complete set of developing organs in contrast to the embryo. Coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation include the entire embryogenesis process. In other species, particularly among chordates, a nearly identical process happens.
Complete answer:
In developmental biology, embryonic development is the development of an embryo, also known as embryogenesis.
The stages involved in embryonic development are as follows:
1.Germinal stage
The germinal process refers to the time from fertilization through early embryo development to completion of implantation in the uterus. It takes about 10 days for the germinal process.
-Fertilization:
When the spermatozoon has successfully reached the ovum, fertilization takes place and the two sets of genetic material transported by the gametes fuse together, resulting in the zygote (a single diploid cell).
-Cleavage:
The division of cells in the early embryo is cleavage in developmental biology. When the zygote divides into two cells through mitosis, the beginning of the cleavage process is marked.
-Blastulation:
The creation of a blastula from a morula is blastulation. Morula is an embryo similarly packed with cells (blastomeres), but a fluid cavity called blastocoel is found in the blastula.
-Implantation:
Implantation is a mechanism in which a developing embryo makes contact with the uterine wall and stays attached to it until birth, passing through the uterus as a blastocyst.
-Embryonic disc
The floor of the amniotic cavity is formed by the embryonic disc (or embryonic disc). It consists of the embryonic ectoderm, a layer of prismatic cells originating from the inner cell mass and lying in opposition to the endoderm.
2.Gastrulation
Gastrulation is defined as an early developmental phase in which an embryo transforms into a multilayered and multidimensional structure called the gastrula, from a one-dimensional layer of epithelial cells (blastula).
3.Neurulation
In vertebrate embryos, neurulation refers to the folding process, which involves the creation of neural tubes from the neural plate. To form the neural tube, the neural plate folds in on itself, which will later separate into the spinal cord and the brain, finally forming the central nervous system.
4.Organogenesis
Organogenesis is the development of the organs, which starts and lasts until birth during the third to eighth week. Often, after birth, complete growth, as in the lungs, continues. In the development of the many organ systems of the body, different organs take part.
Physical Feature Development:
The face and neck grow from the third until the eighth week. From the third week to the tenth week, the eyes start forming. At the end of the fourth week, the growth of limbs continues.

Note: The foetus has more identifiable external characteristics and a more complete set of developing organs in contrast to the embryo. Coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation include the entire embryogenesis process. In other species, particularly among chordates, a nearly identical process happens.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




