
Describe construction and working of a cyclotron.
Answer
600.6k+ views
Hint: Cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator, which is used for obtaining high speed charged particles. It achieves this by accelerating particles through an alternating potential supply and then swirling them around following a semicircular path, with the help of magnetic field in two D shaped metal electrodes called dees. The frequency of alternating potential is kept the same as that of a particle. This accelerates the particle further when it turns around and travels back to the other side.
Complete step by step answer:
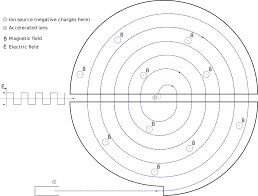
A cyclotron consists of two hollow D shaped conductors, which are known as dees and an alternating potential supply connecting the two dees, placed inside a vacuum chamber. The dees are kept facing each other with a very small gap between them. Magnetic field is set up perpendicular to the dees passing through them.
The particle is injected from the centre a suitable dee. The electric field is set up between the dees which exert a force on charged particles towards other dee and accelerate the particle towards it. The particle on reaching the other dee has gained some velocity which is perpendicular to the applied magnetic field. So, a magnetic force starts acting on the particle which is perpendicular to velocity. Because the force applied on article in a magnetic field is $q\left( v\times B \right)$ , where q is charge of particle, v is velocity of particle and B is magnitude of magnetic field (cross product of two vectors is perpendicular to the plane containing the two vectors). This force acts as a centripetal force and the particle follows a semicircular path. When the particle reaches the end of a semicircular path, its velocity is towards the other dee.
The time taken by a particle to complete the semicircular path is the same as the time taken by an alternating source to change its direction of polarity. Now direction of electric field reverse and particle and particle is exerted by a force towards other dee. This further accelerates the particle. The particle on reaching the other dee again follows the semicircular path. But now as the velocity is increased the radius of the semicircular path will also increase. Because radius of a particle (r), moving with velocity v perpendicular to magnetic field of strength B is given by
$r=\dfrac{mv}{qB}$
So, the particle will go around a longer semicircular path. And the process will be followed again and again.
Each time the particle travels from one dee to another its velocity will increase (and so will the radius). Eventually it will escape from the corner with a very high velocity.
Note: Electric field is only on the surface of the conductor. This is because of the property of the conductor that no electric field can be present inside it. This setup would have failed if the time period of the particle depended on velocity. Here, the time period of the particle is$\dfrac{\pi m}{qB}$. This can be obtained by dividing length of semicircular path by the velocity of particle
$\dfrac{\pi r}{\dfrac{qBr}{m}}=\dfrac{\pi m}{qB}$
If the time period will depend on velocity, it will increase after every semicircular path. But the time period of alternating sources is constant. So, the polarity of the alternating source will not change at the correct time and the system will fail.
Complete step by step answer:
A cyclotron consists of two hollow D shaped conductors, which are known as dees and an alternating potential supply connecting the two dees, placed inside a vacuum chamber. The dees are kept facing each other with a very small gap between them. Magnetic field is set up perpendicular to the dees passing through them.
The particle is injected from the centre a suitable dee. The electric field is set up between the dees which exert a force on charged particles towards other dee and accelerate the particle towards it. The particle on reaching the other dee has gained some velocity which is perpendicular to the applied magnetic field. So, a magnetic force starts acting on the particle which is perpendicular to velocity. Because the force applied on article in a magnetic field is $q\left( v\times B \right)$ , where q is charge of particle, v is velocity of particle and B is magnitude of magnetic field (cross product of two vectors is perpendicular to the plane containing the two vectors). This force acts as a centripetal force and the particle follows a semicircular path. When the particle reaches the end of a semicircular path, its velocity is towards the other dee.
The time taken by a particle to complete the semicircular path is the same as the time taken by an alternating source to change its direction of polarity. Now direction of electric field reverse and particle and particle is exerted by a force towards other dee. This further accelerates the particle. The particle on reaching the other dee again follows the semicircular path. But now as the velocity is increased the radius of the semicircular path will also increase. Because radius of a particle (r), moving with velocity v perpendicular to magnetic field of strength B is given by
$r=\dfrac{mv}{qB}$
So, the particle will go around a longer semicircular path. And the process will be followed again and again.
Each time the particle travels from one dee to another its velocity will increase (and so will the radius). Eventually it will escape from the corner with a very high velocity.

Note: Electric field is only on the surface of the conductor. This is because of the property of the conductor that no electric field can be present inside it. This setup would have failed if the time period of the particle depended on velocity. Here, the time period of the particle is$\dfrac{\pi m}{qB}$. This can be obtained by dividing length of semicircular path by the velocity of particle
$\dfrac{\pi r}{\dfrac{qBr}{m}}=\dfrac{\pi m}{qB}$
If the time period will depend on velocity, it will increase after every semicircular path. But the time period of alternating sources is constant. So, the polarity of the alternating source will not change at the correct time and the system will fail.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




