
Describe the following
i) Synapsis
ii) Bivalent
iii) Charismata
Draw a diagram to illustrate your answer
Answer
511.8k+ views
Hint: i) A chiasma is the point of interaction, or physical connection, between two chromatids and homologous chromosomes.
ii) A chromosomal fusion occurs as genetic material is exchanged between both chromatids at a given chiasma, although this occurs even more often during meiosis than mitosis.
iii) They develop at sites where Spo11-generated programmed DNA breaks go through the entire recombination pathway, resulting in crossovers.
Complete answer:
Meiosis is a form of cell division that occurs in germ cells in sexually reproducing organisms to create gametes such as sperm or egg cells. It entails two rounds of division, resulting in four cells with just one copy of each chromosome (haploid). Furthermore, before separation, genetic material from the paternal and maternal copies of each chromosome is crossed over, resulting in new code variations on each chromosome. During fertilization, the haploid cells formed by meiosis from a male and female will unite to form a zygote, a cell with two copies of each chromosome.
- Synapsis: Synapsis is the pairing of homologous chromosomes. They exchange their genetic material at this point. This happens during the second stage of prophase I, also known as zygotene.
- Bivalent: A bivalent or tetrad is a pair of homologous chromosomes that have synapsed. They have formed during the zygotene stage of meiosis' prophase I.
- Chiasmata: Chiasmata is the location where two non-sister chromatids have collided. It represents the point of intersection. It is produced during the diplotene stage of meiosis' prophase I.
The figure below shows the process of synapsis, bivalent formation and crossing over.
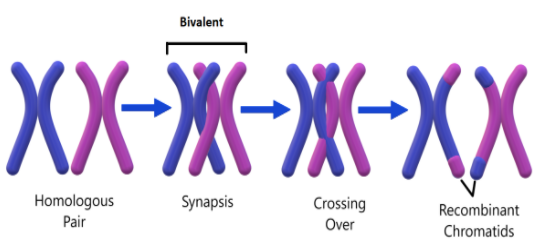
Note:
- During the first division of meiosis, a bivalent is formed (in the pachynema stage of meiotic prophase 1).
- During the leptotene process, each replicated chromosome (composed of two equivalent sister chromatids) induces the development of DNA double-strand breaks in most species.
- Homologous recombination, which uses the homologous chromosome as a basis for reconstruction, is used to repair these breaks.
ii) A chromosomal fusion occurs as genetic material is exchanged between both chromatids at a given chiasma, although this occurs even more often during meiosis than mitosis.
iii) They develop at sites where Spo11-generated programmed DNA breaks go through the entire recombination pathway, resulting in crossovers.
Complete answer:
Meiosis is a form of cell division that occurs in germ cells in sexually reproducing organisms to create gametes such as sperm or egg cells. It entails two rounds of division, resulting in four cells with just one copy of each chromosome (haploid). Furthermore, before separation, genetic material from the paternal and maternal copies of each chromosome is crossed over, resulting in new code variations on each chromosome. During fertilization, the haploid cells formed by meiosis from a male and female will unite to form a zygote, a cell with two copies of each chromosome.
- Synapsis: Synapsis is the pairing of homologous chromosomes. They exchange their genetic material at this point. This happens during the second stage of prophase I, also known as zygotene.
- Bivalent: A bivalent or tetrad is a pair of homologous chromosomes that have synapsed. They have formed during the zygotene stage of meiosis' prophase I.
- Chiasmata: Chiasmata is the location where two non-sister chromatids have collided. It represents the point of intersection. It is produced during the diplotene stage of meiosis' prophase I.
The figure below shows the process of synapsis, bivalent formation and crossing over.

Note:
- During the first division of meiosis, a bivalent is formed (in the pachynema stage of meiotic prophase 1).
- During the leptotene process, each replicated chromosome (composed of two equivalent sister chromatids) induces the development of DNA double-strand breaks in most species.
- Homologous recombination, which uses the homologous chromosome as a basis for reconstruction, is used to repair these breaks.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




