
Describe the mechanism of absorption of water by roots.
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint:
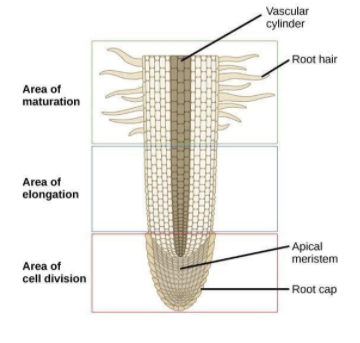
> In higher plants, Water is absorbed through root hairs which are in contact with soil water and form a root hair zone a little behind the root tips.
> The walls of the root hairs are permeable and consist of pectic substances and cellulose which are strongly hydrophilic (water loving) in nature. Root hairs contain vacuoles filled with cell sap.
> When roots elongate, the older hairs die and new root hairs are developed so that they are in contact with fresh supplies of water in the soil.
Complete answer:
Mechanism of water absorption is of two types:
Active absorption:In this process the root cells play an active role in the absorption of water and metabolic activities which produce energy through respiration.
Passive absorption: This process takes place when rate of transpiration is usually high. Rapid evaporation of water from the leaves during transpiration creates a tension in water in xylem of leaves.
During absorption of water by roots, the flow of water from epidermis to endodermis may take place through three different pathways:
> Apoplastic pathway( cell walls and intercellular spaces)
> Transmembrane pathway( by crossing the plasma membranes)
> Simplest pathway( through plasmodesmata)
Note:
Gradient of water potential from the root hair to the xylem vessels is essential for the absorption of water by the roots. The force with which water will be drawn from the soil will depend entirely upon the difference between the osmotic pressure external and osmotic pressure of xylem vessels. The root hair represents a large surface area in contac3rd with the soil particles. Water is an important raw material for photosynthesis. Most metabolic and enzymatic reactions take place in the presence of water.
> In higher plants, Water is absorbed through root hairs which are in contact with soil water and form a root hair zone a little behind the root tips.
> The walls of the root hairs are permeable and consist of pectic substances and cellulose which are strongly hydrophilic (water loving) in nature. Root hairs contain vacuoles filled with cell sap.
> When roots elongate, the older hairs die and new root hairs are developed so that they are in contact with fresh supplies of water in the soil.
Complete answer:
Mechanism of water absorption is of two types:
Active absorption:In this process the root cells play an active role in the absorption of water and metabolic activities which produce energy through respiration.
Passive absorption: This process takes place when rate of transpiration is usually high. Rapid evaporation of water from the leaves during transpiration creates a tension in water in xylem of leaves.
During absorption of water by roots, the flow of water from epidermis to endodermis may take place through three different pathways:
> Apoplastic pathway( cell walls and intercellular spaces)
> Transmembrane pathway( by crossing the plasma membranes)
> Simplest pathway( through plasmodesmata)

Note:
Gradient of water potential from the root hair to the xylem vessels is essential for the absorption of water by the roots. The force with which water will be drawn from the soil will depend entirely upon the difference between the osmotic pressure external and osmotic pressure of xylem vessels. The root hair represents a large surface area in contac3rd with the soil particles. Water is an important raw material for photosynthesis. Most metabolic and enzymatic reactions take place in the presence of water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




