
Describe the structure and life cycle of Ascaris lumbricoides with a neat labelled diagram.
Answer
526.8k+ views
Hint: Ascaris is nematode roundworms that live as parasites in the small digestive tract of humans. These worms belong to the Ascarididae family, the Secernentea class, and the Oxyurida request. These worms, also known as Ascaris suum, are commonly found in pigs.
Complete answer:
The Life Cycle:
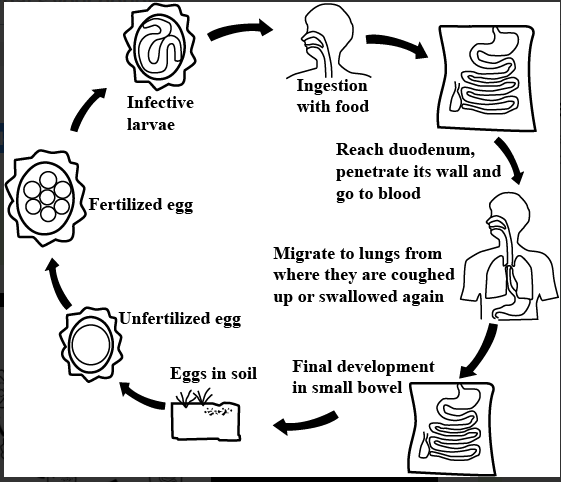
1. The Egg: Adult Ascaris worms inhabit the dividers of the small digestive tract in humans. The female worm can grow to be 35 cm long and lays approximately 20,000 eggs, which are dropped into the environment by the human stool. Unfertilized eggs are ingested but are not infective, whereas treated eggs are infective and progress further in the following stage.
2. The Larvae: The treated eggs hatch into larvae. The hatchling then becomes infectious after 18 days to half a month, depending on natural conditions such as warmth, wetness, and soil district. Following ingestion, the prepared eggs produce hatchlings that attack the intestinal mucosa. They are transported from here to various parts of the body, such as the lungs. They then move toward the throat, where the worms can be gulped and returned to the digestive tracts to develop.
3. The Adult: When the hatchlings reach the small digestive tract, they mature into adult worms. At this stage, the mature worm produces an enormous number of eggs. From the time infective eggs are consumed to the time female grown-up worms oviposit, it takes about 2 to 3 months. Ascaris worms can live for 1 to 2 years when fully grown.
Note:
Individuals become contaminated by these worms when they consume food or water contaminated with Ascaris worm eggs. Ascaris relies on humans and pigs as hosts. Other common hosts for Ascaris include monkeys, dogs, and so on.
Complete answer:
The Life Cycle:
1. The Egg: Adult Ascaris worms inhabit the dividers of the small digestive tract in humans. The female worm can grow to be 35 cm long and lays approximately 20,000 eggs, which are dropped into the environment by the human stool. Unfertilized eggs are ingested but are not infective, whereas treated eggs are infective and progress further in the following stage.
2. The Larvae: The treated eggs hatch into larvae. The hatchling then becomes infectious after 18 days to half a month, depending on natural conditions such as warmth, wetness, and soil district. Following ingestion, the prepared eggs produce hatchlings that attack the intestinal mucosa. They are transported from here to various parts of the body, such as the lungs. They then move toward the throat, where the worms can be gulped and returned to the digestive tracts to develop.
3. The Adult: When the hatchlings reach the small digestive tract, they mature into adult worms. At this stage, the mature worm produces an enormous number of eggs. From the time infective eggs are consumed to the time female grown-up worms oviposit, it takes about 2 to 3 months. Ascaris worms can live for 1 to 2 years when fully grown.

Note:
Individuals become contaminated by these worms when they consume food or water contaminated with Ascaris worm eggs. Ascaris relies on humans and pigs as hosts. Other common hosts for Ascaris include monkeys, dogs, and so on.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




