
What is the difference between Carbocation and Carbanion?
Answer
503.4k+ views
Hint: Carbocation and Carbanion are two terms that are frequently used in organic chemistry. These are organic chemical species bearing an electrical charge on a carbon atom. These are found as intermediates of some reactions.
Complete answer:
Carbocation is generally defined as an ion in which the central carbon atom is positively charged. A carbocation can have one or more positive charges in its central atom, it is normally unstable because due to the loss of electrons, the $ p $ orbitals are free due to loss of electrons. Carbocations are paramagnetic due to incomplete electron pairing. It shows $ s{p^2} $ hybridization.
Types of Carbocations:
There are four types of carbocation:
$ 1. $ Methyl Carbocation- These carbocation contain a positively charged carbon atom that is not attached to any other carbon atoms.

$ 2. $ Primary Carbocation- The positively charged carbon atom in the carbocation is connected to another carbon atom through a covalent bond. This carbocation is stable than methyl carbocation but is less stable than other Carbocations.
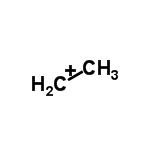
$ 3. $ Secondary Carbocation- The positively charged carbon atom is bonded to two other carbon atoms. These Carbocations are more stable than primary Carbocations.

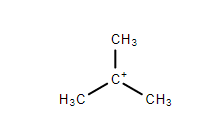
$ 4. $ Tertiary Carbocation- The positively charged carbon atom is attached to three other carbon atoms. This form is very stable.
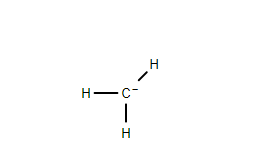
Carbanion is an ion that contains a negatively charged carbon atom. In this a carbon atom bearing negative charge is $ s{p^3} $ hybridized and the geometry is pyramidal. Carbanion is diamagnetic due to completion of electron pairing.
There are four types of carbanion:
$ 1. $ Methyl Carbanion- The negatively charged carbon atom is not bonded to any other carbon atom.
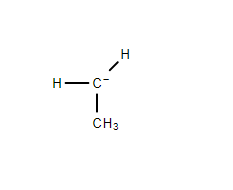
$ 2. $ Primary Carbanion- Here the negatively charged carbon atom in the carbanion is connected to another carbon atom through a covalent bond.
$ 3. $ Secondary Carbanion- The negatively charged carbon atom is bonded to two other carbon atoms.
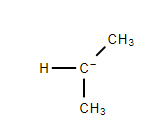
$ 4. $ Tertiary Carbanion- The negatively charged carbon atom is attached to three other carbon atoms.

Difference between Carbocation and Carbanion:
Note:
In various chemical reactions, the carbocation performs as an electrophile; conversely in many chemical reactions, the carbanion acts as a nucleophile.
Carbocation is formed if the organic molecule has a good leaving group, it can leave the molecule through ionization. The ionization gives the bonding electron pairs to the leaving group, resulting in a positive charge on the carbon atom. $ {(C{H_3})_2}CH - \mathop O\limits_{ \bullet \bullet }^{ \bullet \bullet } H \to {(C{H_3})_2}C{H^ + } + \mathop {{}_ \bullet ^ \bullet O}\limits_{ \bullet \bullet }^{ \bullet \bullet } {H^ - } $ .
Complete answer:
Carbocation is generally defined as an ion in which the central carbon atom is positively charged. A carbocation can have one or more positive charges in its central atom, it is normally unstable because due to the loss of electrons, the $ p $ orbitals are free due to loss of electrons. Carbocations are paramagnetic due to incomplete electron pairing. It shows $ s{p^2} $ hybridization.
Types of Carbocations:
There are four types of carbocation:
$ 1. $ Methyl Carbocation- These carbocation contain a positively charged carbon atom that is not attached to any other carbon atoms.

$ 2. $ Primary Carbocation- The positively charged carbon atom in the carbocation is connected to another carbon atom through a covalent bond. This carbocation is stable than methyl carbocation but is less stable than other Carbocations.

$ 3. $ Secondary Carbocation- The positively charged carbon atom is bonded to two other carbon atoms. These Carbocations are more stable than primary Carbocations.

$ 4. $ Tertiary Carbocation- The positively charged carbon atom is attached to three other carbon atoms. This form is very stable.

Carbanion is an ion that contains a negatively charged carbon atom. In this a carbon atom bearing negative charge is $ s{p^3} $ hybridized and the geometry is pyramidal. Carbanion is diamagnetic due to completion of electron pairing.
There are four types of carbanion:
$ 1. $ Methyl Carbanion- The negatively charged carbon atom is not bonded to any other carbon atom.

$ 2. $ Primary Carbanion- Here the negatively charged carbon atom in the carbanion is connected to another carbon atom through a covalent bond.

$ 3. $ Secondary Carbanion- The negatively charged carbon atom is bonded to two other carbon atoms.

$ 4. $ Tertiary Carbanion- The negatively charged carbon atom is attached to three other carbon atoms.

Difference between Carbocation and Carbanion:
| Serial number | Carbocation | Carbanion |
| $ 1. $ | A carbocation is an ion having a central carbon atom which is positively charged | A carbanion is an ion having a central carbon atom which is negatively charged. |
| $ 2. $ | The carbon atom is $ s{p^2} $ hybridized | The carbon atom is $ s{p^3} $ hybridized |
| $ 3. $ | Geometry is trigonal planar | Geometry is Pyramidal |
| $ 4. $ | Carbocation is paramagnetic | Carbanion is Diamagnetic |
| $ 5. $ | It act as an electrophile | It act as an nucleophile |
| $ 6. $ | It is more stabilized due to the presence of three donor methyl groups which donate electrons and therefore greatly stabilize the positive charge. | It is less stabilized. |
| $ 7. $ | An electron deficient specie | An electron rich species. |
| $ 8. $ | There are $ 6 $ electron in the outermost shell | There are $ 8 $ electrons in the outermost shell |
| $ 9. $ | It accepts an electron pair from a nucleophile to produce a covalent bond. | Normally donate an electron pair to an electrophile to produce a covalent bond. |
Note:
In various chemical reactions, the carbocation performs as an electrophile; conversely in many chemical reactions, the carbanion acts as a nucleophile.
Carbocation is formed if the organic molecule has a good leaving group, it can leave the molecule through ionization. The ionization gives the bonding electron pairs to the leaving group, resulting in a positive charge on the carbon atom. $ {(C{H_3})_2}CH - \mathop O\limits_{ \bullet \bullet }^{ \bullet \bullet } H \to {(C{H_3})_2}C{H^ + } + \mathop {{}_ \bullet ^ \bullet O}\limits_{ \bullet \bullet }^{ \bullet \bullet } {H^ - } $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




