
Dimethylglyoxime is an example of a:
A) Monodentate ligand
B) Bidentate ligand
C) Tridentate ligand
D) Hexadentate ligand
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In the coordination compound, the neutral molecules or ions bound to the central atom or ion in the coordination entity are called as a ligand. The dmg is a ligand and it has the oxygen and the nitrogen as the donor atom. This atom can donate their electron to the metal resulting in the formation of a coordinating complex.
Complete step by step solution:
The ligand can be defined as the molecule or ion which is capable of donating a pair of electrons to the central metal or ion to form a coordinate bond with it.
The number of coordinating ligating groups which are present on the ligand is called the denticity of the ligand.
The ligand can be unidentate, bidentate, or polydentate depending on the size of the donation. Ligands that have the two donor atoms and therefore can coordinate to the central ion at two positions are called the dentate or bidentate ligand.
The dimethylglyoxime acts as the ligand. It is also abbreviated as dmg or DMG. The structure of the dimethylglyoxime is as shown below:
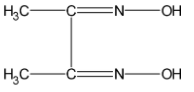
In a basic medium, one of the hydroxyl groups gets deprotonated leaving behind a ${{\text{O}}^{-}}$. The oxygen acquires the extra pair of electrons thus it can act as a ligand. Similarly, the nitrogen on the other hand has an electron pair. Thus it acts as the electron donor. The dmg in the basic medium is as shown below:
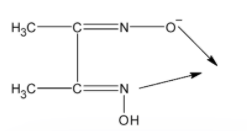
Thus dimethylglyoximato has two donor sites therefore dmg is a bidentate ligand.
Hence, (B) is the correct option.
Additional information:
The DMG forms a complex with nickel. It is a red colour complex which is formed in the basic conditions. The nickel can acquire the eight electrons thus two dimethyl glyoximato ligands arranged around the nickel atom. The dmg ligands are stabilized by hydrogen bonding. The nickel –dmg complex is as follows:
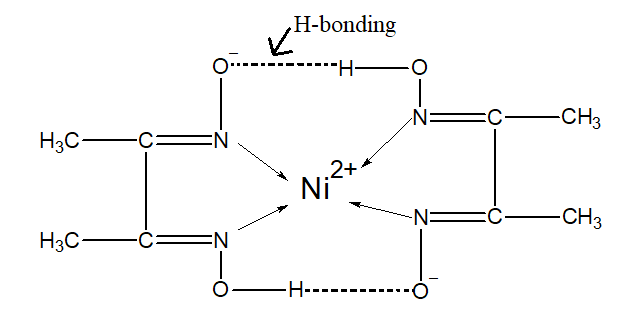
Note: The dmg is also a chelating agent. It means that the ligand uses its two or more donor atoms to bind the same central atom. The two dmg ligands donate their electron to the metal and form the metal complex.
Complete step by step solution:
The ligand can be defined as the molecule or ion which is capable of donating a pair of electrons to the central metal or ion to form a coordinate bond with it.
The number of coordinating ligating groups which are present on the ligand is called the denticity of the ligand.
The ligand can be unidentate, bidentate, or polydentate depending on the size of the donation. Ligands that have the two donor atoms and therefore can coordinate to the central ion at two positions are called the dentate or bidentate ligand.
The dimethylglyoxime acts as the ligand. It is also abbreviated as dmg or DMG. The structure of the dimethylglyoxime is as shown below:

In a basic medium, one of the hydroxyl groups gets deprotonated leaving behind a ${{\text{O}}^{-}}$. The oxygen acquires the extra pair of electrons thus it can act as a ligand. Similarly, the nitrogen on the other hand has an electron pair. Thus it acts as the electron donor. The dmg in the basic medium is as shown below:

Thus dimethylglyoximato has two donor sites therefore dmg is a bidentate ligand.
Hence, (B) is the correct option.
Additional information:
The DMG forms a complex with nickel. It is a red colour complex which is formed in the basic conditions. The nickel can acquire the eight electrons thus two dimethyl glyoximato ligands arranged around the nickel atom. The dmg ligands are stabilized by hydrogen bonding. The nickel –dmg complex is as follows:

Note: The dmg is also a chelating agent. It means that the ligand uses its two or more donor atoms to bind the same central atom. The two dmg ligands donate their electron to the metal and form the metal complex.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

In Carius method of estimation of halogens 015g of class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 8 Redox Reactions (2025-26)

An ideal gas is at pressure P and temperature T in class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses




