
When disruptive selection is operated in a population,
A. Mean value of phenotype is selected
B. Less than mean value of phenotype
C. More than mean value of phenotype is selected
D. Mean value of phenotype are eliminated
Answer
573k+ views
Hint: Natural selection is a basic mechanism of evolution that states that an organism that is more adapted to their environment is more likely to survive and pass on their genes that support their success. Natural selection is a reason behind the evolution of adaptive features.
Complete answer:
The disruptive selection is also known as diversifying selection is one of the types of natural selection which states that extreme points for traits are favored over the intermediate points. Two or more extreme phenotypic traits are being selected over an intermediate trait.
Let's understand the concept by taking one example, in a hypothetical population of rabbits the fur color of rabbits is governed by two dominants traits i.e. white fur and black fur if this population occurred in a rocky environment having white as well as black rocks then the rabbits with black and white fur easily hides from predators attack amongst the white and black rocks. While the rabbit with grey fur in this same rocky environment would not stand in this area and thereby suffer greater predation.
Chart showing a disruptive selection;
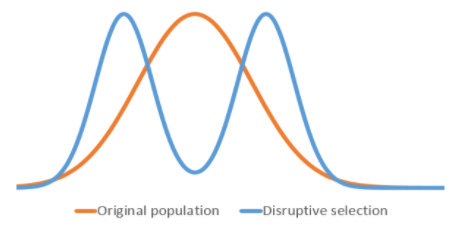
In the given example there is no advantage of intermediate points concerning the survival of the population.
So as a conclusion in this diversifying selection two extreme values that each has their advantages are selected over intermediate. Therefore, when disruptive selection is operated in a population there is an elimination of mean value phenotype because of variation as genotypically.
Hence, the correct answer is option (D).
Note: Disruptive selection also occurs when environmental changes favor the individuals on either end of the phenotypic scope. This selection is the rarest selection type of natural selection occurring in large population size with a lot of pressure for an individual to find the advantages as to compete for resources with each other.
Complete answer:
The disruptive selection is also known as diversifying selection is one of the types of natural selection which states that extreme points for traits are favored over the intermediate points. Two or more extreme phenotypic traits are being selected over an intermediate trait.
Let's understand the concept by taking one example, in a hypothetical population of rabbits the fur color of rabbits is governed by two dominants traits i.e. white fur and black fur if this population occurred in a rocky environment having white as well as black rocks then the rabbits with black and white fur easily hides from predators attack amongst the white and black rocks. While the rabbit with grey fur in this same rocky environment would not stand in this area and thereby suffer greater predation.
Chart showing a disruptive selection;

In the given example there is no advantage of intermediate points concerning the survival of the population.
So as a conclusion in this diversifying selection two extreme values that each has their advantages are selected over intermediate. Therefore, when disruptive selection is operated in a population there is an elimination of mean value phenotype because of variation as genotypically.
Hence, the correct answer is option (D).
Note: Disruptive selection also occurs when environmental changes favor the individuals on either end of the phenotypic scope. This selection is the rarest selection type of natural selection occurring in large population size with a lot of pressure for an individual to find the advantages as to compete for resources with each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




