
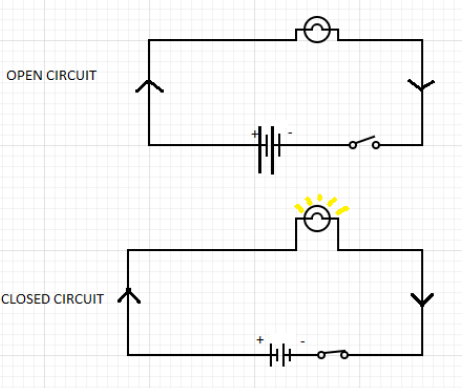
Distinguish between closed circuit and open circuit with the use of a suitable labelled diagram.
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: To ensure the flow of current, the path must be complete. If there is a break anywhere in the path, the current flow stops and the metallic atoms that are present in the wire settle to electrical neutrality. Usually in circuits, the break is determined by the switch and its state, i.e. whether it is off or on.
Complete step by step answer:
Closed circuit:We can say that a circuit is closed when it is fully composed of a conducting material that allows current to pass through it and when it is completed with the help of a switch or key, then current flow begins in the circuit and continuity is maintained in the circuit.The circuit becomes closed when the switch is ON or when the key is added.
This implies that both the terminals are connected and a direct path is provided for current flow with zero resistance.
Open circuit:We can say that a circuit is open when it doesn’t permit the flow of current through it. This occurs when any of the components is non-metallic, when the key is not connected or when the circuit is broken. The circuit becomes open when the switch is OFF. This implies that the two terminals are disconnected and it has infinite resistance, thus preventing current flow, regardless of voltage difference.
Note:Short circuit occurs when two points that aren’t supposed to be connected finds a connection between each other. Since current flows through the path with least resistance, the short circuit leads the current to bypass other paths and travel via this path. There will be flow of large amounts of electrical energy from one side of the power supply to the other. With nothing in the circuit to limit the current and absorb the electrical energy, heat builds up quickly in the wire and in the power supply. A short circuit can melt the insulation around a wire and may cause a fire, an explosion, or a release of harmful chemicals from certain power supplies, such as a rechargeable battery or a car battery.
Complete step by step answer:
Closed circuit:We can say that a circuit is closed when it is fully composed of a conducting material that allows current to pass through it and when it is completed with the help of a switch or key, then current flow begins in the circuit and continuity is maintained in the circuit.The circuit becomes closed when the switch is ON or when the key is added.
This implies that both the terminals are connected and a direct path is provided for current flow with zero resistance.
Open circuit:We can say that a circuit is open when it doesn’t permit the flow of current through it. This occurs when any of the components is non-metallic, when the key is not connected or when the circuit is broken. The circuit becomes open when the switch is OFF. This implies that the two terminals are disconnected and it has infinite resistance, thus preventing current flow, regardless of voltage difference.

Note:Short circuit occurs when two points that aren’t supposed to be connected finds a connection between each other. Since current flows through the path with least resistance, the short circuit leads the current to bypass other paths and travel via this path. There will be flow of large amounts of electrical energy from one side of the power supply to the other. With nothing in the circuit to limit the current and absorb the electrical energy, heat builds up quickly in the wire and in the power supply. A short circuit can melt the insulation around a wire and may cause a fire, an explosion, or a release of harmful chemicals from certain power supplies, such as a rechargeable battery or a car battery.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




