
Distinguish between homologous and analogous organs.
Answer
546.3k+ views
Hint: Out of both i.e homologous and analogous organs one has a similar embryonic origin; analogous organs have a similar function. Some of the organisms may be very closely related to each other, even though there is a minor genetic change caused by a major morphological difference to make them look quite different.
Complete answer:
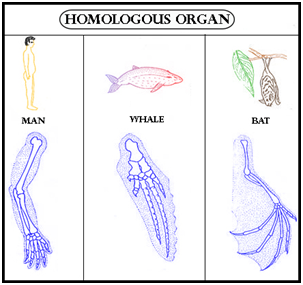
Similar traits are often either homologous or analogous. Homologous structures share an identical embryonic origin; analogous organs have an identical function. For instance, the bones within the front flipper of a whale are homologous to the bones within the human arm. These structures aren't analogous. The wings of a butterfly and therefore the wings of a bird are analogous but not homologous. Some structures are both analogous and homologous: the wings of a bird and therefore the wings of a bat are both homologous and analogous.

Note:
Some of the organisms could also be very closely related, even though a minor genetic change caused a serious morphological difference to make them look quite different. Similarly, unrelated organisms could also be distantly related, but appear considerably alike. This usually happens because of the reason that both of the organisms were in common adaptations that evolved within environmental conditions that were similar.
Complete answer:
Similar traits are often either homologous or analogous. Homologous structures share an identical embryonic origin; analogous organs have an identical function. For instance, the bones within the front flipper of a whale are homologous to the bones within the human arm. These structures aren't analogous. The wings of a butterfly and therefore the wings of a bird are analogous but not homologous. Some structures are both analogous and homologous: the wings of a bird and therefore the wings of a bat are both homologous and analogous.
| Homologous Structure | Analogous Structure |
| They show similar anatomy | They show Dissimilar anatomy |
| Dissimilar functions | Similar Functions |
| They are Inherited from a common ancestor | They are not inherited from ancestors |
| Develops in the related species. | These develop in unrelated species |
| These are the result of divergent evolution | These are the result of convergent evolution |
| They are developed as a result of the adaptation to a different environment | They are developed as a result of the adaptation to a similar environment |
| An arm of a human being, the leg of a dog, or a flipper of a whale or fish are all homologous structures | From wings of the birds, bats, and insects to fins in penguins and fishes are all analogous structures |


Note:
Some of the organisms could also be very closely related, even though a minor genetic change caused a serious morphological difference to make them look quite different. Similarly, unrelated organisms could also be distantly related, but appear considerably alike. This usually happens because of the reason that both of the organisms were in common adaptations that evolved within environmental conditions that were similar.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




