
DNA fragments generated by the restriction endonucleases in a chemical reaction can be separated by
A. Centrifugation
B. Polymerase chain reaction
C. Electrophoresis
D. Restrictions mapping
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: Restriction endonucleases are enzymes that are used in biotechnological experiments to cut the DNA pieces into small fragments of required length and bases. These are extracted from bacteria(micro-organisms). The cut fragments of DNA are negative in charge and thus are separated by providing positive charge in a gel medium.
Complete step by step answer: In biotechnology, the recombinant DNA techniques are the keystone for genetic modification research. The rDNA or recombinant DNA technology requires various tools.
-One of the major tools of rDNA technology is restriction endonucleases. These are enzymes that act like scissors and cut the required segments of DNA that need to be modified or studied. These cut fragments need to be separated based on their molecular charge and weight to find the fragments of interest.
-Electrophoresis is a technique that employs the loading of cut DNA fragments into wells made of gel. These loaded samples then run through the gel matrix towards the positive pole of the container containing the gel. As the DNA fragments are negatively charged they run towards a positive charge based on their molecular weight. The small fragments move ahead of the larger ones. Thus, DNA fragments cut by restriction endonuclease are easily separated using Gel Electrophoresis.
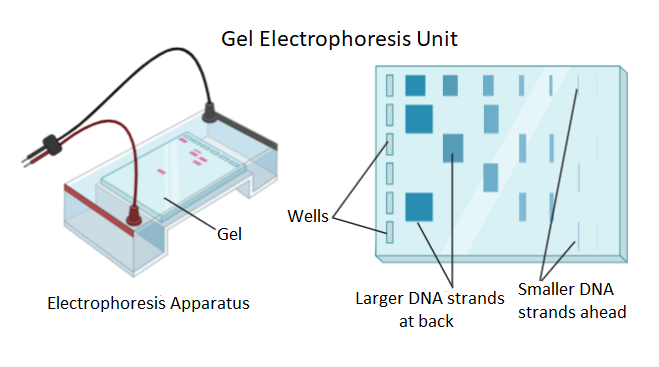
Now let us study other options as well,
-Centrifugation: It is a technique that is used to differentiate or separate solutions based on their densities. It involves fast and continuous rotations that are used to rotate the test tubes containing solutions that need to be separated. For example, separating plasma from the blood is done by the centrifugation process.
-Polymerase chain reaction or PCR: It is simply a technique that is used to make multiple copies of the target DNA sequences.
-Restriction mapping: It is a technique that is employed to know the structural information on the fragments of DNA cut by restriction enzymes. But it has no role in separating the cut DNA fragments.
Note: Electrophoresis is a key technique to separate various other biomolecules also. The basic principle is to separate them based on their size and charge. This is an important technique in rDNA technology. Also, the process of rDNA technology should be learned thoroughly to learn the various tools used in it and their respective functions step by step.
Complete step by step answer: In biotechnology, the recombinant DNA techniques are the keystone for genetic modification research. The rDNA or recombinant DNA technology requires various tools.
-One of the major tools of rDNA technology is restriction endonucleases. These are enzymes that act like scissors and cut the required segments of DNA that need to be modified or studied. These cut fragments need to be separated based on their molecular charge and weight to find the fragments of interest.
-Electrophoresis is a technique that employs the loading of cut DNA fragments into wells made of gel. These loaded samples then run through the gel matrix towards the positive pole of the container containing the gel. As the DNA fragments are negatively charged they run towards a positive charge based on their molecular weight. The small fragments move ahead of the larger ones. Thus, DNA fragments cut by restriction endonuclease are easily separated using Gel Electrophoresis.

Now let us study other options as well,
-Centrifugation: It is a technique that is used to differentiate or separate solutions based on their densities. It involves fast and continuous rotations that are used to rotate the test tubes containing solutions that need to be separated. For example, separating plasma from the blood is done by the centrifugation process.
-Polymerase chain reaction or PCR: It is simply a technique that is used to make multiple copies of the target DNA sequences.
-Restriction mapping: It is a technique that is employed to know the structural information on the fragments of DNA cut by restriction enzymes. But it has no role in separating the cut DNA fragments.
Note: Electrophoresis is a key technique to separate various other biomolecules also. The basic principle is to separate them based on their size and charge. This is an important technique in rDNA technology. Also, the process of rDNA technology should be learned thoroughly to learn the various tools used in it and their respective functions step by step.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




