
Why does adenine pair with thymine and not cytosine?
Answer
481.5k+ views
Hint: There are four chemical bases that are found in DNA. With Adenine (A) being one of these four bases along with cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). Adenine bases on one strand of the DNA molecule establish chemical interactions with thymine bases on the opposing strand.
Complete answer:
In double-stranded nucleic acids, a base pair (bp) consists of two nucleobases linked together by hydrogen bonds. DNA double helix building blocks also contribute to the folded DNA and RNA structures.
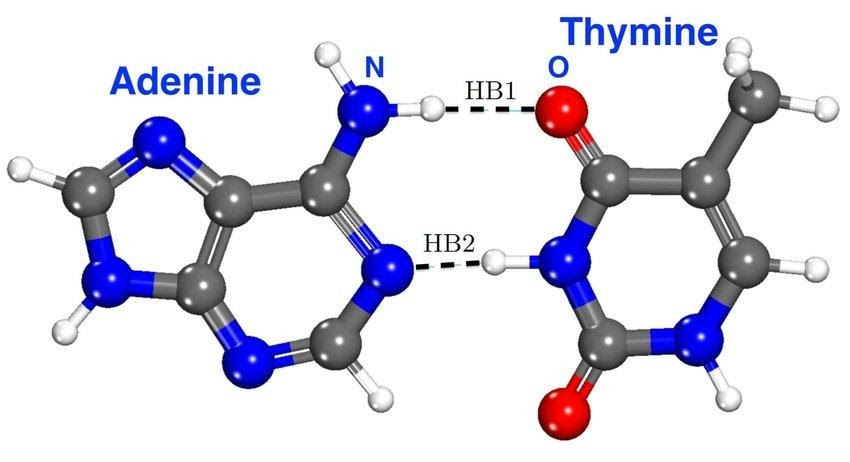
DNA is the only site where adenine and thymine can be paired as the base pairs. The two nitrogenous bases are joined by two hydrogen bonds. An adenine hydrogen-oxygen connection forms between the amino group's C-6 hydrogen atom and thymine's C-4 keto group's oxygen atom. Adenine has another connection between the nitrogen atom at position-1 and the hydrogen atom connected to N-3. In order for the DNA to preserve its double helix structure, adenine and thymine must form hydrogen bonds with each other. It eventually becomes possible to break them at high temperatures because they're not particularly strong bonds.
DNA replication and transcription are typically initiated at A-T rich locations because the breakdown of two hydrogen bonds between adenine and thymine takes less energy than the breakage of three hydrogen bonds than between guanine and cytosine.
Consequently, it can be seen that adenine pairs with thymine and not cytosine adenine and thymine share a beneficial bond arrangement. However, whenever adenine and cytosine are paired together, the different groups get in each other's way making it to be chemically unfavourable for them to bond.
Image showing base pairing of Adenine with Thymine
Image showing base pairing of Adenine with Thymine
Note:
Based on the principle of helical structure of DNA, complementary base pairing is a critical factor for DNA's helical shape as it enables the base pairs to be organised in such a way as to maximise energy efficiency. Thus as a result, semi-conservative replication is possible.
Complete answer:
In double-stranded nucleic acids, a base pair (bp) consists of two nucleobases linked together by hydrogen bonds. DNA double helix building blocks also contribute to the folded DNA and RNA structures.
DNA is the only site where adenine and thymine can be paired as the base pairs. The two nitrogenous bases are joined by two hydrogen bonds. An adenine hydrogen-oxygen connection forms between the amino group's C-6 hydrogen atom and thymine's C-4 keto group's oxygen atom. Adenine has another connection between the nitrogen atom at position-1 and the hydrogen atom connected to N-3. In order for the DNA to preserve its double helix structure, adenine and thymine must form hydrogen bonds with each other. It eventually becomes possible to break them at high temperatures because they're not particularly strong bonds.
DNA replication and transcription are typically initiated at A-T rich locations because the breakdown of two hydrogen bonds between adenine and thymine takes less energy than the breakage of three hydrogen bonds than between guanine and cytosine.
Consequently, it can be seen that adenine pairs with thymine and not cytosine adenine and thymine share a beneficial bond arrangement. However, whenever adenine and cytosine are paired together, the different groups get in each other's way making it to be chemically unfavourable for them to bond.
Image showing base pairing of Adenine with Thymine
Image showing base pairing of Adenine with Thymine

Note:
Based on the principle of helical structure of DNA, complementary base pairing is a critical factor for DNA's helical shape as it enables the base pairs to be organised in such a way as to maximise energy efficiency. Thus as a result, semi-conservative replication is possible.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




