
How does DNA differ in a eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell?
Answer
530.7k+ views
Hint: Prokaryotes are a primitive cell that does not contain a true nucleus and lack membrane-bound cell organelles. They were the first ones to originate on earth while the eukaryotic cells are the advanced ones containing a true and prominent nucleus with membrane-bound organelles.
Complete answer
Note:
All the reactions in prokaryotes occur within the cytosol of the cell. In 1665, Robert Hooke was the first to describe and discover cells. The process of protein synthesis and RNA formation in the case of eukaryotes and prokaryotes differs. The transcription in eukaryotes occurs in the nucleus while in the case of the prokaryotes it occurs in the cytoplasm.
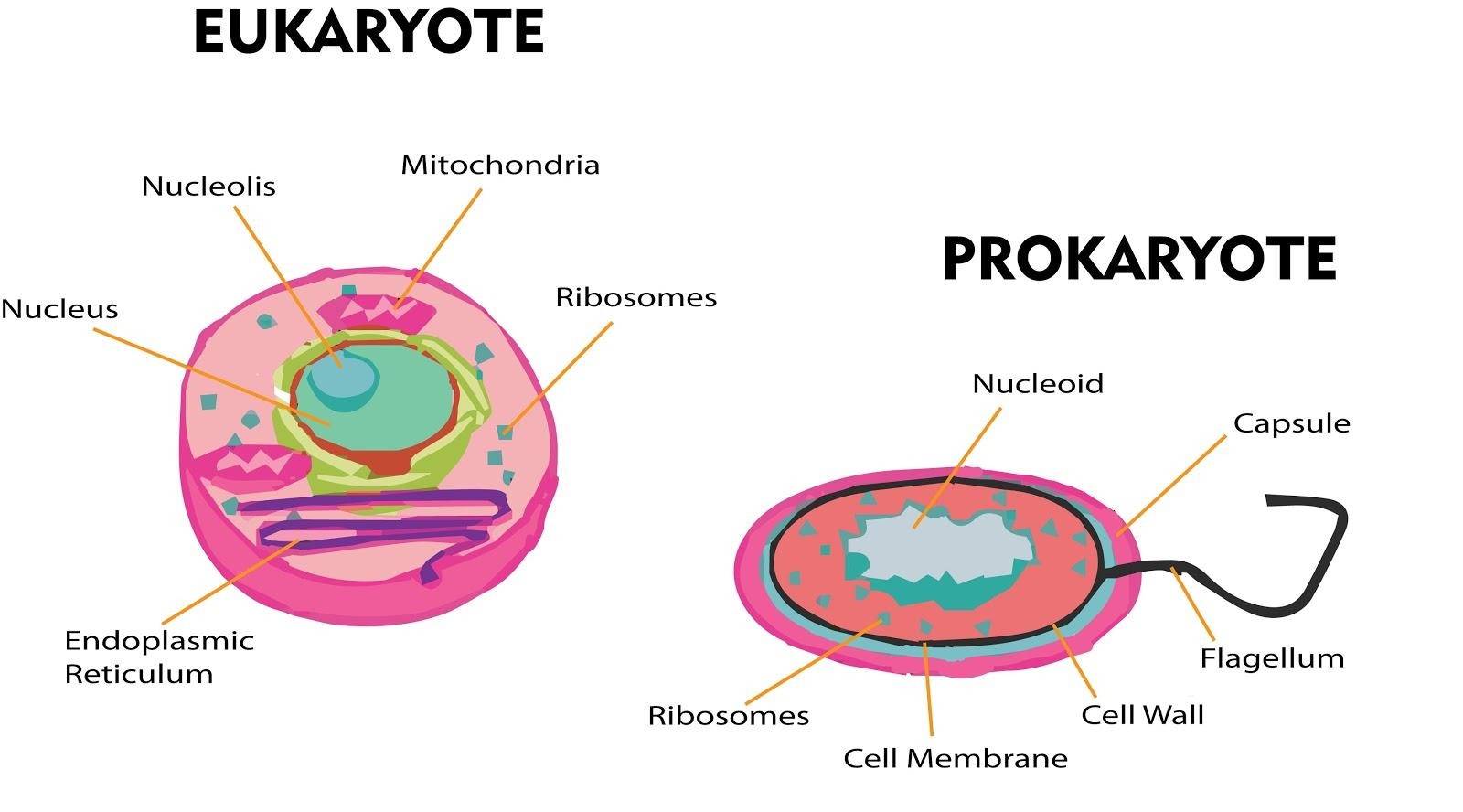
Complete answer
| Prokaryotic cell | Eukaryotic cell |
| The size of the prokaryotic cell is around 1-2µm by 1-4µm. | Greater than 5 µm in diameter. |
| Mostly unicellular(some cyanobacteria may be multicellular). | Mostly multicellular. |
| The true nucleus is absent where the nucleolus and the nuclear membrane are absent. This type of nucleus is called the nucleoid. | The nuclear membrane and nucleolus are present. |
| The DNA is arranged in a circular single-stranded where histones are absent. | DNA arrangements are linear with histones. |
| The complete DNA replication occurs at once. | The DNA replication occurs at certain sites called the origin of replication (ori). |
| Ribosomes here are of 70 S type which is smaller and is found in the cytoplasm. | Ribosomes here are of 80 S type which are larger and are found in the size 80s, found in the endoplasmic reticulum while the mitochondria and the chloroplast contain the 70s type. |
| Asexual reproduction takes place. | Both sexual and asexual reproduction occurs. |
| Examples: bacteria and archaea. | Examples: plant and animal cells. |
Note:
All the reactions in prokaryotes occur within the cytosol of the cell. In 1665, Robert Hooke was the first to describe and discover cells. The process of protein synthesis and RNA formation in the case of eukaryotes and prokaryotes differs. The transcription in eukaryotes occurs in the nucleus while in the case of the prokaryotes it occurs in the cytoplasm.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




