
How does Glucose concentration affect cellular respiration?
Answer
507k+ views
Hint: Cellular respiration is a collection of metabolic processes through which all living cells release energy by turning biochemical energy from food into adenosine triphosphate-ATP. Metabolism is a sequence of chemical reactions that are carried out in order to keep the cells in an organism alive. These can be divided into two categories: The breakdown of molecules to obtain energy is known as catabolism. Anabolism is the process by which cells make all of the chemicals they need.
Complete answer:
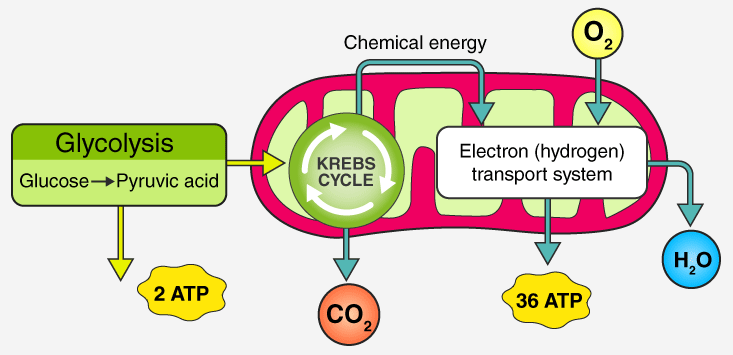
Changes in glucose concentration impact the rate of cellular respiration since all living cells require both glucose and oxygen to function correctly. A cell cannot create energy in the form of ATP molecules if its glucose level is low. The three processes of cellular respiration are glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. The primary role of glucose in each of these phases is to supply energy via its bonds.
Glycolysis is the process of breaking down or dividing carbohydrates. During glycolysis, one molecule of the \[6\]-carbon chemical glucose is broken down into two molecules of three-carbon pyruvic acid. Whether or not there is oxygen in the cytoplasm, this can happen. In all, there are two pyruvic acid molecules, two ATP molecules, and two NADH electron transporter molecules.
The Krebs cycle, also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle, is a metabolic cycle that occurs in the body. Pyruvic acid is produced and transferred to the mitochondrial matrix, where it is converted to acetyl CoA. After a series of steps, two molecules of ATP are produced. In addition, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) are generated (\[FADH{}_2\]). They aid electron transport in the next phase.
The electron transport system and oxidative phosphorylation both require oxygen. An electron gradient is created when high-energy electrons travel through a chain of electron carriers such as NADH.
Additional information:
Fermentation is a series of chemical reactions or a metabolic process that bacteria, yeast, and other microorganisms use to get the energy they need to carry out their biological functions. It's a type of anaerobic pathway that's utilised to make alcoholic drinks, yoghurt, and other foods.
Note:
Based on oxygen requirement, cellular respiration is classified into two categories: aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration is the process of burning or oxidising glucose in the presence of oxygen to release energy (ATP). The three stages of aerobic respiration are glycolysis, Krebs' cycle, and the electron transport system. Anaerobic respiration, often known as fermentation, is a kind of cellular respiration that takes place without the need of oxygen. They won't be a component of the Krebs cycle or the electron transport system. Incomplete glycolysis results in the production of pyruvic acid. Pyruvic acid is reduced further, releasing carbon dioxide, ethanol, and ATP.
Complete answer:
Changes in glucose concentration impact the rate of cellular respiration since all living cells require both glucose and oxygen to function correctly. A cell cannot create energy in the form of ATP molecules if its glucose level is low. The three processes of cellular respiration are glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. The primary role of glucose in each of these phases is to supply energy via its bonds.
Glycolysis is the process of breaking down or dividing carbohydrates. During glycolysis, one molecule of the \[6\]-carbon chemical glucose is broken down into two molecules of three-carbon pyruvic acid. Whether or not there is oxygen in the cytoplasm, this can happen. In all, there are two pyruvic acid molecules, two ATP molecules, and two NADH electron transporter molecules.
The Krebs cycle, also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle, is a metabolic cycle that occurs in the body. Pyruvic acid is produced and transferred to the mitochondrial matrix, where it is converted to acetyl CoA. After a series of steps, two molecules of ATP are produced. In addition, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) are generated (\[FADH{}_2\]). They aid electron transport in the next phase.
The electron transport system and oxidative phosphorylation both require oxygen. An electron gradient is created when high-energy electrons travel through a chain of electron carriers such as NADH.

Additional information:
Fermentation is a series of chemical reactions or a metabolic process that bacteria, yeast, and other microorganisms use to get the energy they need to carry out their biological functions. It's a type of anaerobic pathway that's utilised to make alcoholic drinks, yoghurt, and other foods.
Note:
Based on oxygen requirement, cellular respiration is classified into two categories: aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration is the process of burning or oxidising glucose in the presence of oxygen to release energy (ATP). The three stages of aerobic respiration are glycolysis, Krebs' cycle, and the electron transport system. Anaerobic respiration, often known as fermentation, is a kind of cellular respiration that takes place without the need of oxygen. They won't be a component of the Krebs cycle or the electron transport system. Incomplete glycolysis results in the production of pyruvic acid. Pyruvic acid is reduced further, releasing carbon dioxide, ethanol, and ATP.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




