
Why does glucose not undergo Schiff’s base?
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Schiff’s base: Aldehydes and ketones on treatment with primary aliphatic or aromatic amines in the presence of a trace of acid yields a Schiff’s base.
Complete step by step answer:
It contains a carbon-nitrogen double bond with the nitrogen atom connected to an aryl or alkyl group-but, not hydrogen. They have the general formula ${ R }^{ 1 }{ R }^{ 2 }{ C=NR }^{ 3 }$
where R is an organic side chain. Hence, it is an amine.
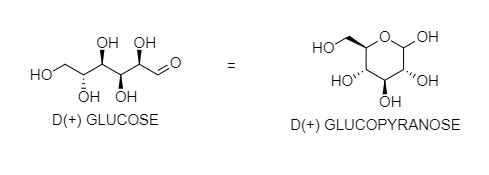
Glucose does not react with Schiff's reagent and ${ 2,4 }$ DNP reagent although it has an aldehydic group. You can see that ${ OH }$ at ${ 5 }$ - carbon reacts with the aldehyde group at 1 carbon to form hemiacetal in a cyclic form. After the internal cyclization, it forms either α- anomer or β-anomer. In these forms, a free aldehyde group is not present. So, it does not give the reaction of the aldehydic group.
Uses of Schiff’s base:
Schiff bases are common enzymatic intermediates
They are common ligands in coordination chemistry.
They were one of the first ligands used for asymmetric catalysis.
Schiff’s reagent is rosaniline hydrochloride (whose pink color is decolorized by passing ${ SO }_{ 2 }$ gas). This reagent is generally used to detect the aldehydic group.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that Schiff’s base is a weak base, not a strong base, so it cannot get broken by this reagent as it is quite stable.
Complete step by step answer:
It contains a carbon-nitrogen double bond with the nitrogen atom connected to an aryl or alkyl group-but, not hydrogen. They have the general formula ${ R }^{ 1 }{ R }^{ 2 }{ C=NR }^{ 3 }$
where R is an organic side chain. Hence, it is an amine.
Glucose does not react with Schiff's reagent and ${ 2,4 }$ DNP reagent although it has an aldehydic group. You can see that ${ OH }$ at ${ 5 }$ - carbon reacts with the aldehyde group at 1 carbon to form hemiacetal in a cyclic form. After the internal cyclization, it forms either α- anomer or β-anomer. In these forms, a free aldehyde group is not present. So, it does not give the reaction of the aldehydic group.

Uses of Schiff’s base:
Schiff bases are common enzymatic intermediates
They are common ligands in coordination chemistry.
They were one of the first ligands used for asymmetric catalysis.
Schiff’s reagent is rosaniline hydrochloride (whose pink color is decolorized by passing ${ SO }_{ 2 }$ gas). This reagent is generally used to detect the aldehydic group.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that Schiff’s base is a weak base, not a strong base, so it cannot get broken by this reagent as it is quite stable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




